You can use an INSERT INTO clause to write query and analysis results from one Logstore to another Logstore. The two Logstores belong to the same project.
Syntax
INSERT INTO target_logstore (key)
SELECT key FROM source_logstoreIn the destination Logstore, you must create an index for the key field that you specify and enable the analysis feature for the field.
target_logstore must be followed by a field that you want to write to the destination Logstore. For example,
* | INSERT INTO target_logstore SELECT...is an invalid statement.If the data types of the specified fields do not match the data types that are supported by Simple Log Service, you must specify a data type conversion function in the SELECT statement to convert the data types of the fields. For more information, see Data type conversion functions.
You can use an INSERT INTO clause to write up to 10,000 data entries to a destination Logstore at a time.
The source and destination Logstores must reside in the Chinese mainland.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
target_logstore | The name of the destination Logstore. Note The destination Logstore must be different from the source Logstore. |
source_logstore | The name of the source Logstore. |
key | The field name or column name. |
Example
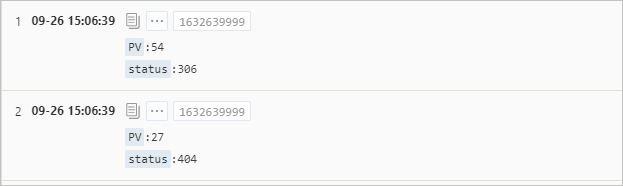
Calculate the number of page views (PVs) for each status code in a Logstore named website_log and write the query and analysis result to a Logstore named test_insert.
Before you execute the following query statement, you must create indexes for the status and PV fields in the test_insert Logstore and enable the analysis feature for the fields.
Query statement
* | INSERT INTO test_insert(status,PV) SELECT status, count(*) AS PV FROM website_log GROUP BY statusQuery and analysis result (source Logstore)
Query and analysis result (destination Logstore)