Simple Log Service provides the Scheduled SQL feature. You can use the feature to analyze data at a scheduled time and aggregate data for storage. You can also use the feature to project and filter data. Simple Log Service allows you to process data in a source Metricstore by configuring a Scheduled SQL job and save the processed data to a destination Metricstore.
Prerequisites
Data is collected to a source Metricstore. For more information, see Collect metric data from hosts.
A destination Metricstore is created. For more information, see Create a Metricstore.
Procedure
The Scheduled SQL feature is in public preview. If you enable the feature, you are charged only for the computing resources that are consumed by Dedicated SQL. For more information, see Billable items of pay-by-feature.
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
In the Projects section, click the project that you want to manage.
On the tab, click the metricstore that you want to manage.
Perform query and analysis operations.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click 15 Minutes(Relative) to specify a time range for the query.
Enter a PromQL statement and click Execute Now.
For more information, see Query and analyze metric data.
NoteThis step allows you to preview data before you create a Scheduled SQL job. You can check whether the query statement that you entered is valid and whether the query and analysis results contain data.
Choose .
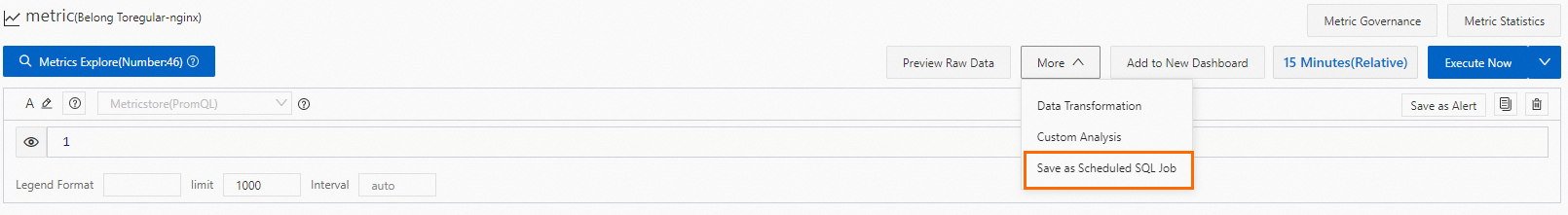
Create a Scheduled SQL job.
In the Compute Settings step, configure the parameters and click Next. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Job Name
The name of the Scheduled SQL job.
Display Name
The display name of the Scheduled SQL job.
Job Description
The description of the Scheduled SQL job.
Resource Pool
The resource pool that is used for data analysis. Simple Log Service provides an enhanced type of resource pool.
The enhanced type of resource pool utilizes the computing capability of Dedicated SQL to meet concurrent analysis requirements. It isolates resources between Scheduled SQL and your SQL analysis operations in the console. You are charged for the enhanced type of resource pool based on the CPU time that is consumed by your SQL analysis operations. For more information, see Enable Dedicated SQL.
Write Mode
Select Import Data from Metricstore to Metricstore. The Scheduled SQL job processes the data in the source Metricstore and saves the processed data to the destination Metricstore.
SQL Code
The query statement. By default, the system displays the statement that you entered in Step 4. The preview operation that is provided for this parameter has the same effect as the preview operation in Step 4. You can click Preview to check whether the query statement is valid and whether the query and analysis results contain data.
When the Scheduled SQL job runs, Simple Log Service executes the query statement to analyze data.
ImportantWe recommend that you use the promql_query function to import metric data of the current point in time to the destination Metricstore. If you use the promql_query_range function, a large amount of data expands.
SQL Settings
Result Metric Name
The new name of the metric that you select for analysis. If you want to change the name of the metric, you can specify a new name for the metric in this parameter. For more information, see Metric.
ImportantIf you select a single metric for analysis, we recommend that you configure this parameter to rename the metric.
If you select multiple metrics for analysis and you configure this parameter, all metrics are renamed with the name that you specify.
Rehash
Specifies whether to enable hashing. If you turn on Rehash, you can configure the Hash Column parameter to write data with the same label to one shard. This improves data locality and query efficiency.
Valid values of the Hash Column parameter vary based on the existing label information of your metrics. For example, if the existing label information of your metrics is
{"alert_id":"alert-1608815762-545495","alert_name":"Alert clearance disabled","status":"inactive"}, the valid values of the Hash Column parameter are alert_id, alert_name, and status. If you set Hash Column to status, the metrics that have the same value for status are written to the same shard.Additional Labels
The static labels that are used to identify the attributes of a metric. Each label is a key-value pair.
For example, you can set label_key to app and label_value to ingress-nginx.
Target
Target Region
The region where the destination project resides.
Target Project
The name of the destination project that stores the results of the query statement.
Target Store
The name of the destination Metricstore that stores the results of the query statement.
Write Authorization
The method that is used to authorize the Scheduled SQL job to write data to the destination Metricstore. Valid values:
Default Role: The Scheduled SQL job assumes the AliyunLogETLRole system role to write the analysis results to the destination Metricstore.
ImportantThe first time that you create a Scheduled SQL job, authorization is required and must be completed by using the Alibaba Cloud account to which the destination project belongs. You do not need to perform authorization when you create subsequent Scheduled SQL jobs.
Custom Role: The Scheduled SQL job assumes a custom role to write the analysis results to the destination Metricstore. You must grant the custom role the permissions to write data to the destination Metricstore. Then, enter the Alibaba Cloud Resource Name (ARN) of the custom role in the Role ARN field. For more information, see Grant the RAM role the permissions to write data to a destination logstore.
SQL Execution Authorization
The method that is used to authorize the Scheduled SQL job to read data from the source Metricstore and analyze the data by using query statements in the current project. Valid values:
Default Role: The Scheduled SQL job assumes the AliyunLogETLRole system role to perform the required operations.
ImportantThe first time that you create a Scheduled SQL job, authorization is required and must be completed by using the Alibaba Cloud account to which the destination project belongs. You do not need to perform authorization when you create subsequent Scheduled SQL jobs.
Custom Role: The Scheduled SQL job assumes a custom role to perform the required operations.
You must grant the custom role the required permissions. Then, enter the ARN of the custom role in the Role ARN field. For more information, see Grant role-a the permissions to analyze data in the source logstore.
In the Scheduling Settings step, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Specify Scheduling Interval
The frequency at which the Scheduled SQL job is scheduled. An instance is generated each time the Scheduled SQL job is scheduled. This parameter determines the scheduled time for each instance. Valid values:
Hourly: The scheduled SQL task is scheduled every hour.
Daily: The scheduled SQL task is scheduled at a fixed time every day.
Weekly: The scheduled SQL task is scheduled at a fixed time on a fixed day of each week.
Fixed Interval: The scheduled SQL task is scheduled at a fixed interval.
Cron: The scheduled SQL task is scheduled at an interval that is specified by using a cron expression.
If you use a cron expression, the specified interval is accurate to minutes based on the 24-hour clock. For example, the expression 0 0/1 * * * indicates that the scheduled SQL task is scheduled every hour from 00:00.
If you need to specify the time zone, select Cron. For a list of common time zones, see Time zones.
Scheduling Time Range
The time range during which the Scheduled SQL job is scheduled. Valid values:
Start at a specified time: specifies the time when the scheduled SQL task is first scheduled.
Within Specific Period: specifies the time range within which the scheduled SQL task is scheduled.
NoteIf you specify the time range, the instances of the Scheduled SQL job can run only within the time range. After the end time, the Scheduled SQL job no longer generates instances.
Scheduling Time Range is the
__time__field. For more information, see Reserved fields.
SQL Time Window
The time window of logs that are analyzed when the Scheduled SQL job runs. This parameter must be configured together with the Scheduling Time Range parameter. The duration specified by this parameter can be up to five times the duration specified by Specify Scheduling Interval. The start time and end time of the SQL time window must be within 24 hours. For more information, see Time expression syntax.
For example, Specify Scheduling Interval is set to Fixed Interval 10 Minutes, Start Time is set to 2021-04-01 00:00:00, Delay Task is set to 30 Seconds, and SQL Time Window is set to [@m-10m,@m). In this example, the first instance of the Scheduled SQL job is generated at 00:00:30 to analyze the logs that fall in the time range [23:50:00 to 00:00:00). For more information, see Scheduling and running scenarios.
NoteSQL Time Window is the
__time__field. For more information, see Reserved fields.If
__time__is not defined in the SQL code, the log time__time__written to the target metricstore defaults to the start time of the scheduled SQL job.
SQL Timeout
The threshold of automatic retries if the SQL analysis operation fails. If an instance is retried for a period that exceeds the maximum time that you specify or the number of retries for an instance exceeds the upper limit that you specify, the instance stops retrying and enters the FAILED state. You can manually retry the instance based on the failure cause. For more information, see Retry a scheduled SQL instance.
Delay Task
The number of seconds for which the instance is delayed from the scheduled time. Valid values: 0 to 120. Unit: seconds.
If latency exists when data is written to the destination metricstore, you can use this parameter to ensure data integrity.
After the Scheduled SQL job is created, you can view the SQL execution result in the destination metricstore.