Hologres supports binary logging (binlog) to capture database events. You can use this feature to replicate or synchronize data. You can also forward these events as a message stream to different consumers. Consuming Hologres binlogs improves data reuse and reduces the end-to-end latency of data transformation. This topic describes how to subscribe to Hologres binlogs and perform related operations.
Introduction to binlogs
Similar to a traditional MySQL database, Hologres uses binary logging to record all data change events in the database. Hologres binlogs enable flexible and convenient data replication and synchronization. However, Hologres binlogs are typically used only for data synchronization. In contrast, traditional database binlogs are also used for high availability (HA) scenarios, such as primary-replica instance synchronization and data restoration. As a result, their implementations differ in several ways:
Binary logging in Hologres does not record DDL operations.
Hologres binlogs are flexible and operate at the table level. You can enable or disable them as needed and set different Time to Live (TTL) values for different tables.
As a distributed real-time data warehouse, Hologres has distributed binlogs.
You can easily query Hologres binlogs.
In big data scenarios, Flink can directly consume Hologres binlogs. Compared with traditional data warehouse layering, the combination of Flink and Hologres binlogs creates a fully event-driven architecture. This architecture facilitates end-to-end real-time data transformation jobs from the operation data store (ODS) to the data warehouse dimension (DWD) layer, and from the DWD layer to the data warehouse service (DWS) layer. This solution provides unified storage that supports layered administration, improves data reusability, and reduces end-to-end data transformation latency to provide a one-stop real-time data warehouse solution.
Limits
Note the following limitations when you subscribe to Hologres binlogs:
Subscribing to Hologres binlogs is supported only in Hologres V0.9 and later. If your instance version is earlier than V0.9, join the online support DingTalk group. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
In Hologres V0.9 and V0.10, you cannot enable binlogs for existing tables by modifying table properties. Instead, you must recreate the tables. In Hologres V1.1 and later, you can enable binlogs as needed.
In versions earlier than Hologres V1.3.14 and V1.1.82, only a superuser can consume binlogs. If you attempt to use an account with fewer permissions to consume binlogs, a permission error occurs:
permission denied for table hg_replication_slot_properties. In Hologres V1.3.14, V1.1.82, and later, an account only needs permission to query the table if you use Flink to consume binlogs. To consume Hologres binlogs using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), the account must have the Replication Role.Hologres supports the binlog feature at the table level for both row-oriented and column-oriented tables. The following table describes the support for subscribing to Hologres binlogs.
Flink classification
Hologres row-oriented table binlog
Hologres column-oriented table binlog
Hologres row-column hybrid table binlog (supported since Hologres V1.1)
Realtime Compute (Blink)
Supported
Supported
Supported
Fully managed Flink
Supported
Supported
Supported
Open source Flink
Not supported
Not supported
Not supported
JDBC
Supported since Hologres V1.1
Supported since Hologres V1.1
Supported since Hologres V1.1
When you use Blink to consume Hologres binlogs, the TIMESTAMP data type is not supported. You must use the TIMESTAMPTZ data type when you create tables in Hologres. Other data types, such as SMALLINT, are also not supported.
You cannot consume binlogs from a parent table of a partitioned table. You must use a child table or a standard (non-partitioned) table. In Hologres V1.3.24 and later, you can modify the binlog TTL for a child table of a partitioned table as needed. If you do not explicitly specify a binlog TTL for a child table, it inherits the binlog TTL of the parent table. Note that the binlog TTL is not a precise value. The system does not guarantee that a binlog is deleted immediately after it expires. The binlog is deleted at some point after expiration.
For scenarios that involve frequent updates, enabling binlogs for a column-oriented table theoretically has more overhead than for a row-oriented table. We recommend that you use a row-oriented table with binlogs enabled. If the table is also used for online analytical processing (OLAP) queries, we recommend that you use a row-column hybrid storage format. For more information, see Table storage formats.
Only Hologres internal tables support binlogs. Foreign tables do not.
Binlog format and principles
A Binlog record consists of Binlog system fields and user table fields, which are described in the table below.
Field name | Field type | Description |
hg_binlog_lsn | BIGINT | A binlog system field that represents the binlog serial number. It increases monotonically within a shard but is not guaranteed to be continuous. It is not guaranteed to be unique or ordered across different shards. Note For more information about how binlog data is distributed in shards, see Distribution Key. |
hg_binlog_event_type | BIGINT | A binlog system field that indicates the type of modification represented by the current record.
|
hg_binlog_timestamp_us | BIGINT | A binlog system field that is the system timestamp in microseconds (us). |
user_table_column_1 | User-defined | A user table field. |
... | ... | ... |
user_table_column_n | User-defined | A user table field. |
An UPDATE operation generates two binlog records: one for the state before the update and one for the state after. The binlog subscription feature ensures that these two records are consecutive. The before-update record precedes the after-update record.
For UPDATE operations that are performed using a Hologres connector, such as Holo Client, Flink Connector, or Data Integration, the connector translates BEFORE_UPDATE to DELETE and AFTER_UPDATE to INSERT. Therefore, you will see the values 2 and 5 in the
hg_binlog_event_typefield. However, the connector ensures the eventual consistency of the data.The
hg_binlog_event_typefield records BEFORE_UPDATE and AFTER_UPDATE only when an UPDATE operation is performed using a pure SQL statement.
A Hologres binlog can be viewed as a special row-oriented table. Enabling the binlog for a table is similar to creating a new row-oriented table where hg_binlog_lsn is the key. The original fields of the business table, along with hg_binlog_event_type and hg_binlog_timestamp_us, are combined to form the value. The fields of the binlog table are fixed, which means it has a strong schema. The order of user fields matches the order defined in the DDL of the business table. Therefore, we recommend that you use row-oriented or row-column hybrid tables when you enable binlogs to achieve better performance when you read binlogs.
Enable binlogs
In Hologres, the binlog feature is disabled by default. You can enable it by setting the binlog.level and binlog.ttl table properties. The following example shows how to enable binlogs. For more information about the parameters used to create a table, see CREATE TABLE.
Theoretically, the overhead of enabling binlogs for a column-oriented table is higher than for a row-oriented table. If your table is frequently updated, we recommend that you use a row-oriented table to enable binlogs.
Syntax supported in V2.1 and later:
The table property names
binlog.levelandbinlog.ttlare updated tobinlog_levelandbinlog_ttl.CREATE TABLE test_message_src ( id int PRIMARY KEY, title text NOT NULL, body text ) WITH ( orientation = 'row', clustering_key = 'id', binlog_level = 'replica', binlog_ttl = '86400' -- The TTL for the binary log, in seconds. );Syntax supported by all versions:
begin; create table test_message_src( id int primary key, title text not null, body text); call set_table_property('test_message_src', 'orientation', 'row');-- Create the row-oriented table test_message_src. call set_table_property('test_message_src', 'clustering_key', 'id');-- Create a clustered index on the id column. call set_table_property('test_message_src', 'binlog.level', 'replica');-- Set a table property to enable the binlog feature. call set_table_property('test_message_src', 'binlog.ttl', '86400');-- The TTL for the binary log, in seconds. commit;
The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter | Description |
| Specifies whether to enable binlogs. Valid values:
|
| The TTL for the binlog, in seconds. The default value is 30 days, which is 2592000 seconds. |
Enable binlogs as needed
In Hologres V1.1 and later, you can enable or disable the binlog feature based on your business needs. You can also configure the TTL to meet the retention period requirements of different business scenarios. You can enable binlogs for existing tables without recreating them, which is a fast and convenient process.
The following features are available only in Hologres V1.1 and later. If your instance version is earlier than V1.1, see Common upgrade preparation failure errors or join the Hologres DingTalk group to provide feedback. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
Enable binlogs
You can use the following statements to enable binlogs for an existing table and set the binlog TTL.
-- Set a table property to enable the binlog feature. begin; call set_table_property('<table_name>', 'binlog.level', 'replica'); commit; -- Set a table property to configure the binlog TTL, in seconds. begin; call set_table_property('<table_name>', 'binlog.ttl', '2592000'); commit;table_name is the name of the table for which you want to enable binlogs.
Disable binlogs
You can use the following statements to disable binlogs for a table.
-- Set a table property to disable the binlog feature. begin; call set_table_property('<table_name>', 'binlog.level', 'none'); commit;table_name is the name of the table for which you want to disable binlogs.
Modify the binlog TTL
You can use the following statement to modify the TTL for a table that has binlogs enabled. This lets you meet the different retention period requirements of your business.
NoteIn Hologres V1.3.24 and later, you can enable the binlog TTL for a child table of a partitioned table as needed. If you do not explicitly modify the binlog TTL for the child table, it inherits the binlog TTL of the parent table by default.
call set_table_property('<table_name>', 'binlog.ttl', '8640000'); -- Unit: secondstable_name is the name of the table for which you want to modify the binlog TTL.
Query binlogs
The binlog data of a Hologres table uses a strong schema format. To query the binlog for a specific table, you can combine the built-in binlog fields with the original table fields. Hologres also provides functions to query the latest or earliest binlog, or to query binlog information using a known LSN and timestamp.
Directly query binlogs using built-in special fields
You can query binlogs by combining the built-in binlog fields with the original table fields. The following code provides an example.
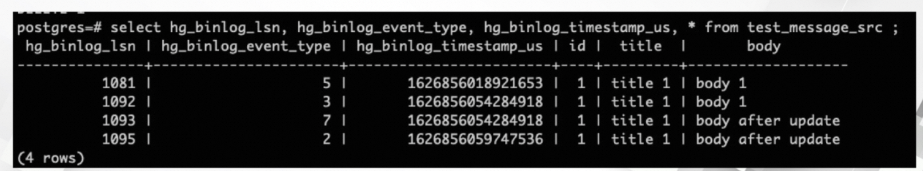
SELECT hg_binlog_lsn,hg_binlog_event_type,hg_binlog_timestamp_us,* FROM test_message_src;The following figure shows a sample query result.
Query the earliest or latest binlog on a specified shard of a table
You can use the hg_get_binlog_cursor function to query binlogs. The syntax is as follows.
-- OLDEST: The earliest binlog on this shard.
SELECT * FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor('<table_name>','OLDEST',<shard_id>);
-- LATEST: The latest binlog on this shard.
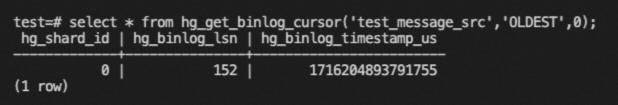
SELECT * FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor('<table_name>','LATEST',<shard_id>);The following code provides an example.
SELECT * FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor('test_message_src','OLDEST',0);The following figure shows a sample query result.
Query the timestamp of a binlog by its LSN
Use the hg_get_binlog_cursor_by_lsn function to query the timestamp of a binlog. This function returns information about the first binlog whose log sequence number (LSN) is greater than or equal to the specified LSN. If the specified LSN does not exist, the hg_binlog_timestamp_us field in the result is the current time. The syntax is as follows.
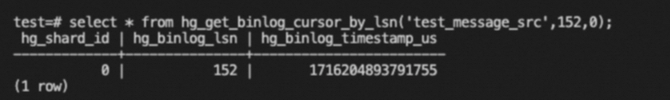
SELECT * FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor_by_lsn('<table_name>',<lsn>,<shard_id>);--LSN value (bigint type)The following provides an example.
SELECT * FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor_by_lsn('test_message_src',152,0);The following shows a sample query result.
Query the LSN of a binlog by its timestamp
You can use the hg_get_binlog_cursor_by_timestamp function to query the Log Sequence Number (LSN) of a binlog. This function returns information about the first binlog with a timestamp that is greater than or equal to the specified time. If the specified time is later than the timestamp of the latest binlog entry, the hg_binlog_timestamp_us field in the result contains the current time, and the hg_binlog_lsn field contains the LSN that will be assigned to the next data insertion. The syntax is as follows.
If the provided timestamp is greater than the current time (returned by the now() function), the SQL query throws a "Get binlog cursor in future time" exception.
SELECT * FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor_by_timestamp('<table_name>',<timestamp>,<shard_id>);For example:
SELECT *,to_timestamp(hg_binlog_timestamp_us/1000000.0) FROM hg_get_binlog_cursor_by_timestamp('test_message_src','2024-05-20 19:34:53.791+08',0);The following shows a sample query result.

Consume Hologres binlogs in real time
You can consume Hologres binlogs using Flink, Blink, and JDBC (including Holo Client). For more information, see the following topics:
To consume binlogs in real time using Flink and Blink, see Consume Hologres binlogs in real time using Flink or Blink.
To consume binlogs in real time using JDBC, see Consume Hologres binlogs using JDBC.
View tables with binlogs enabled
You can use the following SQL statement to view the tables for which binlogs are enabled.
SELECT
*
FROM
hologres.hg_table_properties
WHERE
property_key = 'binlog.level'
AND property_value = 'replica';The following figure shows a sample result.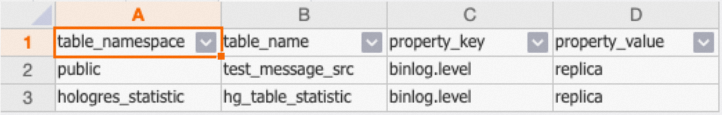
View binlog storage size
Hologres lets you use the
pg_relation_sizefunction to obtain the storage size of a table. This size includes the binlog storage size. For more information, see View the storage size of a table.In Hologres V2.1 and later, you can use the
hologres.hg_relation_sizefunction to view detailed storage information for a table, including data, binlogs, and other storage details. For more information, see View table storage details.
Disable binlogs during DML operations on a table
You can use the following Grand Unified Configuration (GUC) parameter to prevent a table from generating binlogs during DML operations. You must enable this parameter at the session level and execute it together with the DML statement.
--Enable at the session level.
SET hg_experimental_generate_binlog=off;