Function Compute provides built-in runtimes that include common dependencies for your functions to reference. However, if these built-in dependencies cannot meet your business requirements, you can install third-party dependencies. This topic describes how to install third-party dependencies for a function.
Background
For more information about built-in common dependencies in Function Compute, see the following topics:
Install dependencies by using layers
The official public layers of Function Compute are pre-installed with common dependency libraries and can be directly used. If you want to get more public layers, see awesome-layers. You can also build a custom layer to install required dependencies.
Use a public layer
Official public layers
Log on to the Function Compute console, locate the function that you want to manage and click on it. On the Function Details page, choose the Configurations tab, and click Modify on the right side of the Advanced Settings section. In the Layers section of the Advanced Settings panel, choose . Section ① in the following figure shows an example. For more information, see Configure a public layer.
Non-official public layers
Find the layer you want to use from awesome-layers and obtain the Alibaba Cloud Resource Name (ARN) of the layer. On the Function Details page, choose the Configurations tab, and click Modify on the right side of the Advanced Settings section. In the Layers section of the Advanced Settings panel, choose . Section ② in the following figure shows an example.

Build a custom layer
In the Function Compute console
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . For more information, see Create a custom layer.
NoteThis method does not support dependencies that contain dynamic-link libraries (.so files), such as the Puppeteer dependency library for Node.js. If you want to install such a dependency, we recommend that you use a Dockerfile to build the layer.
On an on-premises machine
You can build a custom layer on an on-premises machine, but it's essential to ensure that the on-premises operating system (OS) and processor architecture are completely consistent with the Function Compute runtime. This means you must use an x86-64 Linux OS or make sure that the installed dependency library does not depend on the underlying environment or processor architecture. For more information about how to build a custom layer, see Build a .ZIP file for a layer.
Some dependencies, such as the Python NumPy library, are environment-dependent. For example, if your on-premises machine runs macOS with M1 chips, you cannot install such dependencies on that machine.
By using a Dockerfile
If a dependency contains underlying dynamic-link libraries or fails to be installed on your on-premises machine, you can use a Dockerfile to build a layer and install the dependency. For more information, see Use a Dockerfile to build a layer.
Install dependencies in the Function Compute console
Package and upload dependencies
Bundle third-party dependencies with your code files into a package.
ImportantYou must package all files in the code directory. Make sure the function handler file is in the root directory of the package.
The packaging method differs depending on the OS. Select a method that best fits your OS.
Log on to the Function Compute console and upload the package to deploy your function by using one of the following methods: a ZIP file, a folder, or a package from OSS.
Install dependencies in WebIDE
Log on to the Function Compute console and find the function you want to manage.
On the Function Details page, click the Code tab. On the WebIDE UI, click . In Terminal, run the
pip install -t . <PackageName>command to install dependencies.pip install -t . <PackageName> # PackageName indicates the name of the dependency package. -t indicates the installation path. . indicates to install in the current directory.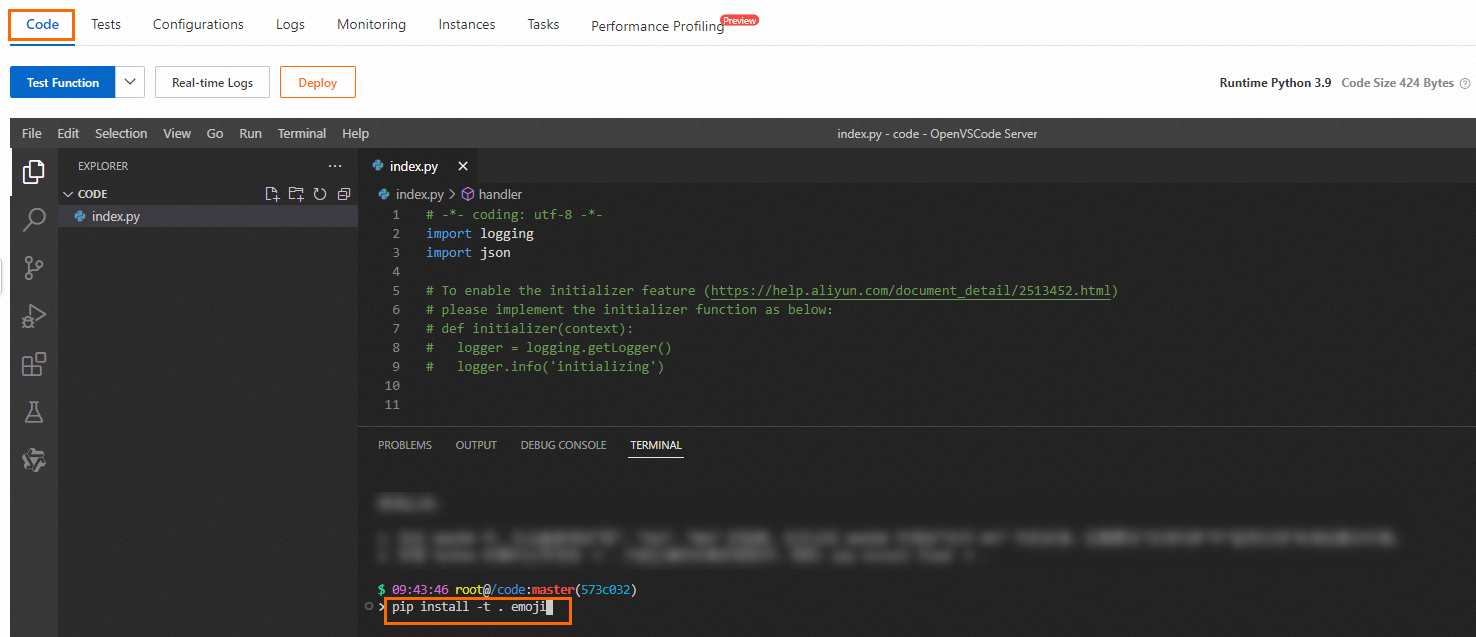
Click Deploy.
Install dependencies by using Serverless Devs
You can also create and deploy a function to Function Compute by using Serverless Devs. For more information, see Common commands of Serverless Devs.