This topic describes how to develop SparkSQL tasks in an Alibaba Cloud E-MapReduce (EMR) Serverless Spark environment. This topic also describes how to access the Spark UI to view task details.
Prerequisites
A workspace and an SQL session instance have been created. For more information, see Create a workspace and Manage SQL sessions.
Create an SQL task
Go to the development page.
Log on to the EMR console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Spark page, click the name of the target workspace.
On the EMR Serverless Spark page, click Development in the navigation pane on the left.
Create a task.
On the Development tab, click the
 (Create) icon.
(Create) icon.In the dialog box that appears, enter a Name, set Type to SparkSQL, and click OK.
In the upper-right corner, select a data catalog, a database, and a running SQL session instance.
You can also select Connect to SQL Session from the drop-down list to create a new SQL session instance. For more information, see Manage SQL sessions.

Enter SQL statements in the editor of the new task.
Example 1: Basic SQL operations
The following example shows how to create a database, switch to the database, create a table, insert data, and execute a query.
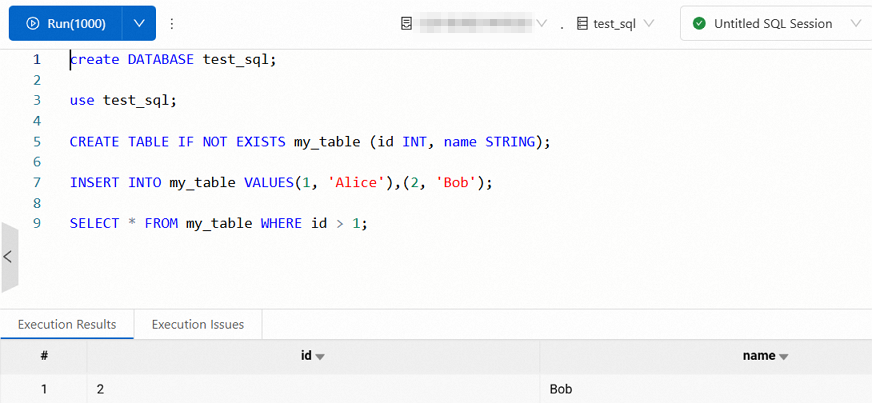
create DATABASE test_sql; use test_sql; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my_table (id INT, name STRING); INSERT INTO my_table VALUES(1, 'Alice'),(2, 'Bob'); SELECT * FROM my_table WHERE id > 1;The results are shown in the following figure.
Example 2: CSV-based foreign table
The following example shows how to create a foreign table based on a CSV file in Object Storage Service (OSS) and execute a query. In the sample code, you must replace the bucket address (
oss://<bucketname>/user/) with your actual bucket address.Create a temporary view.
Create a temporary view named
ordersbased on a CSV file in OSS for subsequent data analytics. The fields of the view are defined as follows:order_id: The order ID.order_date: The date and time of the order, such as'2025-07-01 10:00:00'.order_category: The product category, such as "Electronics" or "Apparel".order_revenue: The order amount.
CREATE TABLE orders ( order_id STRING, -- The order ID order_date STRING, -- The date and time of the order order_category STRING, -- The product category order_revenue DOUBLE -- The order amount ) USING CSV OPTIONS ( path 'oss://<bucketname>/user/', header 'true' );Insert test data.
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE orders VALUES ('o1', '2025-07-01 10:00:00', 'Electronics', 5999.0), ('o2', '2025-07-02 11:30:00', 'Apparel', 299.0), ('o3', '2025-07-03 14:45:00', 'Electronics', 899.0), ('o4', '2025-07-04 09:15:00', 'Home Goods', 99.0), ('o5', '2025-07-05 16:20:00', 'Electronics', 1999.0), ('o6', '2025-07-06 08:00:00', 'Apparel', 199.0), ('o7', '2025-07-07 12:10:00', 'Electronics', 799.0), ('o8', '2025-07-08 18:30:00', 'Home Goods', 59.0), ('o9', '2025-07-09 20:00:00', 'Electronics', 399.0), ('o10', '2025-07-10 07:45:00', 'Apparel', 599.0), ('o11', '2025-07-11 09:00:00', 'Electronics', 1299.0), ('o12', '2025-07-12 13:20:00', 'Home Goods', 159.0), ('o13', '2025-07-13 17:15:00', 'Apparel', 499.0), ('o14', '2025-07-14 21:30:00', 'Electronics', 999.0), ('o15', '2025-07-15 06:10:00', 'Home Goods', 299.0);Execute a complex query.
Execute a complex query on the
orderstable to collect sales performance statistics for different categories over the last 15 days. The query includes the following information:Number of orders: The total number of orders for each category.
Total sales (GMV): The sum of order amounts for each category.
Average order amount: The average order amount for each category.
Latest order time: The time of the most recent order for each category.
SELECT order_category, COUNT(order_id) AS order_count, SUM(order_revenue) AS gmv, AVG(order_revenue) AS avg_order_amount, MAX(order_date) AS latest_order_date FROM orders WHERE CAST(order_date AS TIMESTAMP) BETWEEN '2025-07-01' AND '2025-07-15' GROUP BY order_category HAVING SUM(order_revenue) > 1000 ORDER BY gmv DESC, order_category ASC;
(Optional) On the right side of the development page, click the Version Information tab to view the version details.
On this tab, you can view and compare task versions. The platform highlights the differences in SQL code between versions.
Run and publish the task.
Click Run.
The results are displayed on the Execution Results tab. If an error occurs, you can view the details on the Execution Issues tab. The run history on the right shows the records from the last three days.
After you confirm that the task runs correctly, click Publish in the upper-right corner.
In the Publish dialog box, you can enter release notes and then click OK.
Access the Spark UI
The Spark UI lets you view details such as task execution status, resource usage, and log information. This information helps you analyze and optimize your Spark tasks.
Access from the Results Area
This feature is supported only by the following engine versions:
esr-4.x: esr-4.2.0 and later.
esr-3.x: esr-3.2.0 and later.
esr-2.x: esr-2.6.0 and later.
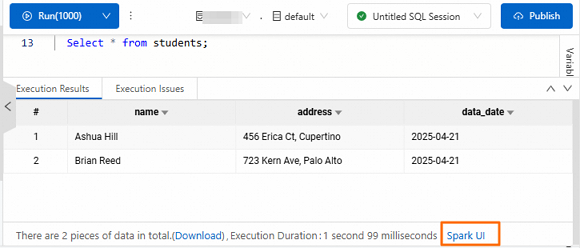
After the SQL statement is executed, click Spark UI at the bottom of the Execution Results tab. The system automatically redirects you to the Spark UI page.
Accessing from the session instance
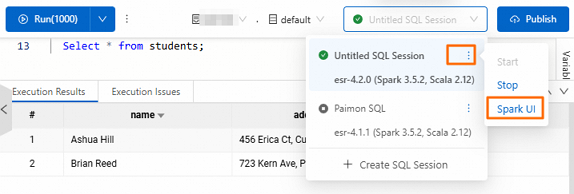
After the SQL statement is executed, find the session instance, and choose . The system automatically redirects you to the Spark UI page.
Keyboard shortcuts
The platform provides the following keyboard shortcuts to help developers write and debug SQL efficiently:
Function | Windows shortcut | Mac shortcut | Description |
Run current script |
| Control + Enter | Executes all or selected SQL statements in the editor. This is the same as clicking the Run button. |
Format SQL |
|
| Automatically formats the SQL code structure. It standardizes indentation, line breaks, and keyword case to improve readability. This is useful for organizing complex queries. |
Find text |
|
| Searches for keywords in the current script. You can locate each matching item one by one. This helps you quickly find fields or table names. |
Save task |
|
| Manually saves the content of the current unpublished task to prevent accidental loss of changes. |
What to do next
After you create a task, you can create a workflow to schedule the task to run periodically. For more information, see Create a workflow. For a complete example of workflow scheduling, see Quick start for SparkSQL development.
 > Spark UI
> Spark UI