Iceberg is an open table format for data lakes. You can use Iceberg to quickly build your own data lake storage service on Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) or Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service (OSS). This topic describes how to read data from and write data to an Iceberg table in EMR Serverless Spark.
Prerequisites
A workspace has been created. For more information, see Create a workspace.
Procedure
Spark SQL and Notebook both support reading from and writing to Iceberg tables. This topic uses a Spark SQL job as an example.
Step 1: Create a session
Go to the Sessions page.
Log on to the EMR console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Spark page, click the name of the workspace that you want to manage.
In the left-side navigation pane of the EMR Serverless Spark page, choose Operation Center > Sessions.
On the SQL Sessions tab, click Create SQL Session.
On the Create SQL Session page, in the Spark Configuration section, configure the following information, and click Create. For more information, see Manage SQL sessions.
Catalogs are required when you read data from or write data to Iceberg in EMR Serverless Spark. You can specify a catalog as needed. For more information, see Manage data catalogs.
Use a Data Catalog
If you use the Data Catalog method, you do not need to configure parameters in the session. Instead, simply click Add Catalog on the Catalogs page, and then directly select the data catalog in SparkSQL development.
NoteIf you want to access Iceberg in DLF (formerly DLF 2.5), use engine versions esr-4.7.0, esr-3.6.0, or later.
If you want to access Iceberg in DLF-Legacy (formerly DLF 1.0) or Hive Metastore, use engine versions esr-4.3.0, esr-3.3.0, esr-2.7.0, or later.
Use a Custom Catalog
DLF (formerly DLF 2.5)
NoteEngine versions esr-4.7.0, esr-3.6.0, or later are required.
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensions spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.catalog-impl org.apache.iceberg.rest.RESTCatalog spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.uri http://<regionID>-vpc.dlf.aliyuncs.com spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.warehouse <catalog_name> spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.io-impl org.apache.iceberg.rest.DlfFileIO spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.auth.type sigv4 spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.auth.sigv4.delegate-auth-type none spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.signing-region <regionID> spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.signing-name DlfNext spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.access-key-id <access_key_id> spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.secret-access-key <access_key_secret>The parameters are described as follows.
Parameter
Description
Example value
spark.sql.extensionsEnable Iceberg Spark extensions.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensionsspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalogRegister a Spark Catalog named iceberg_catalog.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalogspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.catalog-implSpecify the underlying catalog implementation as Iceberg REST Catalog.
org.apache.iceberg.rest.RESTCatalogspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.uriThe REST API address of the DLF Iceberg service. Format:
http://<regionID>-vpc.dlf.aliyuncs.com.http://cn-hangzhou-vpc.dlf.aliyuncs.comspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.warehouseSpecify the associated DLF Catalog name.
NoteDo not associate DLF Catalogs created by data sharing.
<catalog_name>spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.io-implUse the DLF-customized FileIO implementation.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.rest.DlfFileIOspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.auth.typeEnable the AWS SigV4 signature authentication mechanism to authenticate REST requests.
sigv4spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.auth.sigv4.delegate-auth-typeDisable delegated authentication. The client directly provides AccessKey ID (AK) and AccessKey Secret (SK) for signing.
nonespark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.signing-regionSpecify the region used for signing. This must be consistent with the region where the DLF service is located.
cn-hangzhouspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.signing-nameSpecify the service name used for signing.
Static field:
DlfNextspark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.access-key-idThe AccessKey ID of an Alibaba Cloud account or a Resource Access Management (RAM) user.
<access_key_id>spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog.rest.secret-access-keyThe AccessKey Secret of an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user.
<access_key_secret>DLF-Legacy (formerly DLF 1.0)
NoteEngine versions esr-4.3.0, esr-3.3.0, esr-2.7.0, or later are required.
Metadata is stored in DLF-Legacy (formerly DLF 1.0).
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensions spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName> org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.catalog-impl org.apache.iceberg.aliyun.dlf.hive.DlfCatalog spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.dlf.catalog.id <catalog_name>The parameters are described as follows.
Parameter
Description
Example value
spark.sql.extensionsEnable Iceberg Spark extensions.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensionsspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>Register a catalog named
<catalogName>.Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalogspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.catalog-implUse the Alibaba Cloud DLF-Legacy-specific Hive-compatible implementation to directly connect to the DLF-Legacy global meta service.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.aliyun.dlf.hive.DlfCatalogspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.dlf.catalog.idSpecify the associated DLF Catalog name.
<catalog_name>Hive Metastore
Metadata is stored in a specific Hive Metastore.
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensions spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName> org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.catalog-impl org.apache.iceberg.hive.HiveCatalog spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.uri thrift://<yourHMSUri>:<port>The parameters are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Example value
spark.sql.extensionsEnable Iceberg Spark extensions.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensionsspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>Register a catalog named
<catalogName>.Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalogspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.catalog-implSpecify that this catalog uses the official Iceberg HiveCatalog implementation to store and read Iceberg table metadata through Hive Metastore.
Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.hive.HiveCatalogspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.uriThe URI of the Hive Metastore. Format:
thrift://<IP address of a Hive metastore>:9083.<Hive metastore IP address>is the internal IP address of the HMS. To specify an external Metastore service, see Connect to an external Hive Metastore Service.thrift://192.168.**.**:9083File System
Metadata is stored in a file system.
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensions spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName> org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.type hadoop spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.warehouse oss://<yourBucketName>/warehouseThe parameters are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Example value
spark.sql.extensionsEnable Iceberg Spark extensions.
The static field is
org.apache.iceberg.spark.extensions.IcebergSparkSessionExtensions.spark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>Register a catalog named
<catalogName>.Static field:
org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalogspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.typeSpecify the catalog type as
hadoop. This indicates using a HadoopCatalog to store metadata directly in the file system without a Hive Metastore.hadoopspark.sql.catalog.<catalogName>.warehouseSpecify the metadata storage path. In the code,
<yourBucketName>represents the name of the bucket on OSS.oss://<yourBucketName>/warehouse
Step 2: Read and write data in Iceberg tables
You can go to the SQL development page.
On the EMR Serverless Spark page, click Data Development in the navigation pane on the left.
On the Development tab, click the
 icon.
icon.In the New dialog box, enter a name, such as users_task, leave the type as the default SparkSQL, and click OK.
You can copy the following code into the new SparkSQL tab (users_task).
NoteIf a database is not specified, tables are created in the `default` database of the Catalog. You can also create and specify a different database.
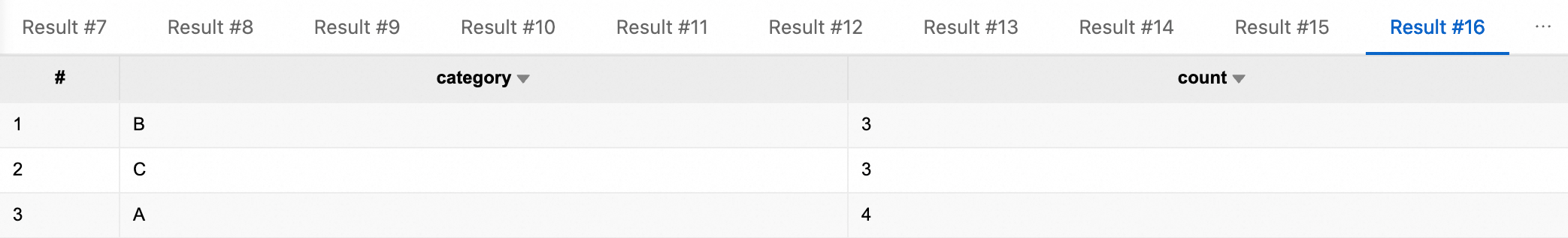
-- Create a database CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS iceberg_catalog.db; -- Create a non-partitioned table CREATE TABLE iceberg_catalog.db.tbl ( id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT 'unique id', data STRING ) USING iceberg; -- Insert data into the non-partitioned table INSERT INTO iceberg_catalog.db.tbl VALUES (1, 'Alice'), (2, 'Bob'), (3, 'Charlie'); -- Query all data from the non-partitioned table SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.tbl; -- Query the non-partitioned table based on a condition SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.tbl WHERE id = 2; -- Update data in the non-partitioned table UPDATE iceberg_catalog.db.tbl SET data = 'David' WHERE id = 3; -- Query again to confirm the update SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.tbl WHERE id = 3; -- Delete data from the non-partitioned table DELETE FROM iceberg_catalog.db.tbl WHERE id = 1; -- Query again to confirm the deletion SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.tbl; -- Create a partitioned table CREATE TABLE iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl ( id BIGINT, data STRING, category STRING, ts TIMESTAMP, dt DATE ) USING iceberg PARTITIONED BY (dt, category); -- Insert data into the partitioned table INSERT INTO iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl VALUES (1 , 'data-01', 'A', timestamp'2026-01-01 10:00:00', date'2026-01-01'), (2 , 'data-02', 'A', timestamp'2026-01-01 11:00:00', date'2026-01-01'), (3 , 'data-03', 'A', timestamp'2026-01-02 09:30:00', date'2026-01-02'), (4 , 'data-04', 'B', timestamp'2026-01-02 12:15:00', date'2026-01-02'), (5 , 'data-05', 'B', timestamp'2026-01-03 08:05:00', date'2026-01-03'), (6 , 'data-06', 'B', timestamp'2026-01-03 14:20:00', date'2026-01-03'), (7 , 'data-07', 'C', timestamp'2026-01-04 16:45:00', date'2026-01-04'), (8 , 'data-08', 'C', timestamp'2026-01-04 18:10:00', date'2026-01-04'), (9 , 'data-09', 'C', timestamp'2026-01-05 07:55:00', date'2026-01-05'), (10, 'data-10', 'A', timestamp'2026-01-05 13:35:00', date'2026-01-05'); -- Query all data from the partitioned table SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl; -- Query data where dt='2026-01-01' SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl WHERE dt='2026-01-01'; -- Query data for a specific category SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl WHERE category = 'A'; -- Query using multiple conditions (day + category) SELECT * FROM iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl WHERE dt='2026-01-01' AND category = 'A'; -- Aggregate and count the number of data entries for each category SELECT category, COUNT(*) AS count FROM iceberg_catalog.db.part_tbl GROUP BY category; -- Delete the database (use with caution). Before deleting, ensure the database has no tables. -- DROP DATABASE iceberg_catalog.db;In the session drop-down list, select the SQL session instance that you just created, and click the Run button. After the code runs successfully, the results are displayed below.
References
For a complete example of the SQL task development and orchestration process, see Quick Start for SparkSQL development.
For more information about Iceberg, see Apache Iceberg.
For more information about how to create SQL session resources, see Manage SQL sessions.
For information about creating Notebook session resources, see Manage notebook sessions.