An instance identity consists of an instance identity document and an instance identity signature. You can use an instance identity to identify and distinguish between Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances, which provides a basis of trust for application access control and software activation. This topic describes what an instance identity is, its common scenarios, and how to obtain and use it.
What is an instance identity
An instance identity consists of a dynamically generated instance identity document (document) and an instance identity signature (signature).
Instance identity document
An instance identity document contains the identity information of an instance, such as its instance ID and IP address. The following table describes the properties included in the document.
Property
Description
owner-account-id
The ID of the Alibaba Cloud account to which the instance belongs.
instance-id
The ID of the instance.
mac
The MAC address of the primary network interface card (NIC) of the instance.
region-id
The ID of the region where the instance is located.
serial-number
The serial number of the instance.
zone-id
The ID of the zone where the instance is located.
instance-type
The instance type.
image-id
The ID of the image that the instance uses.
private-ipv4
The private IPv4 address of the instance.
Instance identity signature
Third parties can use the instance identity signature to verify the authenticity and content of the instance identity document. The signature is encrypted in the PKCS#7 format. It is fully digital, secure, and reliable.
You can use the
audienceparameter in an instance identity signature to prevent the signature from being spoofed. The value of theaudienceparameter can be a random string, a timestamp, information that changes regularly, or data generated by an algorithm. After you configure theaudienceparameter, unauthorized parties cannot guess the value of theaudienceparameter even if they obtain partial information about the identity document and signature. You can also use theaudienceparameter to perform authentication. For more information, see Use an instance identity.
Use cases
You can use an instance identity for authentication, authorization, or environment identification in the following scenarios:
Offline software is typically activated with a single-use license code. This model is not suitable for cloud software with variable usage patterns. When you list an application in the Alibaba Cloud Marketplace, you can use an instance identity for flexible user authorization.
When you write sensitive data to an ECS instance, you can use the instance identity to ensure that the data is written to your ECS instance and not to another environment.
In other scenarios where you need to confirm the source of the target server.
Obtain the instance identity document or signature
(Recommended) Obtain in security hardening mode
Linux instance
# Obtain a server access credential. Set a validity period. Do not include the X-Forwarded-For header. TOKEN=`curl -X PUT "http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/token" -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds:<Validity period of the server access credential>"` # Obtain the instance identity. curl -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token: $TOKEN" http://100.100.100.200/latest/<dynamic data>Windows instance
# Obtain a server access credential. Set a validity period. Do not include the X-Forwarded-For header. $token = Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{"X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds" = "<Validity period of the server access credential>"} -Method PUT -Uri http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/token # Obtain the instance identity. Invoke-RestMethod -Headers @{"X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token" = $token} -Method GET -Uri http://100.100.100.200/latest/<dynamic data><Validity period of the server access credential>: The access credential is used for authentication to improve data security. The validity period can be 1 to 21,600 seconds.You can reuse the command to obtain data within the validity period. After the credential expires, you must obtain a new one.
The access credential is valid for only one instance. If you copy the credential to another instance, access is denied.
<dynamic data>: Replace this placeholder with the specific instance identity document or signature.Instance identity document: dynamic/instance-identity/document
Instance identity signature: dynamic/instance-identity/pkcs7?audience=XXXX
Important?audience=XXXXis optional. For more information, see Instance identity signature.
Obtain in normal mode
Linux instance
curl http://100.100.100.200/latest/<dynamic data>Windows instance (PowerShell)
Invoke-RestMethod http://100.100.100.200/latest/<dynamic data><dynamic data>: Replace this placeholder with the specific instance identity document or signature.Instance identity document: dynamic/instance-identity/document
Instance identity signature: dynamic/instance-identity/pkcs7?audience=XXXX
Important?audience=XXXXis optional. For more information, see Instance identity signature.
Use an instance identity
The following steps show how to use an instance identity in security-hardening mode. An Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 system is used as an example.
Authenticating and using an instance identity requires OpenSSL to ensure security. If OpenSSL is not installed on your instance, go to the OpenSSL official website to download and install it.
Connect to the Linux instance remotely.
For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance.
(Optional) You can run the following commands to view the instance identity document and signature.
# Obtain a server access credential and set the validity period to 3600 seconds. TOKEN=`curl -X PUT "http://100.100.100.200/latest/api/token" -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token-ttl-seconds:3600"` # Obtain the instance identity document. curl -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token: $TOKEN" http://100.100.100.200/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document # Obtain the instance identity signature. curl -H "X-aliyun-ecs-metadata-token: $TOKEN" http://100.100.100.200/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/pkcs7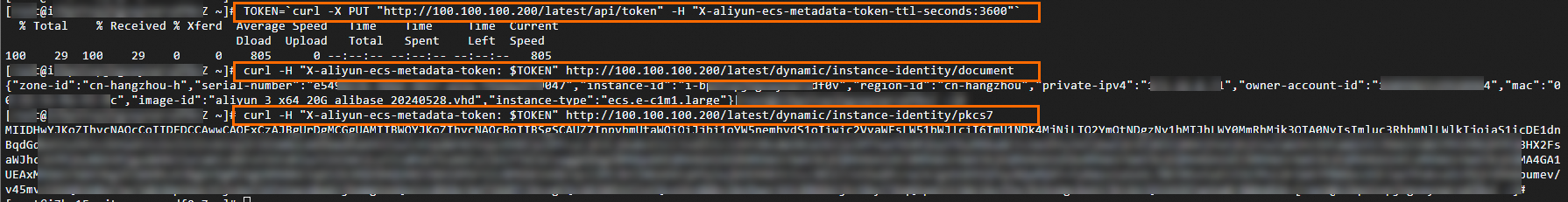
Save the instance identity document, instance identity signature, and Alibaba Cloud public certificate to files.
Run the following command to save the instance identity document to the `document` file.
curl 100.100.100.200/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document > documentRun the following command to save the instance identity signature to the `signature` file.
echo "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" > signature curl 100.100.100.200/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/pkcs7 >> signature echo "" >> signature echo "-----END CERTIFICATE-----" >> signatureRun the following command to save the Alibaba Cloud public certificate to the `cert.cer` file.
cat <<EOF > cert.cer -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDdzCCAl+gAwIBAgIEZmbRhzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADBsMRAwDgYDVQQGEwdV bmtub3duMRAwDgYDVQQIEwdVbmtub3duMRAwDgYDVQQHEwdVbmtub3duMRAwDgYD VQQKEwdVbmtub3duMRAwDgYDVQQLEwdVbmtub3duMRAwDgYDVQQDEwdVbmtub3du MB4XDTE4MDIyMzAxMjkzOFoXDTM4MDIxODAxMjkzOFowbDEQMA4GA1UEBhMHVW5r bm93bjEQMA4GA1UECBMHVW5rbm93bjEQMA4GA1UEBxMHVW5rbm93bjEQMA4GA1UE ChMHVW5rbm93bjEQMA4GA1UECxMHVW5rbm93bjEQMA4GA1UEAxMHVW5rbm93bjCC ASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAIJwy5sbZDiNyX4mvdP32pqM YMK4k7+5lRnVR2Fky/5uwyGSPbddNXaXzwEm+u4wIsJiaAN3OZgJpYIoCGik+9lG 5gVAIr0+/3rZ61IbeVE+vDenDd8g/m/YIdYBfC2IbzgS9EVGAf/gJdtDODXrDfQj Fk2rQsvpftVOUs3Vpl9O+jeCQLoRbZYm0c5v7jP/L2lK0MjhiywPF2kpDeisMtnD /ArkSPIlg1qVYm3F19v3pa6ZioM2hnwXg5DibYlgVvsIBGhvYqdQ1KosNVcVGGQa HCUuVGdS7vHJYp3byH0vQYYygzxUJT2TqvK7pD57eYMN5drc7e19oyRQvbPQ3kkC AwEAAaMhMB8wHQYDVR0OBBYEFAwwrnHlRgFvPGo+UD5zS1xAkC91MA0GCSqGSIb3 DQEBCwUAA4IBAQBBLhDRgezd/OOppuYEVNB9+XiJ9dNmcuHUhjNTnjiKQWVk/YDA v+T2V3t9yl8L8o61tRIVKQ++lDhjlVmur/mbBN25/UNRpJllfpUH6oOaqvQAze4a nRgyTnBwVBZkdJ0d1sivL9NZ4pKelJF3Ylw6rp0YMqV+cwkt/vRtzRJ31ZEeBhs7 vKh7F6BiGCHL5ZAwEUYe8O3akQwjgrMUcfuiFs4/sAeDMnmgN6Uq8DFEBXDpAxVN sV/6Hockdfinx85RV2AUwJGfClcVcu4hMhOvKROpcH27xu9bBIeMuY0vvzP2VyOm DoJeqU7qZjyCaUBkPimsz/1eRod6d4P5qxTj -----END CERTIFICATE----- EOF
Run the following command to use OpenSSL to verify the instance identity.
openssl smime -verify -in signature -inform PEM -content document -certfile cert.cer -noverify > /dev/nullIf
Verification successfulis returned, it indicates that the instance identity is verified.The parameters in the command are described as follows:
document: The file that contains the content of the instance identity document that you obtained.
signature: The file that contains the content of the instance identity signature that you obtained.
NoteIf you specified the `audience` parameter when you obtained the instance identity signature, you must manually append the parameter to the end of the instance identity document. The format is `"audience":""`. Use a comma (,) to separate the `audience` parameter from other parameters.
cert.cer: The file that contains the Alibaba Cloud public certificate.
References
For more information about how to obtain other instance information from within an instance using instance metadata, see Instance metadata.
For more information about how to use instance user data to automatically run commands or scripts when an instance starts, see Configure custom instance initialization.