Packet forwarding rate, network bandwidth, and network latency are important metrics for measuring the network performance of Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. Packet forwarding rate, which is measured in packets per second (pps), is a metric that indicates how many packets can be forwarded per second. Network bandwidth is a metric that indicates the data transfer rate of a network. Network latency is a metric that indicates the amount of time required for a data packet to travel from the sender to the receiver. Testing network performance can help increase network stability and throughput, reduce network latency, and improve user experience and application performance. This topic describes how to use tools, such as Netperf and sockperf, to test the packet forwarding rate, network bandwidth, and network latency of ECS instances. You can estimate the network performance of the instances based on the test results.
To prevent data loss, we recommend that you use a tool to test the network performance of new ECS instances that do not contain data.
Instance type metrics are all verified and obtained within a test environment. In actual scenarios, the performance of an instance may vary based on other factors, such as instance load and networking model.
Prepare a test environment
Make preparations
Create ECS instances that can be used to test different network performance metrics, such as the packet forwarding rate, network bandwidth, and network latency. For information about how to create an ECS instance, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
ImportantTo ensure the accuracy and comparability of test results and eliminate the impacts of other factors, such as different instance specifications, on the test results, we recommend that you use ECS instances of the same instance type in network performance tests.
Make sure that all ECS instances in the same test environment are deployed in the same virtual private cloud (VPC), are connected to the same vSwitch, and belong to the same security group.
Example environments
ECS instances are used as test machines and auxiliary test machines. The packet forwarding rate, network bandwidth, and network latency of the ECS instances are tested. The following tables describe the test items and recommended quantities of test machines or auxiliary test machines in different test environments. Test machines or auxiliary test machines are used as clients or servers in network performance tests. Select the machines that you want to use as servers or clients based on the actual environments.
Test the packet forwarding rate of an ECS instance (This test can be performed only for Linux instances)
NoteNo tools are available to test the packet forwarding rate of Windows instances. This topic does not describe how to test the packet forwarding rate of Windows instances.
Packet forwarding rate lower than 6,000,000 pps
Test item
Test machine
Auxiliary test machine
Instance type
ecs.g7.large
ecs.g7.large
Image
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Number of instances
1
1
Network
Public IP addresses are assigned.
Packet forwarding rate higher than 6,000,000 pps and lower than 20,000,000 pps
Test item
Test machine
Auxiliary test machine
Instance type
ecs.g7.16xlarge
ecs.g7.16xlarge
Image
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Number of instances
1
3
Network
Public IP addresses are assigned.
Packet forwarding rate higher than 20,000,000 pps
Test item
Test machine
Auxiliary test machine
Instance type
ecs.g7.32xlarge
ecs.g7.32xlarge
Image
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Number of instances
1
3
Network
Public IP addresses are assigned.
Test the network bandwidth and network latency of an ECS instance
Linux instance
Test item
Test machine
Auxiliary test machine
Instance type
ecs.g7.large
ecs.g7.large
Image
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3
Number of instances
1
1
Network
Public IP addresses are assigned.
Windows instance
Test item
Test machine
Auxiliary test machine
Instance type
ecs.g7.large
ecs.g7.large
Image
Windows Server 2022
Windows Server 2022
Number of instances
1
1
Network
Public IP addresses are assigned.
Test network performance
Test the packet forwarding rate (for Linux instances only)
No tools are available to test the packet forwarding rate of Windows instances. This section does not describe how to test the packet forwarding rate of Windows instances.
Packet forwarding rate lower than 6,000,000 pps
Connect to the test machine and one or more auxiliary test machines.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following command on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to download the Netperf installation package:
wget https://benchmark-packages.oss-cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/netperf-2.7.0.tar.gzRun the following commands on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to install Netperf and sar.
Run the following commands to decompress the Netperf installation package:
sudo yum install -y gcc autoconf automake libtool sysstat tar -zxvf netperf-2.7.0.tar.gzQuery the version number of GNU Compiler Collection (
GCC).gcc -v 2>&1If the versions of
GCCon the test machine and the auxiliary test machine are later than V10, perform the following operations to ensure thatGCCcan properly compile code. If the versions of GCC on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine are not later than V10, ignore this step.Open the
nettest_omni.cfile.cd netperf vim src/nettest_omni.cPress the i key to enter Insert mode and delete the following declared variables from the
nettest_omni.cfile:/* different options for the sockets */ int loc_nodelay, /* don't/do use NODELAY locally */ rem_nodelay, /* don't/do use NODELAY remotely */ loc_sndavoid, /* avoid send copies locally */ loc_rcvavoid, /* avoid recv copies locally */ rem_sndavoid, /* avoid send copies remotely */ rem_rcvavoid; /* avoid recv_copies remotely */Press the Esc key, enter
:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the file.
Install Netperf and sar.
cd netperf sudo ./configure sudo make && sudo make install
Run the following commands on the test machine to start 64 netserver services:
#!/bin/bash for j in `seq 64`; do netserver -p $[16000+j] > server_$[16000+j].netperf > /dev/null 2>&1 & doneRun the following command on the test machine to query the private IP address of the test machine:
ifconfig || ip addr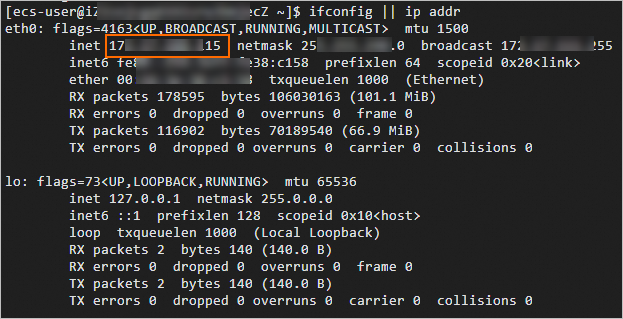
Run the following commands on the auxiliary test machine to send traffic to the test machine:
#!/bin/bash server_ip=<Private IP address of the test machine> for j in `seq 64`; do port=$[16000+j] netperf -H ${server_ip} -l ${run_time:-300} -t UDP_STREAM -p $port -- -m 1 -D > /dev/null 2>&1 & doneReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>with the private IP address of the test machine obtained in the previous step, as shown in the following figure.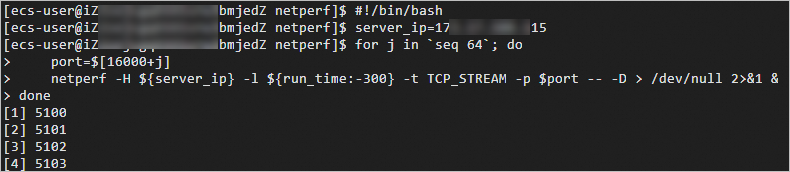
Run the following command on the test machine to test the packet forwarding rate of the test machine:
sar -n DEV 1View the values in the
rxpck/scolumn in the test result. Therxpck/scolumn displays the total number of packets received by the test machine per second. In this example, the average number of packets received by the test machine per second is approximately 940,000, as shown in the following figure.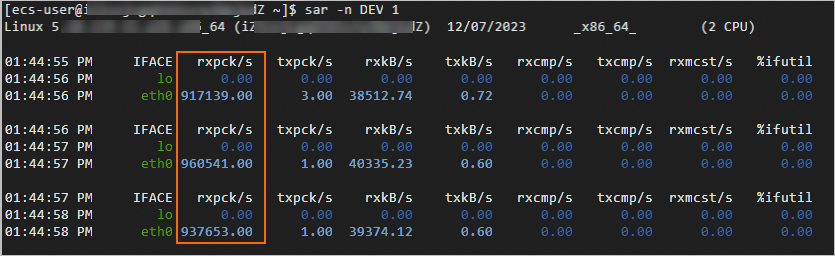
Packet forwarding rate higher than 6,000,000 pps and lower than 20,000,000 pps
Connect to the test machine and one or more auxiliary test machines.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following commands on three auxiliary test machines and one test machine to install sockperf:
sudo yum install -y autoconf automake libtool gcc-c++ cd /opt sudo wget https://github.com/Mellanox/sockperf/archive/refs/tags/3.8.tar.gz sudo tar -zxf 3.8.tar.gz cd sockperf-3.8/ sudo ./autogen.sh sudo ./configure sudo make -j `cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep process | wc -l` sudo make installRun the following command on the test machine to query the private IP address of the test machine:
ifconfig || ip addr
Run the following commands on three auxiliary test machines to send traffic to the test machine:
server_ip="<Private IP address of the test machine>" threads=64 msg_size=14 run_time=60 basePort=6666 for((i=0;i<$threads;++i));do nohup sockperf tp -i $server_ip --pps max -m ${msg_size} -t ${run_time} --port $[${basePort}+${i}] 2>&1 & doneReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>with the actual private IP address of the test machine.run_timespecifies the time period during which traffic is sent.Run the following command on three auxiliary test machines and one test machine to test the packet forwarding rate:
sar -n DEV 1View the values in the
rxpck/scolumn in the test result on the test machine. Therxpck/scolumn displays the total number of packets received by the test machine per second. In this example, the number of packets received by the test machine per second is approximately 12,000,000, as shown in the following figure.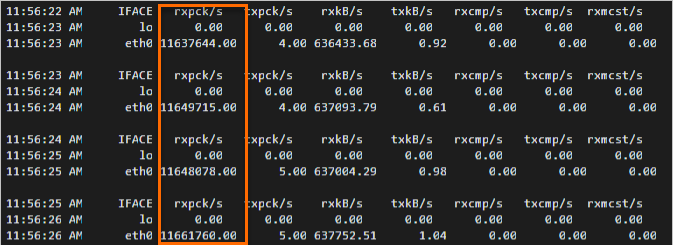
Packet forwarding rate higher than 20,000,000 pps
Connect to the test machine and one or more auxiliary test machines.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following commands on three auxiliary test machines and one test machine to install sockperf:
sudo yum install -y autoconf automake libtool gcc-c++ cd /opt sudo wget https://github.com/Mellanox/sockperf/archive/refs/tags/3.8.tar.gz sudo tar -zxf 3.8.tar.gz cd sockperf-3.8/ sudo ./autogen.sh sudo ./configure sudo make -j `cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep process | wc -l` sudo make installRun the following command on the test machine to bind interrupt requests (IRQs).
In scenarios in which large numbers of packets are forwarded per second, you can bind IRQs to CPU cores to ensure that IRQs are processed by the CPU cores. This way, context switching is reduced and the IRQ processing efficiency is improved.
a=$(cat /proc/interrupts | grep virtio2-input | awk -F ':' '{print $1}') cpu=0 for irq in $a; do echo $cpu >/proc/irq/$irq/smp_affinity_list let cpu+=2 doneRun the following command on the test machine to query the private IP address of the test machine:
ifconfig || ip addr
Run the following commands on three auxiliary test machines to send traffic to the test machine:
server_ip="<Private IP address of the test machine>" threads=64 msg_size=14 run_time=60 basePort=6666 for((i=0;i<$threads;++i));do nohup sockperf tp -i $server_ip --pps max -m ${msg_size} -t ${run_time} --port $[${basePort}+${i}] 2>&1 & doneReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>with the actual private IP address of the test machine.run_timespecifies the time period during which traffic is sent.Run the following command on three auxiliary test machines and one test machine to test the packet forwarding rate:
sar -n DEV 1View the values in the
rxpck/scolumn in the test result on the test machine. Therxpck/scolumn displays the total number of packets received by the test machine per second. In this example, the number of packets received by the test machine per second is approximately 20,000,000, as shown in the following figure.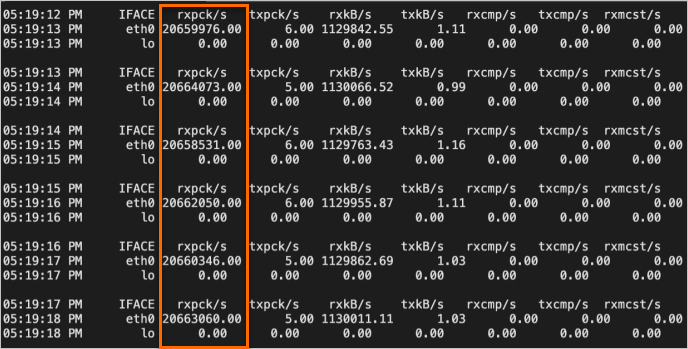
Test network bandwidth
Linux instance
Connect to the test machine and the auxiliary test machine.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following command on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to download the Netperf installation package:
wget https://benchmark-packages.oss-cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/netperf-2.7.0.tar.gzRun the following commands on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to install Netperf and sar.
Decompress the Netperf installation package.
sudo yum install -y gcc autoconf automake libtool sysstat tar -zxvf netperf-2.7.0.tar.gzQuery the version number of
GCC.gcc -v 2>&1If the versions of
GCCon the test machine and the auxiliary test machine are later than V10, perform the following operations to ensure thatGCCcan properly compile code. If the versions of GCC on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine are not later than V10, ignore this step.Open the
nettest_omni.cfile.cd netperf vim src/nettest_omni.cPress the i key to enter Insert mode and delete the following declared variables from the
nettest_omni.cfile:/* different options for the sockets */ int loc_nodelay, /* don't/do use NODELAY locally */ rem_nodelay, /* don't/do use NODELAY remotely */ loc_sndavoid, /* avoid send copies locally */ loc_rcvavoid, /* avoid recv copies locally */ rem_sndavoid, /* avoid send copies remotely */ rem_rcvavoid; /* avoid recv_copies remotely */Press the Esc key, enter
:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the file.
Install Netperf and sar.
cd netperf sudo ./configure sudo make && sudo make install
Run the following commands on the test machine to start 64 netserver services:
#!/bin/bash for j in `seq 64`; do netserver -p $[16000+j] > server_$[16000+j].netperf 2>&1 & doneRun the following command on the test machine to query the private IP address of the test machine:
ifconfig || ip addr
Run the following commands on the auxiliary test machine to send traffic to the test machine:
#!/bin/bash server_ip=<Private IP address of the test machine> for j in `seq 64`; do port=$[16000+j] netperf -H ${server_ip} -l ${run_time:-300} -t TCP_STREAM -p $port -- -D > /dev/null 2>&1 & doneReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>with the private IP address of the test machine obtained in the previous step, as shown in the following figure.
Run the following command on the test machine to test the network bandwidth:
sar -n DEV 1View the values in the
rxkB/scolumn in the test result as shown in the following figure. TherxkB/scolumn displays the size of packets received by the test machine per second. Unit: KB/s. One byte equals eight bits. You can multiply a packet size in the rxkB/s column by eight to obtain a network bandwidth value in Kbit/s.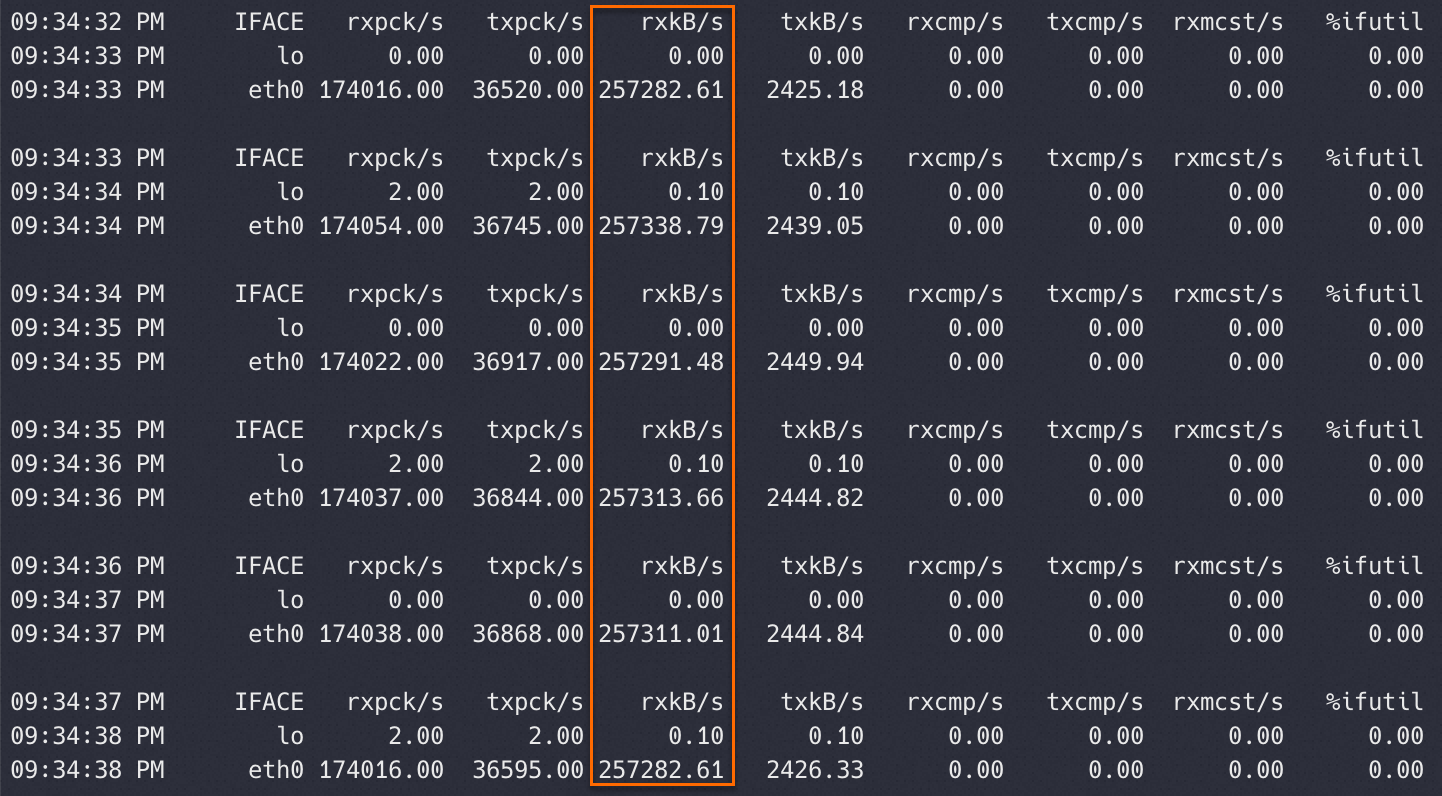
Windows instance
Connect to the test machine and the auxiliary test machine.
For more information, see Connect to a Windows instance by using a password or a key.
Install test tools and disable the firewall on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine.
Download the ntttcp.exe tool and obtain the path in which the tool is stored.
Open the Run dialog box. Enter powershell and click OK to start PowerShell.
To prevent the firewall from blocking connections to the test machine and the auxiliary test machine, run the following command on the machines to disable the firewall:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile * -Enabled:falseAlternatively, run the following commands on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to create an inbound firewall rule that allows NTTTCP (ntttcp.exe) packets:
$ntttcpPath = "<Path of ntttcp.exe>" New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName ntttcp -Protocol Any -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Enabled True -Profile Any -Program $ntttcpPathNoteReplace
<Path of ntttcp.exe>with an actual value.
Run the following commands on the test machine to configure receive side scaling (RSS) for a network adapter (also called network interface controller).
RSS is a network driver technology that enables the efficient distribution of packets across receive queues on multiple CPU cores to improve network performance and allow concurrent network processing. In the commands:
If the test machine has up to 16 CPU cores, set the number of RSS receive queues to the number of CPU cores to ensure that each CPU core has an independent RSS receive queue to process network traffic.
If the test machine has more than 16 CPU cores, disable RSS. Many network adapters support up to 16 RSS queues. If you use RSS on the test machine that has more than 16 CPU cores, resources may not be evenly allocated or management complexity may increase.
$cpuNum = (Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_Processor).NumberOfLogicalProcessors if ($cpuNum -le 16) { Set-NetAdapterRss -Name <Name of the network adapter on the test machine> -NumberOfReceiveQueues $cpuNum } else { Disable-NetAdapterRss -Name <Name of the network adapter on the test machine> }NoteReplace
<Name of the network adapter on the test machine>with an actual value. You can run theGet-NetAdapter | Select-Object Namecommand to obtain the names of network adapters on the test machine.After you modify the RSS configuration of a network adapter, you must restart the network adapter service, which may interrupt the network connections on the network adapter. Wait until the network connections are re-established and perform the subsequent operations.
Run the following commands on the test machine to prepare to receive data:
$serverIp = (Get-NetIPConfiguration -InterfaceAlias <Name of the network adapter on the test machine>).IPv4Address.IPAddress $cpuNum = (Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_Processor).NumberOfLogicalProcessors $threadNum = $cpuNum & <Path of ntttcp.exe on the test machine> -r -m $threadNum,0,$serverIp -t 300NoteReplace
<Name of the network adapter on the test machine>and<Path of ntttcp.exe on the test machine>with actual values.Run the following commands on the auxiliary test machine to send data:
$serverIp = "<Private IP address of the test machine>" $threadNum = "<Thread number of the test machine>" <Path of ntttcp.exe on the auxiliary test machine> -s -m $threadNum,*,$serverIp -t 100NoteReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>,<Thread number of the test machine>, and<Path of ntttcp.exe on the auxiliary test machine>with actual values. You can run theipconfigcommand to obtain the private IP address of the test machine and run the$cpuNumcommand to obtain the thread number of the test machine.View the tested network bandwidth on the test machine.
The following figure shows the test result, in which the
Throughput(MB/s)value indicates the network bandwidth.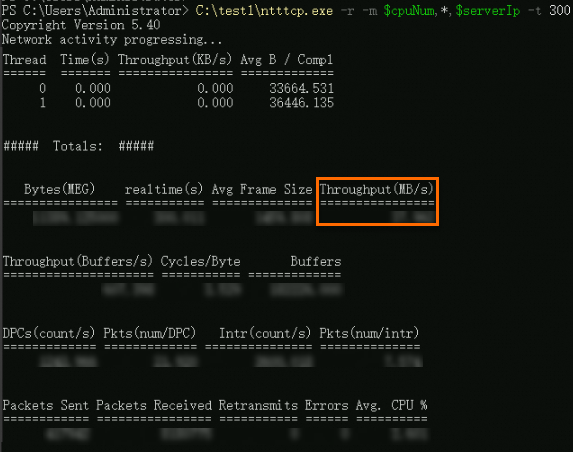
Test network latency
Linux instance
Connect to the test machine and the auxiliary test machine.
For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance using Workbench.
Run the following commands on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to install
sockperf:sudo yum install -y autoconf automake libtool gcc-c++ cd /opt sudo wget https://github.com/Mellanox/sockperf/archive/refs/tags/3.8.tar.gz sudo tar -zxf 3.8.tar.gz cd sockperf-3.8/ sudo ./autogen.sh sudo ./configure sudo make -j `cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep process | wc -l` sudo make installRun the following command on the test machine to query the private IP address of the test machine:
ifconfig || ip addr
Run the following command on the test machine to start sockperf:
sockperf sr --tcp --daemonizeRun the following commands on the auxiliary test machine to send traffic to the test machine:
sockperf pp -i <Private IP address of the test machine> --tcp -t 30 -m 14 --full-log=result.jsonReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>with the private IP address of the test machine obtained in the previous step.View the tested network latency on the test machine.
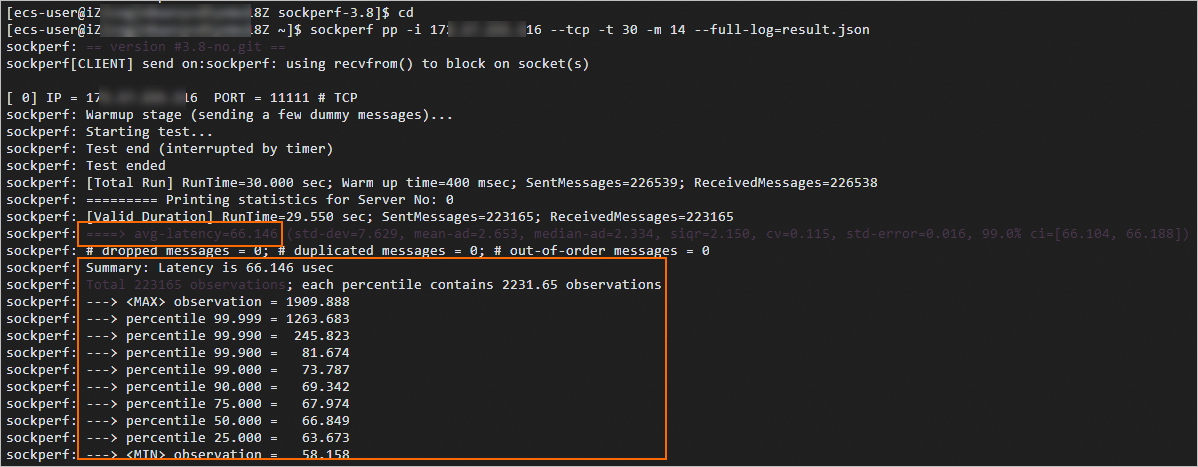
View the returned data, as shown in the following figure.
The returned data starting with
avg-latencyindicates the average latency in microseconds.The returned data starting with
percentile 99.000indicates the 99-percentile latency in microseconds.
Windows instance
Connect to the test machine and the auxiliary test machine.
For more information, see Connect to a Windows instance by using a password or a key.
Install test tools and disable the firewall on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine.
Download the latte.exe tool and obtain the path in which the tool is stored.
Open the Run dialog box. Enter powershell and click OK to start PowerShell.
To prevent the firewall from blocking connections to the test machine and the auxiliary test machine, run the following command on the machines to disable the firewall:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile * -Enabled:falseAlternatively, run the following commands on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine to create an inbound firewall rule that allows Latte (latte.exe) packets:
$lattePath = "<Path of latte.exe>" New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName Latte -Protocol Any -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Enabled True -Profile Any -Program $lattePathNoteReplace
<Path of latte.exe>with the actual path of latte.exe on the test machine.
Run the following commands on the test machine to prepare to receive data:
$serverIp = (Get-NetIPConfiguration | Where-Object {$_.InterfaceAlias -eq '<Name of the network adapter on the test machine>'} | Select-Object -ExpandProperty IPv4Address).IPAddress $port = <Communication port> & "<Path of latte.exe on the test machine>" -a "$serverIp`:$port" -i 65535NoteReplace
<Name of the network adapter on the test machine>and<Path of latte.exe on the test machine>with actual values. You can run theGet-NetAdapter | Select-Object Namecommand to obtain the names of network adapters on the test machine.Specify a port number to replace
<Communication port>and make sure that the specified port numbers on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine are the same.
Run the following commands on the auxiliary test machine to send data:
$serverIp = "<Private IP address of the test machine>" $port = <Communication port> & "<Path of latte.exe on the auxiliary test machine>" -c -a "${serverIp}:$port" -i 65535NoteReplace
<Private IP address of the test machine>and<Path of latte.exe on the auxiliary test machine>with actual values. You can run theipconfigcommand to obtain the private IP address of the test machine.Specify a port number to replace
<Communication port>and make sure that the specified port numbers on the test machine and the auxiliary test machine are the same.
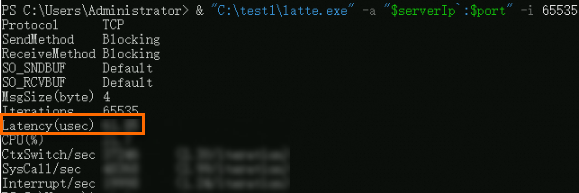
View the tested network latency on the test machine.
The following figure shows the test result. The
Latency(usec)value indicates the average network latency in microseconds.