Data Management (DMS) provides the SQL review optimization feature in security rules. After you submit SQL statements for data change or on the SQLConsole tab, DMS reviews the submitted SQL statements based on the specifications in security rules. For example, the table must contain remarks or the table must have specific columns. Then, DMS offers the corresponding optimization suggestions, such as the lock-free data change recommendation. This feature helps database administrators (DBAs) review SQL statements and improve development quality. This topic describes how to configure security rules to review SQL statements and perform a data change.
Background information
DMS provides the default SQL specifications in security rules. For example, the table must contain remarks, a NULL value cannot be inserted into a NOT NULL column in the INSERT statement, and the names of fields in the INSERT statement cannot be duplicated.
For more information about SQL specifications and SQL optimization suggestions, see SQL review optimization.
Preparations
Execute the following SQL statement to create a table named migration_job:
CREATE TABLE `migration_job` (
`id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Primary key',
`gmt_create` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT 'Creation time',
`ref_id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT '',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='Test';If a database instance is managed in Security Collaboration mode, you can create a custom security rule set and associate the instance with the security rule set. For more information, see the Create security rules and Apply security rules sections of the "Manage security rules" topic.
Step 1: Configure security rules
This step shows how to configure the Security Collaboration security rule set. If you want to configure the Flexible Management or Stable Change security rule set, find the security rule set that you want to configure and click SQL audit optimization recommendations in the Actions column.
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
Move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose . Note
icon in the upper-left corner and choose . NoteIf you use the DMS console in normal mode, choose in the top navigation bar.
Find the security rule set that you want to configure and click Edit in the Actions column.
- On the Details page, click the SQL audit optimization recommendations tab in the left-side pane.
Find the rule named The table must have a primary key and click Edit in the Actions column.
NoteYou can click the
 icon next to Tag, Behavioral action, and Status to filter rules. The Tag parameter specifies the scope within which a rule is effective, including DDL statements and DML statements.
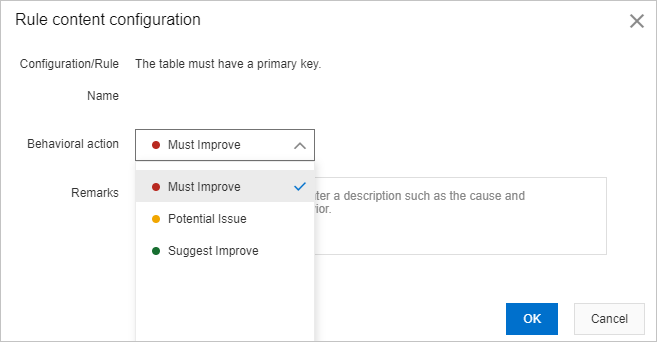
icon next to Tag, Behavioral action, and Status to filter rules. The Tag parameter specifies the scope within which a rule is effective, including DDL statements and DML statements. In the Rule content configuration dialog box, configure the required parameters. In this example, the Behavioral action parameter is set to Must Improve.
 Note
NoteThe default security rules that DMS provides for SQL review do not contain the Must Improve value. For more information about behavioral actions, see the Behavioral actions section of the "SQL review optimization" topic.
Click OK.
If you use the features such as data development, data change, and SQL review, the SQL review optimization feature verifies SQL statements based on the configured security rules.
Step 2: Perform a data change
- Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the console and choose . On the Data Change Ticket Application page, configure the required parameters and click Submit.
NoteFor more information about the Normal Data Modify feature, see Normal data modify.
Select the database instance that is associated with the security rule set that you configured.
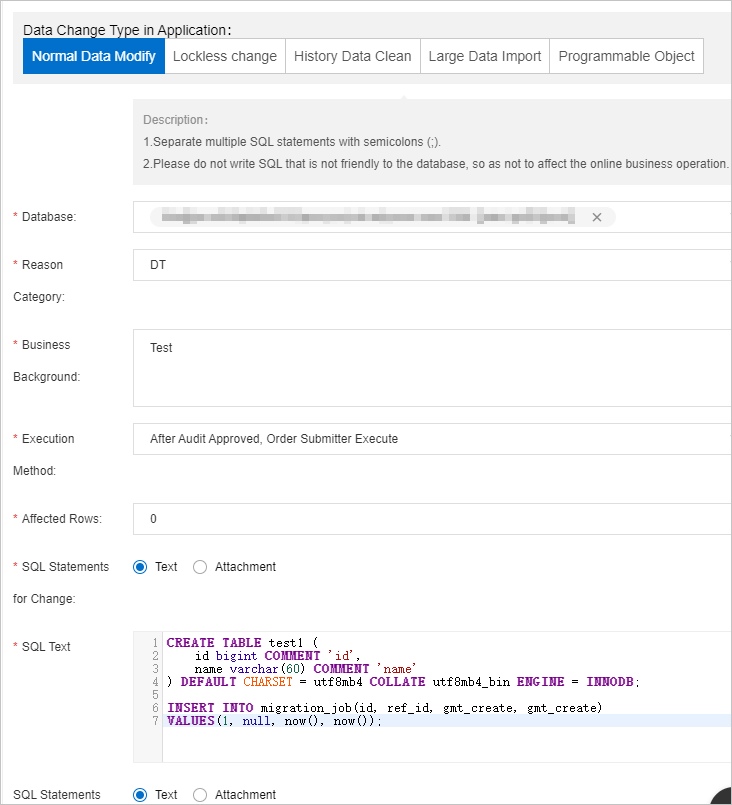
Execute the following SQL statements to perform a data change:
CREATE TABLE test1 ( id bigint COMMENT 'id', name varchar(60) COMMENT 'name' ) DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin ENGINE = INNODB; INSERT INTO migration_job(id, ref_id, gmt_create, gmt_create) VALUES(1, null, now(), now());
After you submit the ticket, DMS reviews the submitted SQL statements based on the security rule set that you configured in Step 1.
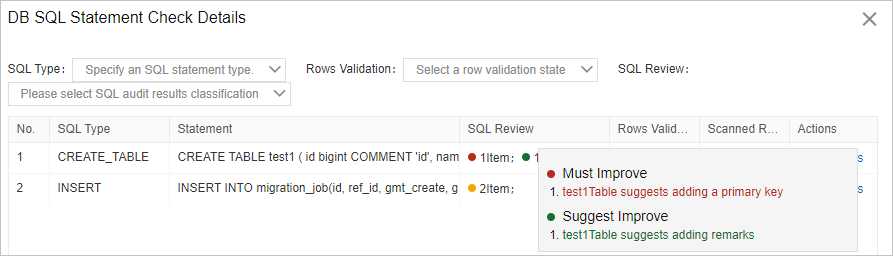
The SQL review optimization feature reviews the submitted SQL statements and returns suggestions. In this example, the following suggestions are returned: One item must be improved, two potential issues exist, and one item can be improved.
Click View Details. Move the pointer over the items in the SQL Review column to view details.
Click SQL Statements for Modification. Optimize the SQL statements based on the suggestions and click Confirm Change.
You can modify the SQL statements by performing the following operations:
In the
CREATE TABLEstatement, add a primary key and remarks for thetest1table.In the
INSERTstatement, remove the duplicate field namedgmt_createand insert values for theref_idfield.
The following SQL statements are obtained after modification:
CREATE TABLE test1 ( id bigint PRIMARY KEY COMMENT 'id', name varchar(60) COMMENT 'name' ) DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin ENGINE = INNODB COMMENT = 'Remarks'; INSERT INTO migration_job(id, ref_id, gmt_create) VALUES(1, 2, now());DMS reviews the SQL statements again.
The SQL statements pass the review.
Click Submit for Approval and wait for approval.
After approval, a data change task is generated.
After the application is approved, click Execute Change. In the Task Settings dialog box, set the task execution parameters described in the following table and click Confirm Execution.
NoteThis step is automatically skipped if you set the Execution Method parameter to Automatically Execute Upon Approval in the Apply step.
After a suspended task is resumed, the script can be executed from the position at which the script was suspended.
Parameter
Description
Execution Strategy
Specifies whether to run the task for the ticket immediately or at a scheduled time. Valid values:
Running immediately: If you select this option, DMS immediately runs the task after you click Confirm Execution.
Schedule: If you select this option, you need to specify a time. After you click Confirm Execution, DMS runs the task at the scheduled time. For example, you can specify that the task is run at 00:00:00 on May 22, 2024.
Enable Submit as Single Transaction
Specifies whether to submit all the statements as a single transaction. By default, this switch is turned off. Valid values:
on: All SQL statements that are involved in this change are submitted as a transaction. If an SQL statement fails, all the executed DML statements in the same transaction are rolled back. DDL statements cannot be rolled back.
off: Each SQL statement is submitted as a transaction. If an SQL statement fails, the transaction is stopped, but the executed SQL statements are not rolled back.
Enable Backup
Specifies whether to back up data. By default, this switch is turned off. Valid values:
NoteData backup is supported for only UPDATE and DELETE statements.
You cannot back up data for MongoDB or Redis databases.
on: DMS generates specific statements to back up the data that is affected when
UPDATEorDELETEstatements are executed.If the database is a MySQL or MariaDB database, DMS generates a
REPLACE INTOstatement.NoteThe supported MySQL database types include ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, PolarDB for MySQL, PolarDB-X, and MySQL databases that are not on Alibaba Cloud.
If the database is not a MySQL or MariaDB database, DMS generates an
INSERTstatement.
off: DMS does not generate statements for data backup.
NoteThe execution of SQL tasks is monitored by the checkpoints that are configured in security rules to control the SQL execution. Examples of the checkpoints include Database lock timeout mechanism before SQL execution, Database load check before SQL execution, and sleep policy after SQL execution. To check the checkpoints that are configured in a security rule to control SQL execution, go to the details page of the security rule, and click SQL execution control in the left-side pane. For more information about how to modify the default checkpoint settings, see Configure the control on SQL execution.
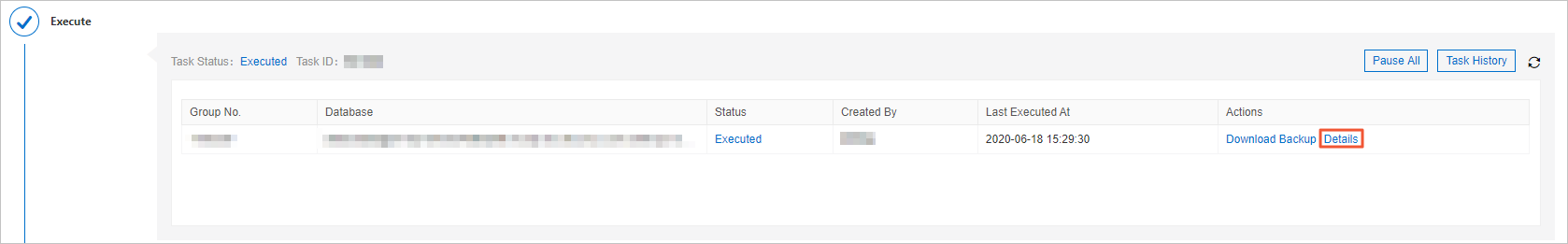
After the task is complete, you can click Details in the Actions column of the ticket to view the status of the ticket, number of times the task is run, number of affected rows, executed statements, and logs.
After the task is complete, you can go to the SQLConsole tab of the database to check whether the data is changed as expected.
What to do next
After the data change task is complete, you can click Details to view the execution logs that contain detailed information. such as the executed SQL statements, execution duration, and scheduling details.