This topic describes how to combine the lifecycle hook feature of Auto Scaling and a CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) template to automate the task of mounting an File Storage NAS file system to an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance that runs Linux.
Prerequisites
A scaling group is created and is in the Enabled state.
An NAS file system is prepared, and a mount target is added. For more information about the mount target, see Manage mount targets. The mount target of the NAS file system must meet the following requirements:
If the network type of the scaling group is virtual private cloud (VPC), the network type of the mount target must also be VPC. The mount target and the scaling group must reside in the same VPC.
If the network type of the scaling group is classic network, the network type of the mount target must also be classic network.
The protocol of the mount target must be Network File System (NFS).
A RAM role is created for CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS). The trusted entity of the RAM role must be Alibaba Cloud Service, the trusted service must be CloudOps Orchestration Service, and the RAM role must have the permissions to perform operations on the OOS template. For more information, see Use RAM to grant permissions to OOS.
NoteIn this topic, the OOSServiceRole RAM role is used as an example. You can also use other roles.
Background information
An NAS file system functions as a distinct file storage entity. Mounting an NAS file system to an ECS instance enables you to interact with the NAS file system as if it were part of the local file system. This integration reinforces data protection and operational resiliency. Auto Scaling currently does not support the integration of NAS file systems into scaling configurations. However, you can combine the lifecycle hook feature and an OOS template to automatically mount an NAS file system to an ECS instance. This way is more efficient than manual mounting of the NAS file system after you create the ECS instance.
Procedure
In this example, the ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAttachNASFileSystemToInstance public template is used to show how to automate the task of mounting an NAS file system to an ECS instance that runs Linux. Perform the following steps:
Step 1: Grant a RAM role the permissions on OOS
You must have the permissions to execute OOS templates. The ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAttachNASFileSystemToInstance template includes ECS, Auto Scaling, and NAS file system resources that are required to perform O&M tasks.
Log on to the RAM console.
Create a policy.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
On the Create Policy page, click the JSON tab, configure parameters based on your business requirements, and then click OK.
The following table describes the settings that are used in this example. Any parameters not covered in the following table default to their predefined settings.
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter ESSHookPolicyForAttachNAS.
Policy document
Enter the following content:
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "ecs:DescribeInvocations", "ecs:RunCommand", "ecs:DescribeInvocationResults", "ecs:DescribeInstances" ], "Resource": "*", "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "ess:CompleteLifecycleAction" ], "Resource": "*", "Effect": "Allow" } ] }
Attach the policy to the OOSServiceRole RAM role.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Find the OOSServiceRole RAM role and click Grant Permission in the Actions column.
Add the required permissions for the OOSServiceRole RAM role that is assumed by OOS to complete the authorization.
In the Grant Permission panel, configure Resource Scope and Policy. After you complete the configuration, click Grant permissions.
The following table describes the settings that are used in this example. Any parameters not covered in the following table default to their predefined settings.
Parameter
Description
Resource Scope
Set the value to Account.
Policy
Select the following custom policy: ESSHookPolicyForAttachNAS.
Step 2: Create a lifecycle hook for scale-out purposes and trigger a scale-out event
Log on to the Auto Scaling console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Scaling Groups.
In the top navigation bar, select a region.
Find the desired scaling group and use one of the following methods to open the scaling group details page.
Click the ID of the scaling group in the Scaling Group Name/ID column.
Click Details in the Actions column.
Create a lifecycle hook.
In the upper part of the details page, click the Lifecycle Hook tab.
Click Create Lifecycle Hook.
Configure parameters based on your business requirements and click OK.
The following table describes the settings that are used in this example. Any parameters not covered in the following table default to their predefined settings.
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter ESSHookForAttachNAS.
Scaling Activity
Select Scale-out Event.
Timeout Period
Configure Timeout Period based on your business requirements. In this example, set the value to 300. Unit: seconds.
NoteThe timeout period is the period of time during which you can perform custom operations on instances. If the timeout period is shorter than the period of time that is required to perform custom operations, the operations may fail. We recommend that you estimate the period of time that is required to perform custom operations on instances and configure Timeout Period based on your estimates.
Default Execution Policy
Select Continue.
Send Notification When Lifecycle Hook Takes Effect
Configure the following parameters for the template:
Select OOS Template.
Select Public Templates.
Select ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAttachNASFileSystemToInstance.
In the ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAttachNASFileSystemToInstance public template, you must configure the following parameters:
mountTargetDomain: Enter the domain name of the mount target of the NAS file system.
MountDir: Specify the directory on the desired ECS instance to which that you want to mount the NAS file system. The default directory is /mnt.
FileSystemVersion: Specify a protocol type. A value of 0 indicates that the NFSv4 protocol is used to mount the NAS file system. A value of 1 indicates that the NFSv3 protocol is used to mount the NAS file system. In this example, 0 is used.
RateControl: Specify a rate control type. Valid values: Batch-based Control and Concurrency-based Control. In this example, Concurrency-based Control is used.
OOSAssumeRole: Select OOSServiceRole. In Step 1, OOSServiceRole is granted the permissions on the ECS, Auto Scaling, and NAS file system resources. OOS obtains the preceding permissions after it assumes the RAM role.
Trigger a scale-out event.
In this example, a scale-out event is manually triggered by executing a scaling rule. You can also trigger scale-out events by using scheduled or event-triggered tasks.
NoteIf scaling activities are triggered when you manually execute scaling rules, lifecycle hooks take effect. Lifecycle hooks do not take effect when you manually add or remove ECS instances to or from a scaling group.
In the upper part of the page that appears, click the Scaling Rules and Event-triggered Tasks tab.
On the Scaling Rules tab, click Create Scaling Rule.
In the Create Scaling Rule dialog box, configure parameters based on your business requirements and click OK.
The following table describes the settings that are used in this example. Any parameters not covered in the following table default to their predefined settings.
Parameter
Description
Rule Name
Enter Add1.
Rule Type
Select Simple Scaling Rule.
Operation
Set the value to Add 1 Instances.
On the Scaling Rules tab, find the Add1 scaling rule and click Execute in the Actions column.
In the Execute Scaling Rule message, click OK.
After the scaling rule is executed, Auto Scaling adds one ECS instance to the scaling group. However, the ECS instance enters the Pending Add state because of the ESSHookForAttachNAS lifecycle hook that is in effect. During the timeout period of the lifecycle hook, Auto Scaling notifies OOS to execute the O&M tasks that are defined in the ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAttachNASFileSystemToInstance public template.
Check whether the automatically created ECS instance meets your expectations.
In the upper part of the details page, click the Instances tab.
Find the automatically created ECS instance and click its ID in the ECS Instance ID/Name column.
In the Basic Information section, click Connect.
Log on to the ECS instance and run the following command to view the mount result.
df -h | grep aliyunIf the mount path of the NAS file system exists in the command output as shown in the following figure, the NAS file system is mounted. You can also run the
nfsstat -ccommand to view the protocol version. TheClient nfs v4indicates that the protocol version is v4.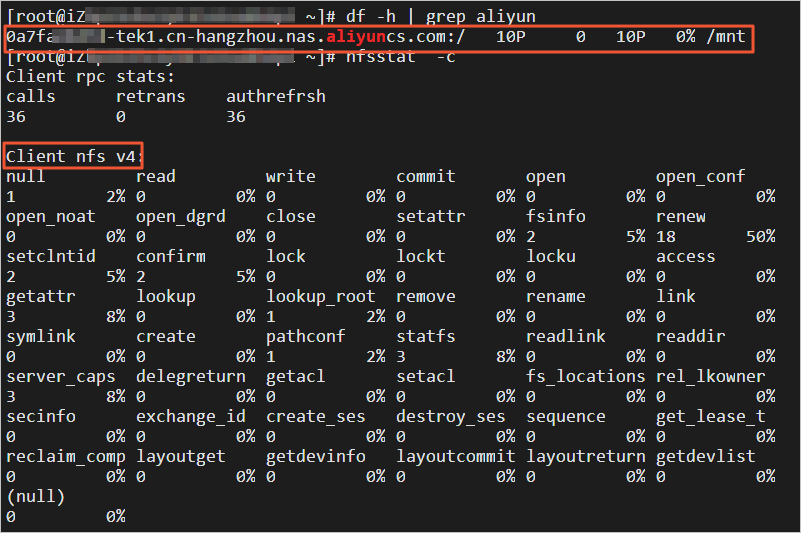
If the ECS instance is created but has no associated NAS file system, go to the OOS console to view the execution of the O&M operations. For more information, see Step 3: (Optional) View the OOS execution.
Step 3: (Optional) View the OOS execution
Log on to the OOS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Find the execution task by time and click Details in the Actions column.
On the execution details page that appears, view the related information.
For example, in the Basic Information section, you can view the execution ID and status. In the Execution Steps and Results section, you can click a task node to view the execution details. For more information, see View the details of an execution.
NoteIf the execution fails, an error message is displayed on the execution details page.
FAQ
If you fail to execute an O&M task, troubleshoot the issue based on the error message in the execution result. For more information, see FAQ.
The following table describes the common error message.
Error message | Cause | Solution |
Forbidden.Unauthorized message: A required authorization for the specified action is not supplied. | You have not authorized Auto Scaling to perform the current action. | Check whether the OOSServiceRole RAM role has the required permissions. |
Forbidden.RAM message: User not authorized to operate on the specified resource, or this API doesn't support RAM. | The RAM user or RAM role does not have the permissions to operate the corresponding resources. | Check whether the OOSServiceRole RAM role has the required permissions. For example, you can grant the OOS permissions to the RAM role. Before OOS can manage the resources that are declared in the OOS template, you must grant the required permissions to the RAM role. |
LifecycleHookIdAndLifecycleActionToken.Invalid message: The specified lifecycleActionToken and lifecycleActionId you provided does not match any in process lifecycle action. | The ongoing lifecycle hook action has ended or been stopped. | Assess the timeout period of the lifecycle hook to make sure that the O&M tasks specified in the OOS template can be complete within the allotted time limit. |