If you use a cloud certificate or a custom certificate to enable SSL encryption for an ApsaraDB RDS instance, a client validates the RDS instance before the client connects to the RDS instance. If you want the RDS instance to validate the client, you must also configure a client certificate authority (CA) certificate. This topic describes how to configure a client CA certificate on an RDS instance.
Prerequisites
A cloud certificate or a custom certificate is configured to enable the SSL encryption feature. For more information, see Configure a cloud certificate to enable the SSL encryption feature or Configure a custom certificate to enable the SSL encryption feature.
OpenSSL is installed.
NoteLinux operating systems are provided with OpenSSL. If you use a Linux operating system, you do not need to install OpenSSL. If you use a Windows operating system, you must download the OpenSSL software package and install OpenSSL. For more information, visit the Win32/Win64 OpenSSL page.
Usage notes
After a client CA certificate is enabled, you must close the existing connection and establish a new connection to make SSL encryption take effect.
When you enable a client CA certificate, change the content of the configured client CA certificate, or modify the client certificate revocation list (CRL), the RDS instance restarts. The restart process requires approximately 3 minutes. We recommend that you perform these operations during off-peak hours.
Procedure
Step 1: Create a client certificate
In this example, CentOS is used. If you use a Windows operating system, you can configure the openssl command by using the same configuration that you use in CentOS.
Create a self-signed certificate and a private key for the self-signed certificate. The self-signed certificate is saved in a file named client-ca.crt. The private key is saved in a file named client-ca.key.
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -nodes -out client-ca.crt -keyout client-ca.key -subj "/CN=root-client-ca"Create a certificate signing request (CSR) and a private key for the client certificate. The CSR is used to request a client certificate and is saved in a file named client.csr. The private key is saved in a file named client.key.
openssl req -new -nodes -text -out client.csr -keyout client.key -subj "/CN=<Username that is used for logons from the client>"NoteIn the preceding command, the CN parameter follows the -subj parameter. You must set the CN parameter to the username of the account that is used to connect to the RDS instance from the client.
Create a client certificate. The client certificate is saved in a file named client.crt.
openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -text -days 365 -CA client-ca.crt -CAkey client-ca.key -CAcreateserial -out client.crt
After the preceding configuration is complete, run the ls command to view the created file.
# ls
client-ca.crt client-ca.key client-ca.srl client.crt client.csr client.keyThe following list describes the files:
client.crt: the file that contains the client certificate
client.key: the file that contains the private key of the client certificate
client-ca.crt: the file that contains the self-signed certificate
client-ca.key: the file that contains the private key of the self-signed certificate
Step 2: Configure a client CA certificate
After a client CA certificate is configured, the status of the RDS instance changes from Running to Modifying SSL Settings. After about 3 minutes, the status changes back to Running.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
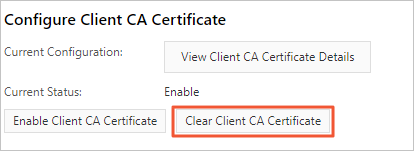
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click . On the page that appears, click the SSL tab.
Click Enable Client CA Certificate.
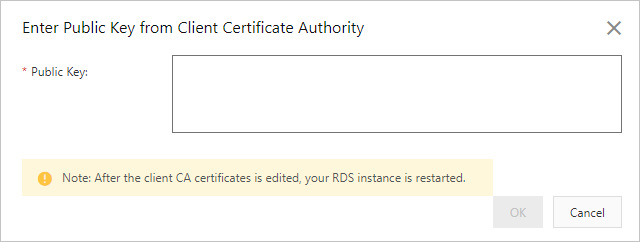
In the dialog box that appears, copy the content of the client-ca.crt file to the Public Key field. Then, click OK.
NoteFor more information about how to obtain the client-ca.crt file, see Step 1: Create a client certificate. Make sure that all the content from -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- to -----END CERTIFICATE----- is copied to this field.
Step 3: Connect to the RDS instance from the client
You can connect to the RDS instance from the client over SSL. For more information, see Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance over SSL.
Step 4: (Optional) Configure a CRL file
If you no longer need the client certificate, you can revoke the client certificate. After the client certificate is revoked, the RDS instance denies access requests from the client.
After a CRL file is configured, the status of the RDS instance changes from Running to Modifying SSL Settings. After about 3 minutes, the status changes back to Running.
Prepare the configuration file
touch /etc/pki/CA/index.txt echo 1000 > /etc/pki/CA/crlnumberNoteIf you use a Windows operating system, you must perform the following operations:
Create a CA folder in the Installation directory of OpenSSL\bin directory.
Create a file named index.txt in the CA folder.
Run the following command by using the PostgreSQL CLI:
echo 1000 > <Installation directory of OpenSSL>\bin\CA\crlnumberModify the openssl.cnf file in C:\Program Files\Common Files\SSL\.
# Find the [ CA_default ] configuration item. dir = "<Installation directory of OpenSSL>\\bin\\CA"
Revoke the client certificate, which is contained in the client.crt file.
openssl ca -revoke client.crt -cert client-ca.crt -keyfile client-ca.keyNoteThe preceding command requires the self-signed certificate and the private key of the self-signed certificate. The self-signed certificate is contained in the client-ca.crt file, and the private key of the self-signed certificate is contained in the client-ca.key file. For more information, see the Step 1: Create a client certificate.
Create a CRL. The CRL is saved in a file named client.crl.
openssl ca -gencrl -out client.crl -cert ca.crt -keyfile ca.keyIn the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click . On the page that appears, click the SSL tab.
Click Enable Certificate Revocation File.
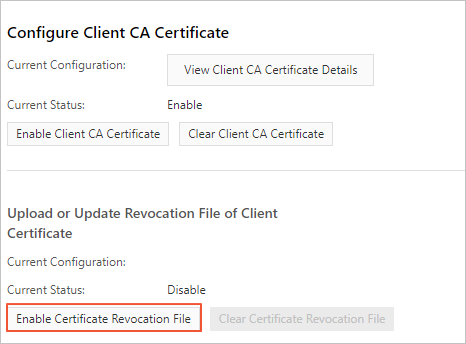
In the dialog box that appears, copy the content of the client.crl file to the Revocation File field.
Step 5: (Optional) Update the client certificate
This operation triggers a restart of the RDS instance. Proceed with caution.
On the SSL tab, click Clear Client CA Certificate. Then, click Enable Client CA Certificate.