AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark enables you to use a Docker image to start the interactive JupyterLab development environment. This environment helps you connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark and perform interactive testing and computing using elastic resources of AnalyticDB for MySQL.
Prerequisites
An AnalyticDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition, Basic Edition, or Data Lakehouse Edition cluster is created.
A job resource group is created for the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
A database account is created for the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
If you use an Alibaba Cloud account, you need to only create a privileged account.
If you use a Resource Access Management (RAM) user, you must create a privileged account and a standard account and associate the standard account with the RAM user.
You have completed account authorization.
The log storage path of Spark applications is configured.
NoteLog on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console. Find the cluster that you want to manage and click the cluster ID. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . Click Log Settings. In the dialog box that appears, select the default path or specify a custom storage path. You cannot set the custom storage path to the root directory of OSS. Make sure that the custom storage path contains at least one layer of folders.
Usage notes
AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark supports interactive Jupyter jobs only in Python 3.7 or Scala 2.12.
Interactive Jupyter jobs automatically release Spark resources after remaining idle for a period of time. The default release time is 1,200 seconds (the resources are automatically released 1,200 seconds after the last code block is executed). You can use the following command in a Jupyter Notebook Cell to configure the
spark.adb.sessionTTLSecondsparameter and modify the automatic release time of Spark resources.%%configure -f { "spark.adb.sessionTTLSeconds": "3600" }
Connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark
Use JupyterLab in the AnalyticDB for MySQL provided image to connect to Spark
Pull the Jupyter image of AnalyticDB for MySQL. Run the following command:
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/adb-public-image/adb-spark-public-image:adb.notebook.0.5.preStart the interactive JupyterLab development environment.
Command syntax:
docker run -it -p {Host port}:8888 -v {Host file path}:{Docker file path} registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/adb-public-image/adb-spark-public-image:adb.notebook.0.5.pre -d {ADB Instance Id} -r {Resource Group Name} -e {API Endpoint} -i {AK Id} -k {AK Sec} -t {StsToken} # Choose either StsToken or AKThe following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Required
Description
-p
No
Maps a host port to a container port. Specify the parameter in the
-p {Host port}:{Container port}format.Specify a random value for the host port and set the container port to
8888. Example:-p 8888:8888.-v
No
If you do not mount the host path and disable the Docker container, the editing files may be lost. After you disable the Docker container, the container attempts to terminate all interactive Spark jobs that are running. You can use one of the following methods to prevent loss of the editing files:
When you start the interactive JupyterLab development environment, mount the host path to the Docker container and store the job files in the corresponding file path. Specify the parameter in the
-v {Host path}:{Docker file path}format. Specify a random value for the file path of the Docker container. Recommended value:/root/jupyter.Before you disable the Docker container, make sure that all files are copied and stored.
Example:
-v /home/admin/notebook:/root/jupyter. In this example, the host files that are stored in the/home/admin/notebookpath are mounted to the/root/jupyterpath of the Docker container.NoteSave the editing notebook files to the
/tmpfolder. After you disable the Docker container, you can view the corresponding files in the/home/admin/notebookpath of the host. After you re-enable the Docker container, you can continue to execute the files. For more information, see Volumes.-d
Yes
The ID of the AnalyticDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition, Basic Edition, or Data Lakehouse Edition cluster.
You can log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console and go to the Clusters page to view cluster IDs.
-r
Yes
The name of the Job resource group in the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
You can log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console, choose in the left-side navigation pane, and then click the Resource Groups tab to view resource group names.
-e
Yes
The endpoint of the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
For more information, see Endpoints.
-i
Yes (in specific scenarios)
The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user.
For information about how to view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret, see Accounts and permissions.
-k
-t
Yes (in specific scenarios)
The Security Token Service (STS) token, which is the temporary identity credential of the RAM role.
A RAM user with permissions can call the AssumeRole - Obtain temporary identity credentials of a RAM role API operation with their own AccessKey pair to obtain the STS token of a RAM role and use the STS token to access Alibaba Cloud resources.
Example:
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 -v /home/admin/notebook:/root/jupyter registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/adb-public-image/adb-spark-public-image:adb.notebook.0.5.pre -d amv-bp164l******** -r test -e adb.aliyuncs.com -i LTAI**************** -k ****************After you start the interactive JupyterLab development environment, the following information is returned. You can copy and paste the
http://127.0.0.1:8888/lab?token=1e2caca216c1fd159da607c6360c82213b643605f11ef291URL to your browser and use JupyterLab to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark.[I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.852 ServerApp] nbclassic | extension was successfully loaded. [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.852 ServerApp] sparkmagic extension enabled! [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.853 ServerApp] sparkmagic | extension was successfully loaded. [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.853 ServerApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /root/jupyter [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.853 ServerApp] Jupyter Server 1.24.0 is running at: [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.853 ServerApp] http://419e63fc7821:8888/lab?token=1e2caca216c1fd159da607c6360c82213b643605f11ef291 [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.853 ServerApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8888/lab?token=1e2caca216c1fd159da607c6360c82213b643605f11ef291 [I 2023-11-24 09:55:09.853 ServerApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).NoteIf an error message appears when you start the interactive JupyterLab development environment, you can view the
proxy_{timestamp}.logfile for troubleshooting.
Use locally installed Jupyter Notebook to connect to Spark
Install and configure the Jupyter Notebook environment
Install the SparkMagic plugin in Jupyter to run interactive Spark jobs. Choose the appropriate method based on your Jupyter version. The following example is for JupyterLab 3.x.
ImportantAll optional steps must be performed in strict order without skipping or reordering. If you skip any step, the on-duty engineer will not be able to analyze environment issues through Jupyter startup logs, and you will need to resolve any errors on your own.
Install SparkMagic.
pip install sparkmagicInstall ipywidgets.
pip install ipywidgets(Optional) Install wrapper kernels. Run
pip show sparkmagic, which will display the installation path of sparkmagic. Switch to that directory and run:jupyter-kernelspec install sparkmagic/kernels/sparkkernel jupyter-kernelspec install sparkmagic/kernels/pysparkkernel jupyter-kernelspec install sparkmagic/kernels/sparkrkernel(Optional) Modify the SparkMagic
config.jsonconfiguration file (default path is~/.sparkmagic/config.json), changing127.0.0.1:5000to the IP and port you want to listen on. Below is a partial configuration structure example. For more details, refer to the related examples."kernel_python_credentials": { "username": "", "password": "", "url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000", "auth": "None" }, "kernel_scala_credentials": { "username": "", "password": "", "url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000", "auth": "None" }, "kernel_r_credentials": { "username": "", "password": "", "url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000" },(Optional) Enable server extensions to change clusters through code.
jupyter server extension enable --py sparkmagic
Start the AnalyticDB for MySQL proxy
You can use any of the following methods to start the AnalyticDB for MySQL proxy.
Method 1: Start the proxy using Docker
Pull the Jupyter image of AnalyticDB for MySQL. Run the following command:
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/adb-public-image/adb-spark-public-image:adb.notebook.0.5.preStart the Docker proxy. Execute the following command to start the container and listen on local port 5000.
docker run -it -p 5000:5000 -v {Host file path}:{Docker file path} registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/adb-public-image/adb-spark-public-image:adb.notebook.0.5.pre -d {ADB Instance Id} -r {Resource Group Name} -e {API Endpoint} -i {AK Id} -k {AK Sec} -t {StsToken} # Choose either StsToken or AKThe following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Required
Description
-p
No
Maps a host port to a container port. Specify the parameter in the
-p {Host port}:{Container port}format.Specify a random value for the host port and set the container port to
5000. Example:-p 5000:5000.-v
No
If you do not mount the host path and disable the Docker container, the editing files may be lost. After you disable the Docker container, the container attempts to terminate all interactive Spark jobs that are running. You can use one of the following methods to prevent loss of the editing files:
When you start the interactive JupyterLab development environment, mount the host path to the Docker container and store the job files in the corresponding file path. Specify the parameter in the
-v {Host path}:{Docker file path}format. Specify a random value for the file path of the Docker container. Recommended value:/root/jupyter.Before you disable the Docker container, make sure that all files are copied and stored.
Example:
-v /home/admin/notebook:/root/jupyter. In this example, the host files that are stored in the/home/admin/notebookpath are mounted to the/root/jupyterpath of the Docker container.NoteSave the editing notebook files to the
/tmpfolder. After you disable the Docker container, you can view the corresponding files in the/home/admin/notebookpath of the host. After you re-enable the Docker container, you can continue to execute the files. For more information, see Volumes.-d
Yes
The ID of the AnalyticDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition, Basic Edition, or Data Lakehouse Edition cluster.
You can log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console and go to the Clusters page to view cluster IDs.
-r
Yes
The name of the Job resource group in the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
You can log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console, choose in the left-side navigation pane, and then click the Resource Groups tab to view resource group names.
-e
Yes
The endpoint of the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
For more information, see Endpoints.
-i
Yes (in specific scenarios)
The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user.
For information about how to view the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret, see Accounts and permissions.
-k
-t
Yes (in specific scenarios)
The Security Token Service (STS) token, which is the temporary identity credential of the RAM role.
A RAM user with permissions can call the AssumeRole - Obtain temporary identity credentials of a RAM role API operation with their own AccessKey pair to obtain the STS token of a RAM role and use the STS token to access Alibaba Cloud resources.
Method 2: Install the proxy using the command line
Download and install the proxy
pip install aliyun-adb-livy-proxy-0.0.1.zipExecute the following command to start the proxy.
NoteAfter the AnalyticDB for MySQL proxy is successfully installed, you can run
adbproxy --helpto view the parameter list.adbproxy --db {ADB Instance Id} --rg {Resource Group Name} --endpoint {API Endpoint} --host 127.0.0.1 --port 5000 -i {AK Id} -k {AK Sec} -t {StsToken} # Choose either StsToken or AKThe following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Required
Description
--db
Yes
The ID of the AnalyticDB for MySQL Enterprise Edition, Basic Edition, or Data Lakehouse Edition cluster.
You can log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console and go to the Clusters page to view cluster IDs.
--rg
Yes
The name of the Job resource group in the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
You can log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console, choose in the left-side navigation pane, and then click the Resource Groups tab to view resource group names.
--endpoint
Yes
The endpoint of the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
For more information, see Endpoints.
--host
No
The local IP address to which the adbproxy service binds. The default value is
127.0.0.1.--port
No
The port number that the adbproxy service listens on. The default value is
5000.-i
Yes (in specific scenarios)
The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user with AnalyticDB for MySQL access permissions.
For information about how to obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret, see Accounts and permissions.
-k
-t
Yes (in specific scenarios)
The Security Token Service (STS) token, which is the temporary identity credential of the RAM role.
A RAM user with permissions can call the AssumeRole - Obtain temporary identity credentials of a RAM role API operation with their own AccessKey pair to obtain the STS token of a RAM role and use the STS token to access Alibaba Cloud resources.
After successful startup, the console will display relevant log information.
Start Jupyter
Use the following command to start the Jupyter interactive development environment.
jupyter labIf you have set a custom listening address, execute jupyter lab --ip=*** to start Jupyter, where *** is your custom listening address.
After successful startup, the following information is returned. You can copy and paste the http://127.0.0.1:8888/lab?token=1e2caca216c1fd159da607c6360c82213b643605f11ef291 URL to your browser to use Jupyter to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark.
[I 2025-07-02 17:36:16.051 ServerApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/newuser
[I 2025-07-02 17:36:16.052 ServerApp] Jupyter Server 2.16.0 is running at:
[I 2025-07-02 17:36:16.052 ServerApp] http://419e63fc7821:8888/lab?token=1e2caca216c1fd159da607c6360c82213b643605f11ef291
[I 2025-07-02 17:36:16.052 ServerApp] http://127.0.0.1:8888/lab?token=1e2caca216c1fd159da607c6360c82213b643605f11ef291
[I 2025-07-02 17:36:16.052 ServerApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).Run jobs in Jupyter
Start resources and define the maximum ACU usage for jobs
After connecting to AnalyticDB for MySQL Spark using Jupyter, click PySpark on the page to create a new PySpark job. The Spark job will run with the following default configuration parameters:
{ "kind": "pyspark", "heartbeatTimeoutInSecond": "60", "spark.driver.resourceSpec": "medium", "spark.executor.resourceSpec": "medium", "spark.executor.instances": "1", "spark.dynamicAllocation.shuffleTracking.enabled": "true", "spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled": "true", "spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors": "0", "spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors": "1", "spark.adb.sessionTTLSeconds": "1200" }To modify the Spark application configuration parameters, you can use the
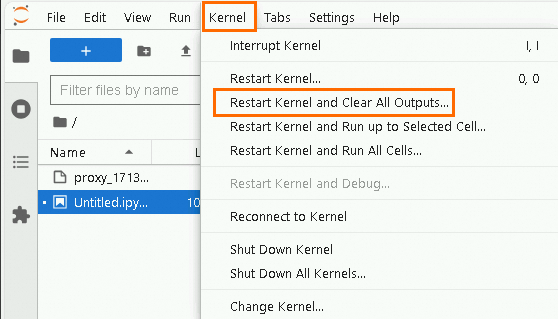
%%configure -fstatement.Restart the kernel.
In the top navigation bar, choose . Make sure that no running Spark applications are displayed on the Jupyter development page.
Enter custom Spark application configuration parameters in the Jupyter Notebook Cell.
ImportantWhen you specify custom Spark application configuration parameters, you must set the spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled parameter to false.
Example:
This configuration allocates 32 Executors for the Spark job, with each Executor having a specification of
medium(2 cores and 8 GB memory). The entire job can allocate a total of 64 ACUs of computing resources.%%configure -f { "spark.driver.resourceSpec":"large", "spark.sql.hive.metastore.version":"adb", "spark.executor.resourceSpec":"medium", "spark.adb.executorDiskSize":"100Gi", "spark.executor.instances":"32", "spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false", "spark.network.timeout":"30000", "spark.memory.fraction":"0.75", "spark.memory.storageFraction":"0.3" }For more information about Spark application configuration parameters, see Spark application configuration parameters and the Spark official website.
Click the
 button to modify the Spark application configuration parameters.Important
button to modify the Spark application configuration parameters.ImportantAfter you close the Jupyter Notebook page, the specified custom configuration parameters no longer take effect. If you do not specify Spark application parameters after you re-open the Jupyter Notebook page, the default configuration parameters are used to run a Spark job.
When you run a Spark job on the Jupyter Notebook page, all configurations of the job are written directly to a JSON structure, instead of the
confobject of a JSON structure required when you submit a batch job.
Run jobs
Enter the
sparkcommand to start a SparkSession. Note
NoteClick Link in the return value to access the Spark UI interface and view information such as Spark job logs.
Execute Spark SQL in the Jupyter Notebook Cell to query the list of available databases in the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
ImportantYou must add
%%sqlbefore executing Spark SQL code, otherwise it will be parsed as Python code by default. You can run%%helpto learn more about Magic commands and their usage.%%sql show databases The query results are consistent with those in AnalyticDB for MySQL.
The query results are consistent with those in AnalyticDB for MySQL.