This topic answers frequently asked questions about GPUs, including performance optimization, driver installation, and troubleshooting.
Problem categorization | Description | Link |
GPU errors and troubleshooting | This section covers issues related to GPU drivers, monitoring tools such as DCGM and Prometheus, and runtime errors such as NVML initialization failures and XID errors. |
|
cGPU (containerized GPU) issues | This section covers cGPU configuration, startup, runtime errors, and permission issues related to kernel modules. | |
GPU node and cluster management | This section covers cluster-level operations, including GPU card usage detection, virtualization support, node maintenance such as kernel upgrades, and faulty card isolation. |
Why are the GPU ECC configurations in my cluster inconsistent?
Error-Correcting Code (ECC) mode improves GPU stability and reliability by detecting and correcting GPU memory errors. However, enabling this mode slightly reduces the available GPU memory.
ECC mode recommendations:
Disable ECC: Suitable for cost-sensitive scenarios and low-latency inference, such as online real-time inference.
Enable ECC: Suitable for applications that require high data consistency and integrity, such as database servers, financial systems, scientific computing, and high-performance computing (HPC).
For these reasons, we do not initialize ECC mode uniformly. This can result in inconsistent ECC configurations across the GPU nodes in a cluster.
How to set the ECC mode for a GPU node
You can run the following command to check the current ECC mode status.
nvidia-smiExpected output:
Fri Jun 6 11:49:05 2025 +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 535.161.07 Driver Version: 535.161.07 CUDA Version: 12.2 | |-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | | | | MIG M. | |=========================================+======================+======================| | 0 Tesla T4 On | 00000000:00:08.0 Off | 0 | | N/A 31C P8 9W / 70W | 0MiB / 15360MiB | 0% Default | | | | N/A | +-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: | | GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory | | ID ID Usage | |=======================================================================================| | No running processes found | +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+In the output, the Volatile Uncorr. ECC column shows the status. A value of
0indicates that ECC is enabled and no errors have occurred. A value ofOffindicates that ECC is disabled.You can run one of the following commands to enable or disable ECC mode as needed.
Enable ECC mode for all GPUs on the node.
nvidia-smi -e 1Disable ECC mode for all GPUs on the node.
nvidia-smi -e 0
After you change the ECC mode, you must restart the operating system for the change to take effect.
ImportantSave all necessary data before you restart the node.
After the restart, you can run
nvidia-smiagain to check the ECC mode status and confirm that it is enabled or disabled. The following output shows that ECC mode is disabled:Fri Jun 6 11:52:15 2025 +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 535.161.07 Driver Version: 535.161.07 CUDA Version: 12.2 | |-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | | | | MIG M. | |=========================================+======================+======================| | 0 Tesla T4 On | 00000000:00:08.0 Off | Off | | N/A 31C P8 9W / 70W | 0MiB / 16384MiB | 0% Default | | | | N/A | +-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: | | GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory | | ID ID Usage | |=======================================================================================| | No running processes found | +---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Does Container Service for Kubernetes support vGPU-accelerated instances?
vGPU-accelerated instances require a GRID License from NVIDIA to function correctly. To use vGPU-accelerated instances, you must purchase a GRID License from NVIDIA and build your own license server.
Because Alibaba Cloud does not provide license servers, vGPU-accelerated instances cannot be used directly, even in a vGPU-accelerated cluster. Therefore, the Container Service for Kubernetes console no longer supports selecting vGPU-accelerated instances as cluster nodes.
Unsupported vGPU-accelerated instances include ECS instances with prefixes such as ecs.vgn5i, ecs.vgn6i, ecs.vgn7i, and ecs.sgn7i. To use these instances, you must purchase a GRID License from NVIDIA and build your own license server.
You need a license server to update the NVIDIA driver license for vGPU-accelerated instances in an ACK cluster.
You can purchase an ECS instance and follow the official NVIDIA tutorial to build a license server. For more information, see NVIDIA.
If you have already set up your license server, you can follow these steps to add vGPU-accelerated instances to an ACK cluster.
Add vGPU-accelerated instances to an ACK cluster
Go to Privilege Quota and request the custom OS image feature.
Create a custom OS image based on CentOS 7.x or Alibaba Cloud Linux 2. The image must have the NVIDIA GRID driver installed and the GRID License correctly configured. For more information, see Create a custom image from an instance and Install a GRID driver on a vGPU-accelerated instance (Linux).
Create a node pool. For more information, see Create and manage a node pool.
Add the vGPU-accelerated instances to the node pool created in Step 3. For more information, see Add existing nodes.
Next step: Update the NVIDIA driver license for vGPU-accelerated instances in an ACK cluster
For information about how to update the NVIDIA driver license for vGPU-accelerated instances in an ACK cluster, see Update the NVIDIA driver license for vGPU-accelerated (vGPU) instances in an ACK cluster.
How to manually upgrade the kernel on a GPU node in an existing cluster
This section describes how to manually upgrade the kernel on a GPU node in an existing cluster.
Upgrade the kernel if its version is earlier than
3.10.0-957.21.3.Confirm the target kernel version and proceed with caution.
This solution does not cover the kernel upgrade itself. It only describes how to upgrade the NVIDIA driver after you upgrade the kernel.
Set the GPU node to unschedulable. This example uses the node cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345.
kubectl cordon cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 node/cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 already cordonedDrain the GPU node on which you want to upgrade the driver.
kubectl drain cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 --grace-period=120 --ignore-daemonsets=true node/cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 cordoned WARNING: Ignoring DaemonSet-managed pods: flexvolume-9scb4, kube-flannel-ds-r2qmh, kube-proxy-worker-l62sf, logtail-ds-f9vbg pod/nginx-ingress-controller-78d847fb96-5fkkw evictedUninstall the current NVIDIA driver.
NoteThis step uninstalls driver version 384.111. If your driver version is different, download the corresponding driver installation package from the NVIDIA website and replace the version number accordingly.
Log on to the GPU node and run
nvidia-smito check the driver version.sudo nvidia-smi -a | grep 'Driver Version' Driver Version : 384.111Download the NVIDIA driver installation package.
sudo cd /tmp/ sudo curl -O https://cn.download.nvidia.cn/tesla/384.111/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-384.111.runNoteYou must use the installation package to uninstall the NVIDIA driver.
Uninstall the current NVIDIA driver.
sudo chmod u+x NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-384.111.run sudo sh ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-384.111.run --uninstall -a -s -q
Upgrade the kernel.
Restart the GPU instance.
sudo rebootLog on to the GPU node again and install the corresponding kernel-devel package.
sudo yum install -y kernel-devel-$(uname -r)Go to the NVIDIA website to download and install the required NVIDIA driver. This example uses version 410.79.
sudo cd /tmp/ sudo curl -O https://cn.download.nvidia.cn/tesla/410.79/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-410.79.run sudo chmod u+x NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-410.79.run sudo sh ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-410.79.run -a -s -q # warm up GPU sudo nvidia-smi -pm 1 || true sudo nvidia-smi -acp 0 || true sudo nvidia-smi --auto-boost-default=0 || true sudo nvidia-smi --auto-boost-permission=0 || true sudo nvidia-modprobe -u -c=0 -m || trueCheck the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file to confirm that it contains the following configuration. If not, add it manually.
sudo nvidia-smi -pm 1 || true sudo nvidia-smi -acp 0 || true sudo nvidia-smi --auto-boost-default=0 || true sudo nvidia-smi --auto-boost-permission=0 || true sudo nvidia-modprobe -u -c=0 -m || trueRestart kubelet and Docker.
sudo service kubelet stop sudo service docker restart sudo service kubelet startSet the GPU node to schedulable again.
kubectl uncordon cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 node/cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 already uncordonedVerify the driver version in the device plugin pod on the GPU node.
kubectl exec -n kube-system -t nvidia-device-plugin-cn-beijing.i-2ze19qyi8votgjz12345 nvidia-smi Thu Jan 17 00:33:27 2019 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 410.79 Driver Version: 410.79 CUDA Version: N/A | |-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | |===============================+======================+======================| | 0 Tesla P100-PCIE... On | 00000000:00:09.0 Off | 0 | | N/A 27C P0 28W / 250W | 0MiB / 16280MiB | 0% Default | +-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: GPU Memory | | GPU PID Type Process name Usage | |=============================================================================| | No running processes found | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+NoteIf you run the
docker pscommand and find that no containers are started on the GPU node, see Fix container startup issues on GPU nodes.
Fix container startup issues on GPU nodes
On GPU nodes with specific Kubernetes versions, you may find that no containers are started after you restart kubelet and Docker.
sudo service kubelet stop
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop kubelet.service
sudo service docker stop
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop docker.service
sudo service docker start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start docker.service
sudo service kubelet start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start kubelet.service
sudo docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESRun the following command to check the Cgroup driver for Docker.
sudo docker info | grep -i cgroup
Cgroup Driver: cgroupfsThe output shows that the Cgroup driver is `cgroupfs`.
Follow these steps to fix the issue.
Back up the /etc/docker/daemon.json file. Then, run the following command to update /etc/docker/daemon.json.
sudo cat >/etc/docker/daemon.json <<-EOF { "default-runtime": "nvidia", "runtimes": { "nvidia": { "path": "/usr/bin/nvidia-container-runtime", "runtimeArgs": [] } }, "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"], "log-driver": "json-file", "log-opts": { "max-size": "100m", "max-file": "10" }, "oom-score-adjust": -1000, "storage-driver": "overlay2", "storage-opts": ["overlay2.override_kernel_check=true"], "live-restore": true } EOFRestart Docker and kubelet.
sudo service kubelet stop Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop kubelet.service sudo service docker restart Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart docker.service sudo service kubelet start Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start kubelet.serviceConfirm that the Cgroup driver for Docker is systemd.
sudo docker info | grep -i cgroup Cgroup Driver: systemd
What do I do if adding an ECS Bare Metal Instance node fails?
ECS Bare Metal Instances (ecs.ebmgn7) support multi-instance GPU (MIG). To prevent existing MIG settings from affecting node deployment, the system resets any existing MIG settings each time a node of this type is added to a cluster. This reset time is variable. If the reset takes too long, the script for adding the node may time out, causing the operation to fail.
If adding a node of this instance family fails, you can run the following command on the node's host:
sudo cat /var/log/ack-deploy.logCheck if the output contains the following error:
command timeout: timeout 300 nvidia-smi --gpu-resetIf this error is present, the failure was caused by the MIG reset. You can add the node again. For more information, see Add existing nodes.
What do I do if "Failed to initialize NVML: Unknown Error" occurs when running a GPU container on Alibaba Cloud Linux 3?
Symptom
When you run nvidia-smi in a GPU container, the following error is reported.
sudo nvidia-smi
Failed to initialize NVML: Unknown ErrorCause
When you use systemd on Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, operations such as systemctl daemon-reload and systemctl daemon-reexec update cgroup-related configurations. This can interfere with the normal operation of NVIDIA GPU devices in containers. For more details, see community issues 1671 and 48.
Solution
If this issue occurs, you can try the following solutions.
Case 1: If your application pod requests GPU resources by setting the NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all environment variable for the container, evaluate whether you can add privileged permissions to the container. The following example shows how to add privileged permissions.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: test-gpu-pod spec: containers: - name: test-gpu-pod image: centos:7 command: - sh - -c - sleep 1d securityContext: # Add privileged permissions to the container. privileged: trueCase 2: For applications that use shared GPU scheduling, we recommend using Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or CentOS 7.
Case 3: Recreate the application pod. Before you perform this action, evaluate the potential impact on your business. This solution does not guarantee that the issue will not recur.
Case 4: If none of the preceding solutions are applicable, evaluate whether your business can use a different operating system, such as Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or CentOS 7.
What do I do if a GPU card becomes unavailable due to XID 119 or XID 120 errors?
Symptom
When you use a GPU, the card may become unavailable. For example, when you use a GPU on a Linux system, an error message may indicate that the GPU card failed to initialize. After you run the sh nvidia-bug-report.sh command, you may see XID 119 or XID 120 error messages in the generated log. The following image shows an example of an XID 119 error:
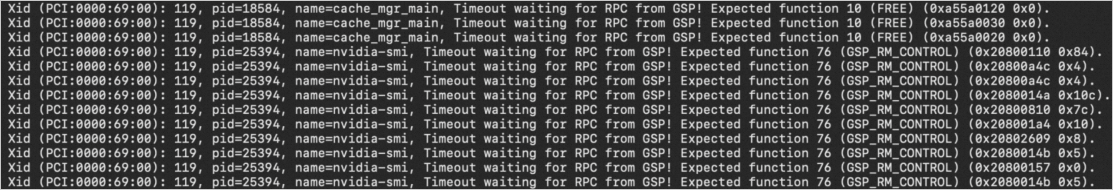
For information about other XID errors, visit NVIDIA Common XID Errors.
Cause
The preceding issue may occur because an exception occurs in the GSP component. You can update the NVIDIA driver to the latest version. If the issue persists after the update, we recommend that you disable the GSP component.
For more information about GSP, see Chapter 42. GSP Firmware in the official NVIDIA documentation.
Solution
The following sections describe how to disable GSP in different scenarios.
Scaling out new nodes
You can create a new node pool or edit the configuration of an existing node pool. In the advanced configuration, add the tag ack.aliyun.com/disable-nvidia-gsp=true to the node pool. When you scale out new nodes, ACK automatically applies the necessary configurations to disable GSP on those nodes.
For more information about the operation entry point and node pool configuration items, see Create and manage a node pool.
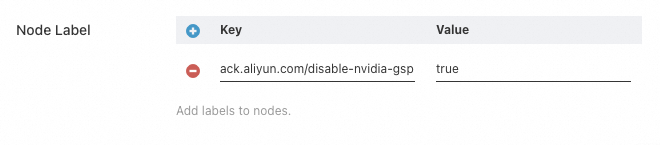
The steps to disable GSP may increase the latency of scaling out nodes.
Adding existing nodes
You can create a new node pool or edit the configuration of the node pool to which you want to add nodes. In the advanced configuration, add the tag
ack.aliyun.com/disable-nvidia-gsp=trueto the node pool. After you add existing nodes to the node pool, ACK automatically applies the necessary configurations to disable GSP on those nodes.For more information about the operation entry point and node pool configuration items, see Create and manage a node pool.
 Note
NoteThe steps to disable GSP may increase the latency of adding nodes to the cluster.
Add the existing nodes to the node pool. For more information about the operation entry point and related notes, see Add existing nodes.
Managing existing nodes in a cluster
You can disable GSP on existing nodes in the following ways.
Disable GSP using a node pool tag
Add the tag
ack.aliyun.com/disable-nvidia-gsp=trueto the node's node pool.For more information about the operation entry point and node pool configuration items, see Edit a node pool.

Remove the node from the cluster, but do not release the ECS instance. For more information, see Remove a node.
Re-add the removed node to the cluster as an existing node. For more information about the operation entry point and related notes, see Add existing nodes.
Log on to the node to manually disable GSP
If you cannot disable GSP on your node by removing and then re-adding it to the cluster, you can log on to the node and manually perform the steps to disable GSP. For more information, see FAQ.
NVIDIA introduced GSP in driver version 510. For example, if you log on to a node and manually upgrade the driver from version 470 to 525, you do not need to disable GSP for version 470. However, a GSP bug may be triggered after you upgrade to version 525. After the driver upgrade is complete, see FAQ to manually perform the steps to disable GSP.
How to manually isolate a faulty GPU in a cluster?
When you use shared GPU scheduling, a faulty GPU in the cluster can cause a Job to fail. If a Job restarts, it may be scheduled to the same faulty GPU and fail again. To prevent repeated failures, you can manually mark the faulty GPU. The scheduler will no longer use the marked GPU, which provides fault isolation.
Your scheduler and cluster versions must meet the following requirements:
For clusters that run Kubernetes 1.24 or later, the scheduler version must be 1.xx.x-aliyun-6.4.3.xxx or later.
For clusters that run Kubernetes 1.22, the scheduler version must be 1.22.15-aliyun-6.2.4.xxx or later.
The cluster must use shared GPU scheduling.
To mark a faulty GPU, you can submit a special ConfigMap to the cluster as shown in the following example:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: <node-name>-device-status # Replace <node-name> with the actual node name.
namespace: kube-system
data:
devices: |
- deviceId: 0 # Run nvidia-smi to get the GPU ordinal number.
deviceType: gpu
healthy: falseThe ConfigMap must be in the kube-system namespace. The name of the ConfigMap must be the name of the node that hosts the faulty GPU, with the -device-status suffix. In the data field, deviceId is the GPU ordinal number that is obtained from the nvidia-smi command, deviceType is gpu, and healthy is false. After you submit the configuration, the scheduler isolates the corresponding GPU.
Resolve the "Failed to initialize NVML: Unknown Error" message in GPU containers
Symptoms
When you run nvidia-smi in a GPU container, you may receive the following error. This issue occurs on nodes that run Ubuntu 22.04 or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9.3 64-bit.
sudo nvidia-smi
Failed to initialize NVML: Unknown ErrorCause
Running operations such as systemctl daemon-reload or systemctl daemon-reexec on a node updates cgroup configurations. This change can affect the normal operation of NVIDIA GPU devices within containers.
The issue affects pods that request GPU resources in the following ways:
The pod specifies the
aliyun.com/gpu-memresource inresources.limits.The pod sets the
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICESenvironment variable for a container to access GPU resources on the node.The pod uses a container image that has the
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICESenvironment variable set by default, and the pod needs to access GPU resources on the node.
Pods that request GPU resources by specifying the
nvidia.com/gpuresource inresources.limitsare not affected.The NVIDIA Device Plugin and ack-gpu-exporter components set the
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=allenvironment variable for pods by default.
Solutions
You can recreate the application pod to temporarily fix this issue. Before you perform this operation, assess the potential impact on your services. If the issue reoccurs, you must recreate the pod again.
If your application pod requests GPU resources by setting the
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=allenvironment variable, addprivilegedpermissions to the application container. The following example shows the configuration:ImportantUsing
privilegedpermissions introduces security risks. As an alternative, you can recreate the application pod. Recreating the pod is a temporary fix and does not prevent the issue from recurring.apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: test-gpu-pod spec: containers: - name: test-gpu-pod image: centos:7 command: - sh - -c - sleep 1d securityContext: # Add privileged permissions to the container. privileged: true
How to prevent the /run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io/<container ID>/log.json file from growing continuously on GPU nodes
Symptoms
The /run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io/<container ID>/log.json file on a GPU node grows continuously.
Analysis
Prerequisite: The nvidia-container-toolkit version on the node is earlier than 1.16.2.
Cause: The issue is caused by frequent `exec` calls to a container on the GPU node, such as when a pod is configured with an `exec` probe. Each time an `exec` operation is called, the NVIDIA container runtime prints an informational log.
Result: The /run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io/<container ID>/log.json file grows continuously and consumes disk space.
Solution
You can log on to the node and run the following script:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
export CONFIG=/etc/nvidia-container-runtime/config.toml
export CONTAINER_ROOT_PATH="/run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io"
if [ -f $CONFIG ];then
# Change the log level in the nvidia-container-runtime configuration from "info" to "error".
sed -i 's@^log-level = "info"@log-level = "error"@g' $CONFIG
# Clear the content of the container's log.json file.
find $CONTAINER_ROOT_PATH -mindepth 2 -maxdepth 2 -name log.json -type f -exec sh -c 'echo "" > "{}"' \;
fi