If you need to reset an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance or erase data from its system disk, you can re-initialize the disk to restore it to its initial state. This topic describes how to re-initialize a system disk.
Limitation
You can continue to use an instance created from a custom image that was later deleted. However, you cannot re-initialize its system disk.
Effects of re-initialization
Before re-initializing the disk, make sure you understand the following effects.
Re-initializing a system disk erases all data on it. To prevent data loss, create a snapshot to back up the system disk data beforehand. For more information, see Create a snapshot manually.
Item | Description |
System disk effects |
|
Data disk effects |
|
Procedure
Step 1: Prepare for re-initialization
Re-initializing a system disk erases all written data. To prevent data loss, back up the target disk first. For more information, see Create a snapshot manually.
NoteSnapshots are a paid service. For more information, see Snapshot billing.
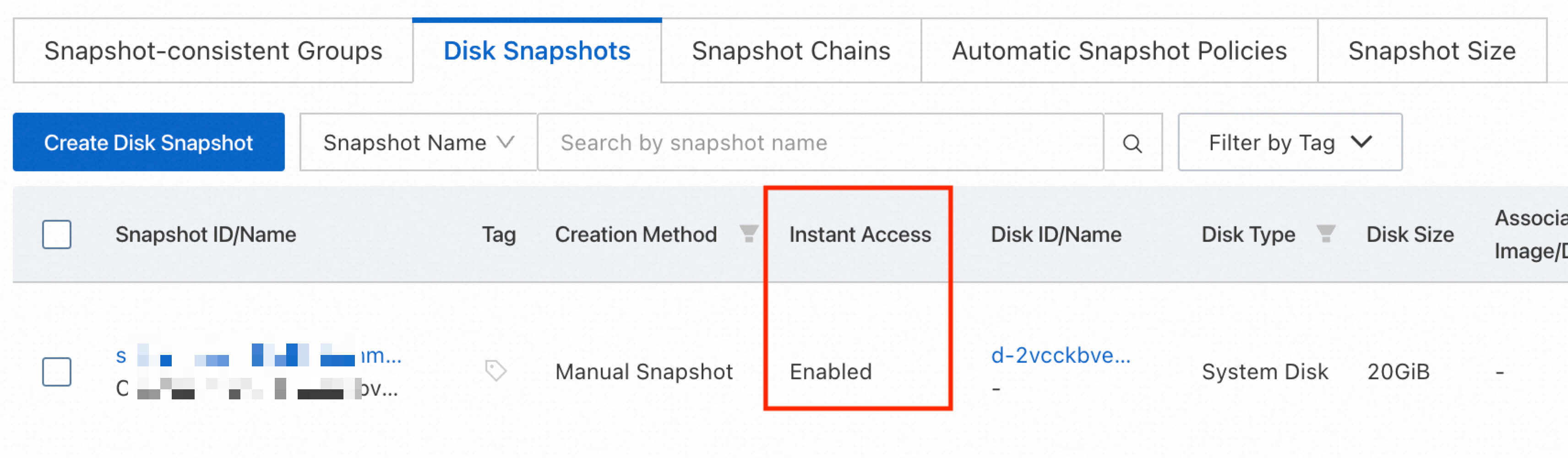
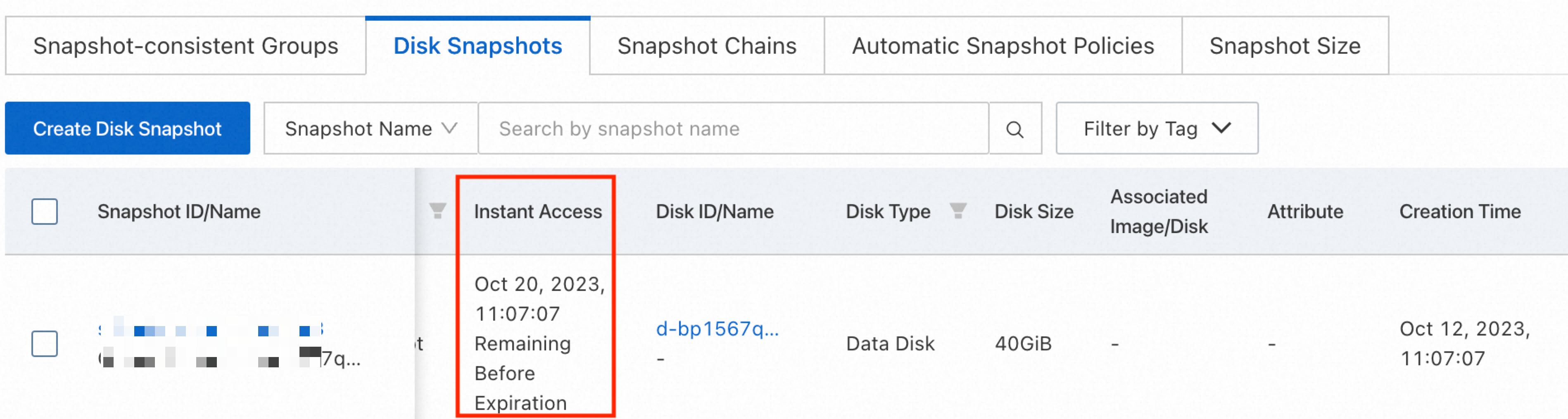
Make sure that the legacy instant access feature is not enabled for snapshots of ESSD disks. You cannot re-initialize a disk if its snapshots have the legacy instant access feature enabled. The new version of instant access is enabled by default and does not affect the re-initialization operation.
(For Linux instances only) To use an SSH key pair for authentication after re-initialization, create or import one first. For more information, see Create an SSH key pair and Import an SSH key pair.
(For Linux instances only) After you re-initialize the system disk, you must re-mount any data disks. To use the same mount points, run the following command beforehand to record the current mount information for your data disks.
sudo mount |grep "<Data disk name>"For example, to view the mount information for the data disk
/dev/vdb, run the command. The output shows that the data disk/dev/vdbhas two partitions:/dev/vdb1is mounted to/tmp, and/dev/vdb2is mounted to/mnt.[ecs-user@ecs ~]$ sudo mount |grep "/dev/vdb" /dev/vdb1 on /tmp type ext4 (rw,relatime) /dev/vdb2 on /mnt type ext4 (rw,relatime)Stop the ECS instance. For more information, see Stop an instance.
ImportantIf an ECS instance uses the pay-as-you-go billing method and resides in a VPC, you must enable the standard mode when you stop the instance. If you enable the economical mode, you may be unable to start the instance after you re-initialize the disks attached to the instance.
Step 2: Re-initialize the disk
Re-initializing a system disk erases all data on it. To prevent data loss, create a snapshot to back up the system disk data beforehand. For more information, see Create a snapshot manually.
Go to ECS console - Instances.
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Find the instance whose system disk you want to re-initialize and click the instance ID to go to the Instance Details page.
Click the Block Storage tab, find the system disk you want to re-initialize, and then click Re-initialize Disk in the Actions column.

In the Re-initialize Disk dialog box, configure the parameters.
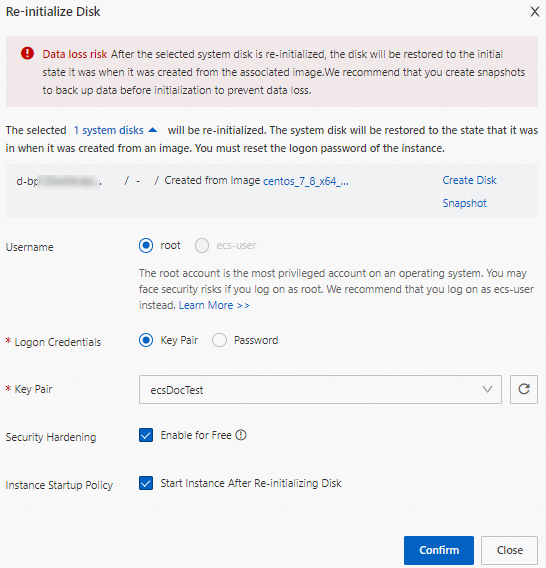
Parameter
Description
Username
Select a username to log on to the operating system.
Logon Credentials
For a Windows instance, reset the logon password. You can reuse the old password or specify a new one.
For a Linux instance, select Key Pair or Password.
Key Pair: Bind an SSH key pair to the instance for logon.
Password: Reset the logon password. You can reuse the old password or specify a new one.
Security Hardening
The Enable for Free option is selected by default. This option installs the free Security Agent on your instance to provide features like backdoor detection, unusual logon alerts, and brute-force attack prevention.
Instance Startup Policy
The Start Instance After Re-initializing Disk option is selected by default. The instance automatically starts after re-initialization is complete. If you clear this option, you must start the instance manually.
Click Confirm. The disk status changes to Initializing.
Re-initialization is complete when the disk status returns toe In Use.
(Conditionally required) If you are re-initializing a Linux instance that has data disks attached, you must re-mount them. The re-initialization operation does not change or erase data on the data disks, but their mount information is lost. You must create new mount points and mount the file systems. For more information, see How do I re-attach data disks after I re-initialize the system disk of a Linux instance?
For Windows instances, data disks automatically come online after re-initialization. No further action is needed.
After the system disk is re-initialized, redeploy your applications and configurations to restore your services.