本文对使用数据灾备时所遇到的一些常见问题提供解决方案。
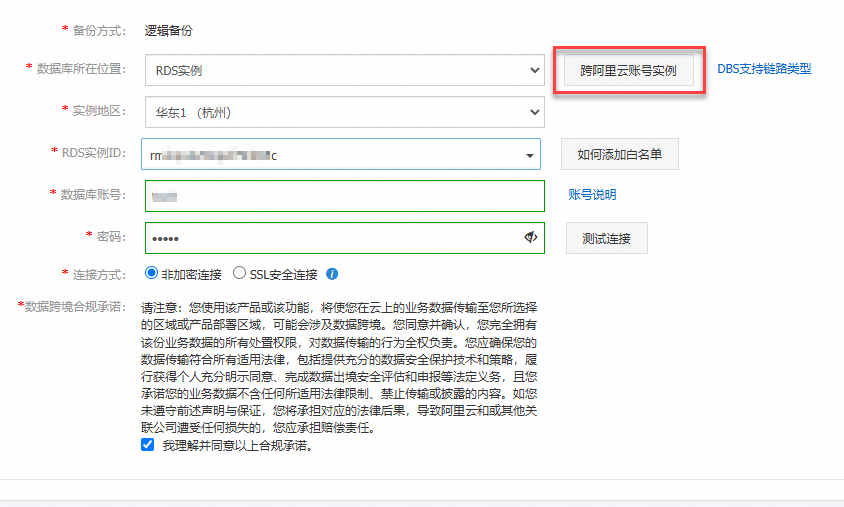
跨阿里云账号备份或恢复数据时如何配置RAM授权?
使用源数据库实例所属的阿里云账号登录RAM控制台。
说明请确保源数据库实例所属账号拥有AliyunDBSDefaultRole权限。
在左侧导航栏,单击身份管理 > 角色。
创建角色:
单击创建角色,选择信任主体类型为云账号。
选择信任主体名称为
当前云账号164882xxxx,单击确定。在弹出层中输入需要创建的角色名(如:
ram-for-dbs),单击确定。
角色授权:
进入当前角色的详情页面,选择权限管理页签,单击新增授权。
在弹出的面板中,选择权限类型为系统策略。

根据数据库所在位置,勾选对应的策略。
RDS实例:
AliyunRDSReadOnlyAccess和AliyunVPCReadOnlyAccess通过专线/VPN网关/智能网关接入的自建数据库:
AliyunVPCReadOnlyAccessPolarDB:
AliyunPolardbFullAccess
单击确认新增授权。
编辑信任策略:
在当前角色基本信息中单击信任策略 > 编辑信任策略。
在编辑信任策略页面中,单击脚本编辑,在输入框中写入如下内容:
将其中的
<账号ID>替换为您操作备份计划的主账号ID。{ "Statement": [ { "Action": "sts:AssumeRole", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "RAM": [ "acs:ram::<账号ID>:root" ], "Service": [ "<账号ID>@dbs.aliyuncs.com" ] } } ], "Version": "1" }
单击确定,即可完成RAM授权。
如何跨阿里云账号备份恢复数据?
配置跨账号备份
配置跨账号恢复
跨账号备份恢复配置具体操作请参见配置备份计划及恢复数据。
控制台无法实现跨账号备份集的迁移。
如何将备份集自动归档到备份服务器?
创建备份计划,此操作使用运维账号。
管理备份计划,此操作使用运维账号。
在备份服务器上安装备份网关,此操作使用备份账号。
说明若还没有备份服务器,可先购买服务器。
在备份计划列表中,点击目标备份计划操作列下的管理按钮,在备份任务配置页,最下方备份集下载栏,单击设置备份集下载规则,在弹出的对话框中,配置对应参数,请参考下表,此操作使用运维账号。
说明如果备份实例的数据库引擎不支持备份集下载,或者备份目标存储类型不是DBS内置存储,控制台上将不会显示该按钮。
参数名
操作说明
自动下载状态
选择开启。
目标类型
默认为已安装备份网关的服务器目录,固定配置。
备份网关
选择备份网关,DBS通过备份网关与本地设备进行连接。
重要备份集自动下载功能目前尚未正式商业化,性能可能存在一定的瓶颈。因此请您不要将同一个备份网关配置于下载多个备份计划的备份数据,避免数据堆积及其他异常情况的发生。
目标位置
请选择目标位置的类型,并设置对应的目录或路径,备份数据将存储在对应路径中。当前支持如下4种位置:
服务器目录
FTP路径
NAS目录
Minio路径
全量数据格式
系统默认,无法修改。
说明全量与增量备份集的数据格式,请参见上文的功能限制与格式说明。
增量数据格式
系统默认为原生格式,无法修改。
配置完成之后单击确定保存。
在备份任务配置页,单击左侧备份集下载,查看备份集下载进度,此操作使用运维账号。
如何修改备份生命周期?
登录数据管理DMS 5.0。
在顶部菜单栏中,选择安全与规范(DBS) > 数据灾备(DBS) > 备份计划。
说明若您使用的是极简模式的控制台,请单击控制台左上角的
 图标,选择全部功能 > 安全与规范(DBS) > 数据灾备(DBS) > 备份计划。
图标,选择全部功能 > 安全与规范(DBS) > 数据灾备(DBS) > 备份计划。单击备份计划操作列的管理,进入备份任务配置页面。
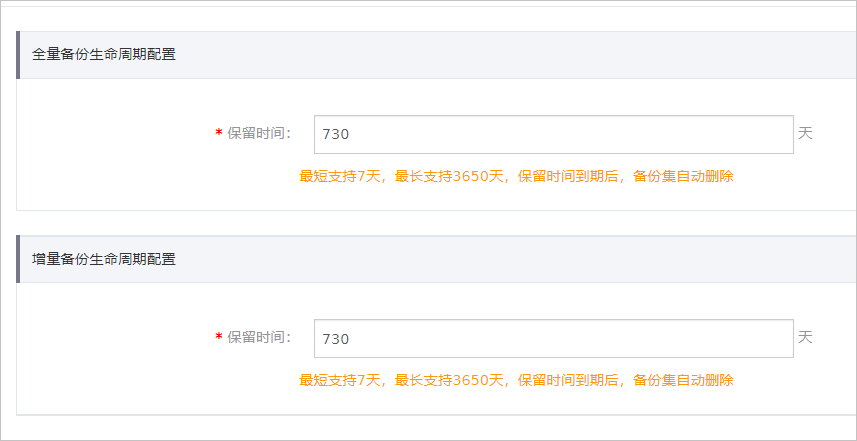
单击生命周期信息区域的设置生命周期。
设置全量或增量备份生命周期保留时间,完成后单击保存。
 重要
重要生命周期最短支持7天,最长支持3650天,保留时间到期后,备份集自动删除,不可恢复。
如果您没有开启增量备份,控制台仅会显示全量备份生命周期一个配置项。如何开启增量备份,请参见开启或关闭增量日志备份。
如何设置备份集最小保留策略?
您可以在最初配置备份计划时按需设置备份集的生命周期,或者后续根据实际业务需求修改备份集的生命周期。方法如下:
配置备份计划时,如果将备份数据存储至用户OSS,将不会产生DBS存储费用;如果将备份数据存储至DBS内置存储,将产生DBS存储费用,存储费用按实际存储数据量大小和时长计算。更多详情,请参见DBS内置存储与用户OSS的区别、存储计费。
说明当您的数据量较大时,推荐您购买DBS备份实例存储包抵扣备份计划所产生的存储费用。更多详情,请参见使用存储包。
必要时您也可以手动删除备份集,以减少存储费用。
如何将通过专线访问的本地自建数据库备份到云存储?
创建备份计划,并选择备份方式为逻辑备份。
通过物理专线将本地IDC(Internet Data Center)连接到阿里云,使云上专有网络VPC(Virtual Private Cloud)和本地IDC的网络互通。具体方法,请参见通过物理专线实现本地IDC与云上VPC互通。
在本地IDC客户侧接入设备上,添加指向DBS IP地址段的静态路由。添加方法为
ip route DBS地址段{阿里侧互联ip}。DBS IP地址段详情请参见DBS IP地址段。请参见管理备份计划,选择数据库所在位置为通过专线/VPN网关/智能网关接入的自建数据库。
如何将自建Redis备份上云?
创建备份计划,并选择备份方式为逻辑备份。
说明购买时,选择数据源类型为Redis,选择备份方式为逻辑备份。
如需了解数据灾备在备份和恢复Redis数据库时的具体粒度,请参见支持的数据库引擎与功能。
配置备份计划,选择数据库所在位置为ECS上的自建数据库。
如何进行自建MySQL云灾备?
前提条件
已完成逻辑备份。
仅支持逻辑备份计划,物理备份不支持库表级恢复。
PolarDB分布式版的逻辑备份仅支持备份整个实例,因此不支持库表级恢复能力。
备份与恢复
详情请参见跨云或自建MySQL逻辑备份与恢复。
DBS IP地址段
地域 | DBS IP地址段 |
华东1(杭州) | 100.104.217.0/24 |
华北2(北京) | 100.104.119.0/24 |
华北1(青岛) | 100.104.183.0/24 |
华东2(上海) | 100.104.191.0/24 |
华南1(深圳) | 100.104.81.0/24 |
西南1(成都) | 100.104.133.128/26 |
华北6(乌兰察布) | 100.104.76.192/26 |
华南2(河源) | 100.104.127.0/26 |
韩国(首尔) | 100.104.150.192/26 |
泰国(曼谷) | 100.104.119.128/26 |
中国香港 | 100.104.10.0/24 |
新加坡 | 100.104.10.0/24 |
日本(东京) | 100.104.144.0/24 |
华北5(呼和浩特) | 100.104.40.0/24 |
华北3(张家口) | 100.104.48.0/24 |
美国(弗吉尼亚) | 100.104.220.0/24 |
美国(硅谷) | 100.104.17.0/24 |
德国(法兰克福) | 100.104.133.0/24 |
马来西亚(吉隆坡) | 100.104.10.0/24 |
印度尼西亚(雅加达) | 100.104.209.0/24 |
金融云Server网段
金融云地域 | 金融云Server网段 |
华东1(杭州) | 100.104.255.64/26 |
华南1(深圳) | 100.104.194.128/26 |
华东2(上海) | 100.104.45.64/26 |