
In this generation, we’ve made major improvements across multiple dimensions: whether it’s understanding and generating text, perceiving and reasoning about visual content, supporting longer context lengths, understanding spatial relationships and dynamic videos, or interacting with AI agents — Qwen3-VL shows clear and significant progress in every area.
Firstly, we are open-sourcing the flagship model of this series: Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B, available in both Instruct and Thinking versions. The Instruct version matches or even exceeds Gemini 2.5 Pro in major visual perception benchmarks. The Thinking version achieves state-of-the-art results across many multimodal reasoning benchmarks.
The goal of Qwen3-VL is not just to "see" images or videos — but to truly understand the world, interpret events, and take action. To achieve this, we’ve systematically upgraded key capabilities, pushing visual models from simple “perception” toward deeper "cognition", and from basic "recognition" to advanced “reasoning and execution.”
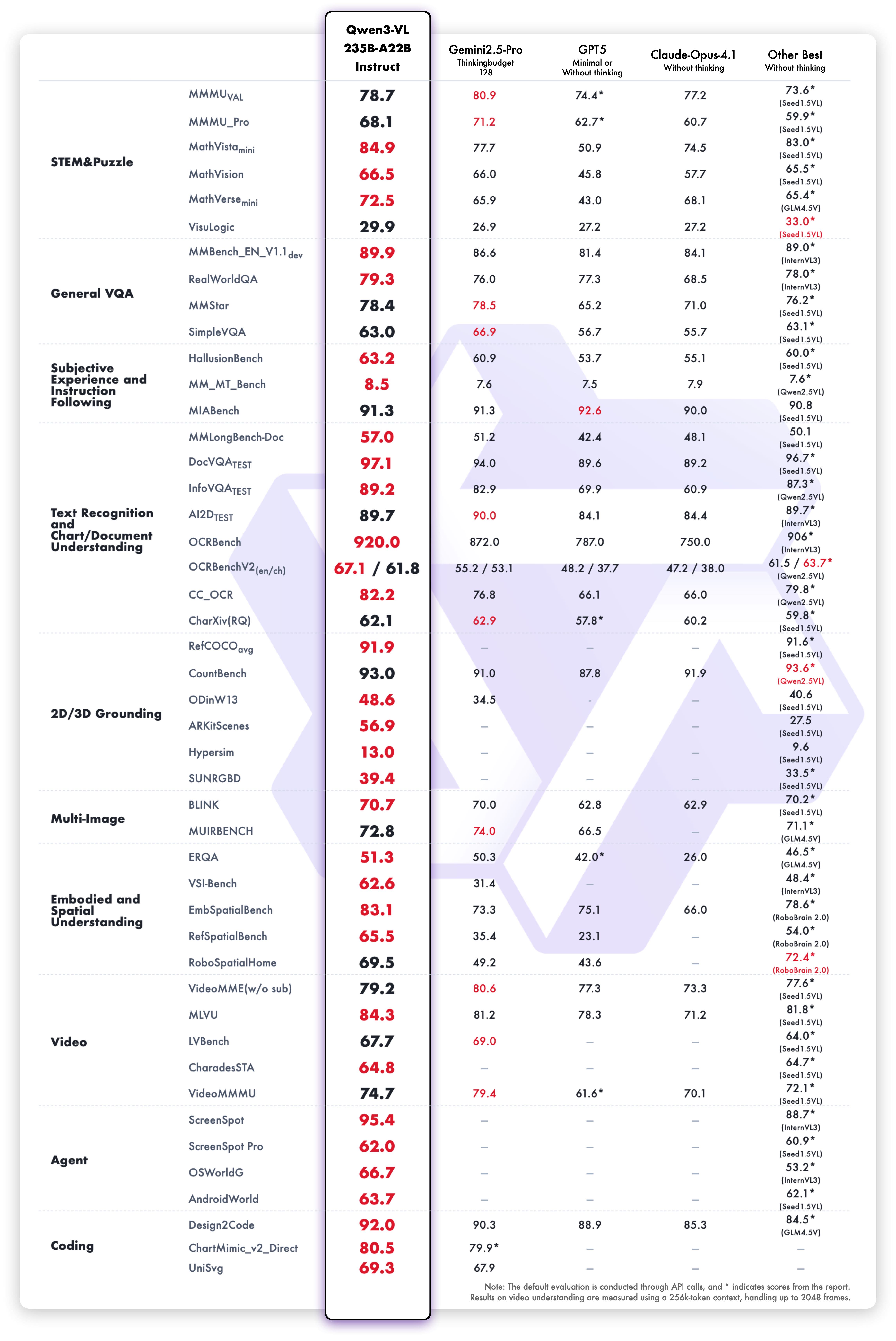
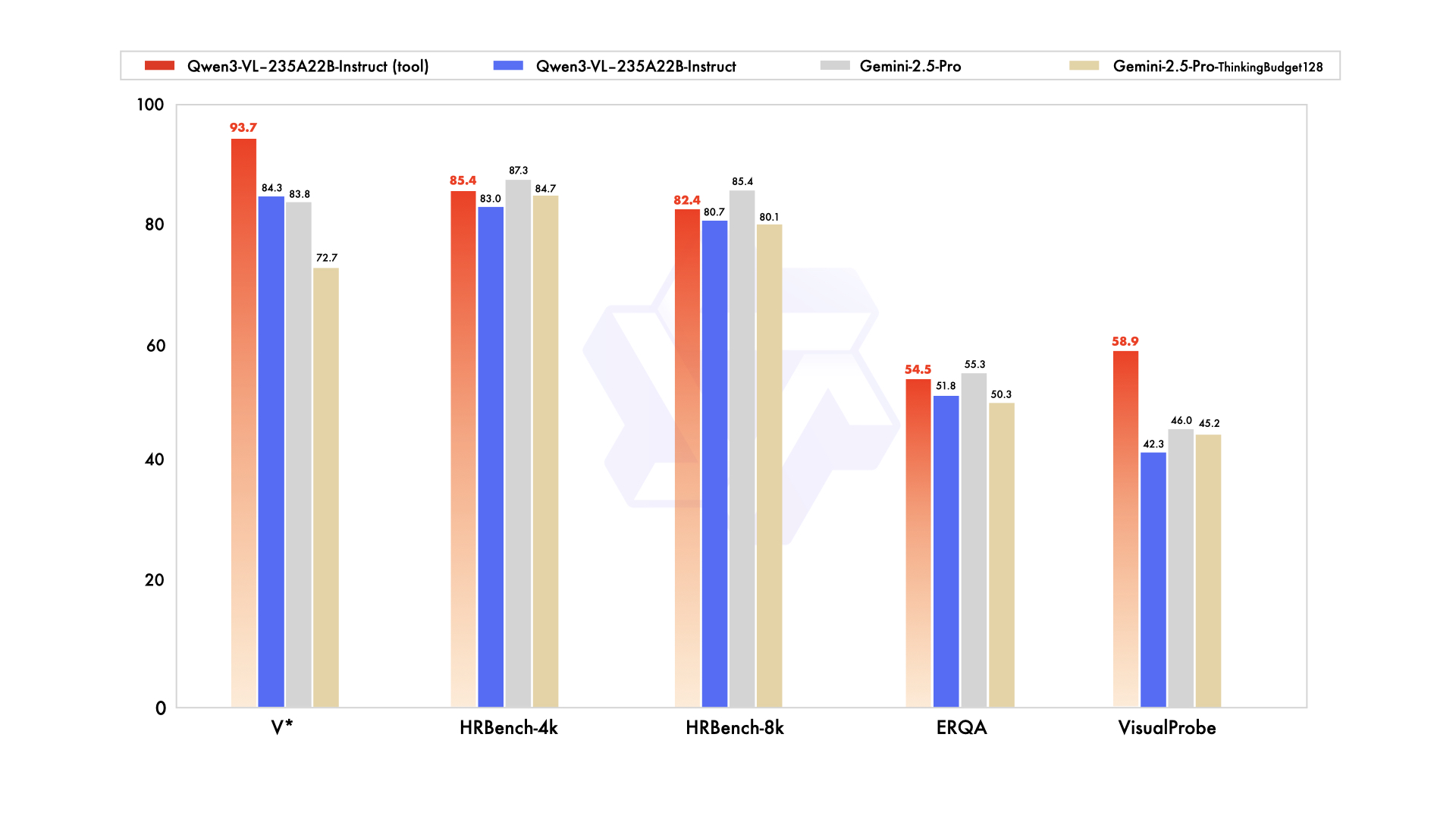
We comprehensively evaluated the model's visual capabilities across ten dimensions, covering university-level comprehensive problems, mathematical and scientific reasoning, logic puzzles, general visual question answering, subjective experience and instruction following, multilingual text recognition and chart/document parsing, 2D/3D object grounding, multi-image understanding, embodied and spatial perception, video understanding, agent task execution, and code generation. Overall, Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct achieves top performance on most metrics among non-reasoning models, significantly outperforming closed-source models such as Gemini 2.5 Pro and GPT-5, while also setting new state-of-the-art results among open-source multimodal models, demonstrating its strong generalization ability and comprehensive performance on complex visual tasks.
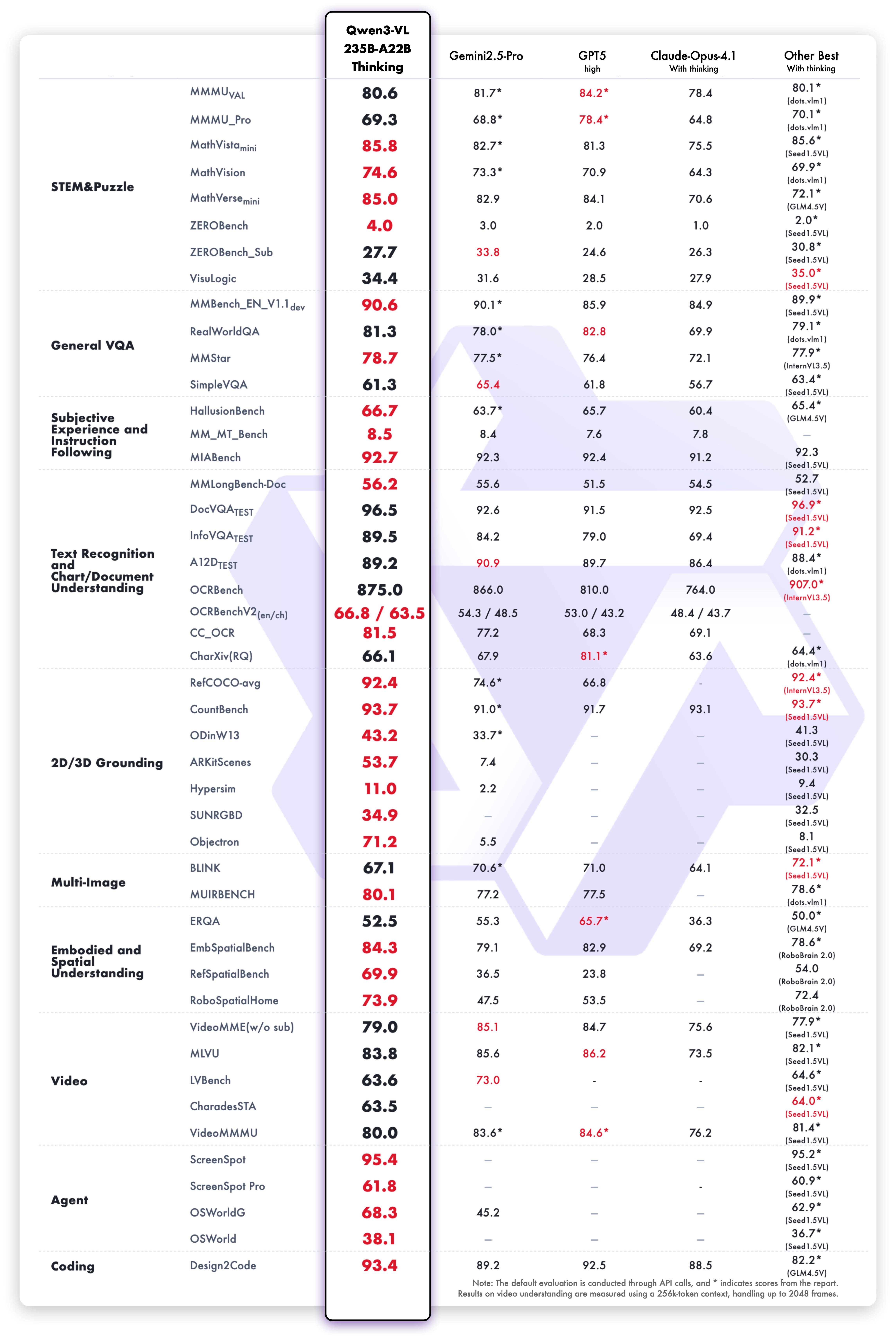
In terms of reasoning models, Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Thinking also sets new records on most metrics among open-source multimodal models, showing competitive performance against top closed-source models like Gemini 2.5 Pro and GPT-5. Notably, on complex multimodal math problems such as Mathvision, it even outperforms Gemini 2.5 Pro. Although it still lags behind closed-source SOTA models in multidisciplinary problems, visual reasoning, and video understanding, it demonstrates clear advantages in agent capabilities, document understanding, and 2D/3D grounding tasks.
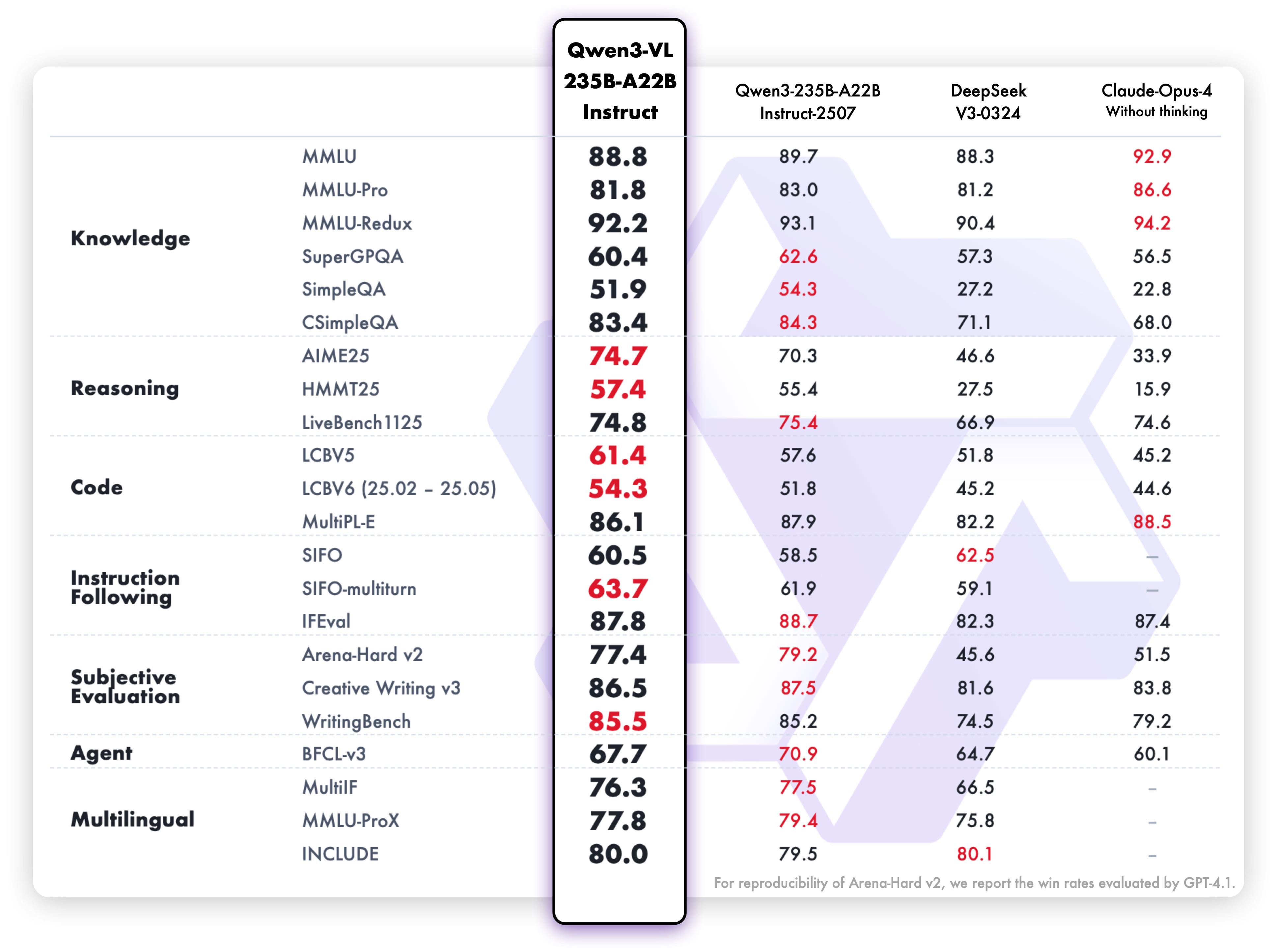
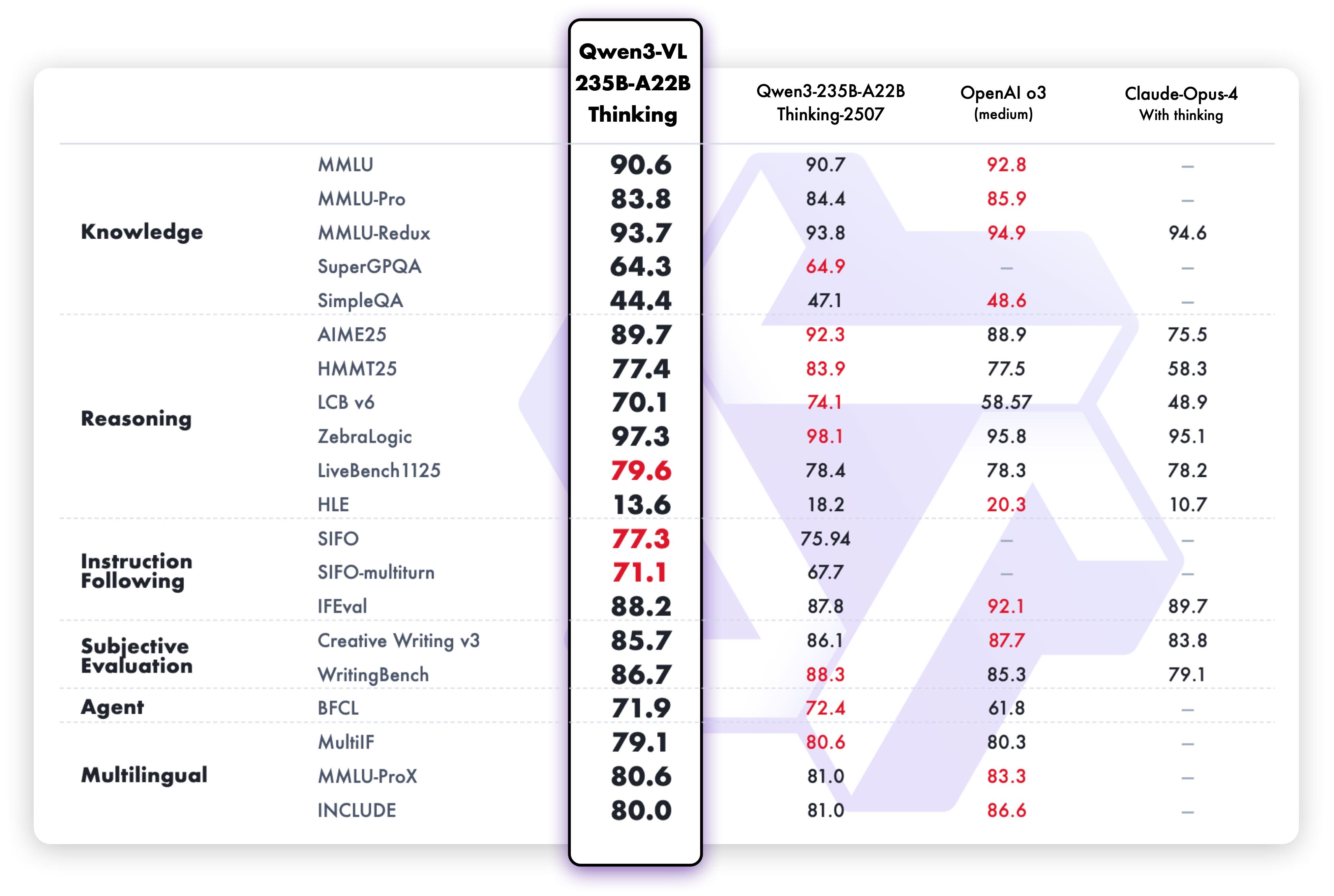
On text-centric tasks, both Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct and Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Thinking demonstrate strong performance, comparable to the language model Qwen3-235B-A22B-2507.
Additionally, Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct supports image-based reasoning with tool use. We tested this on four fine-grained perception and embodied interaction tasks. Results show consistent performance gains across all four benchmarks — proving that combining “image analysis + tool calling” is key to boosting visual perception.
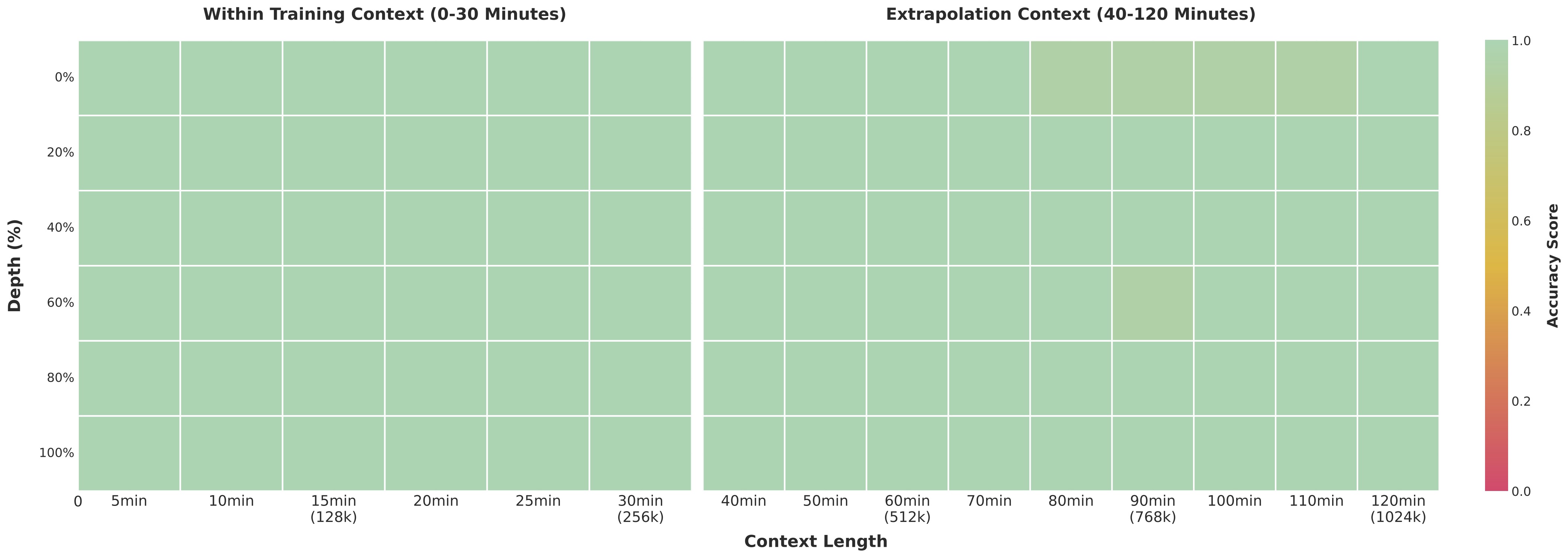
In long-context testing, we ran a “needle-in-a-haystack” experiment using ultra-long videos. Results show 100% accuracy with 256K context length. Even when expanded to 1M tokens, equivalent to approximately two hours of continuous video, accuracy remains at 99.5% — demonstrating extremely strong long-sequence modeling ability.
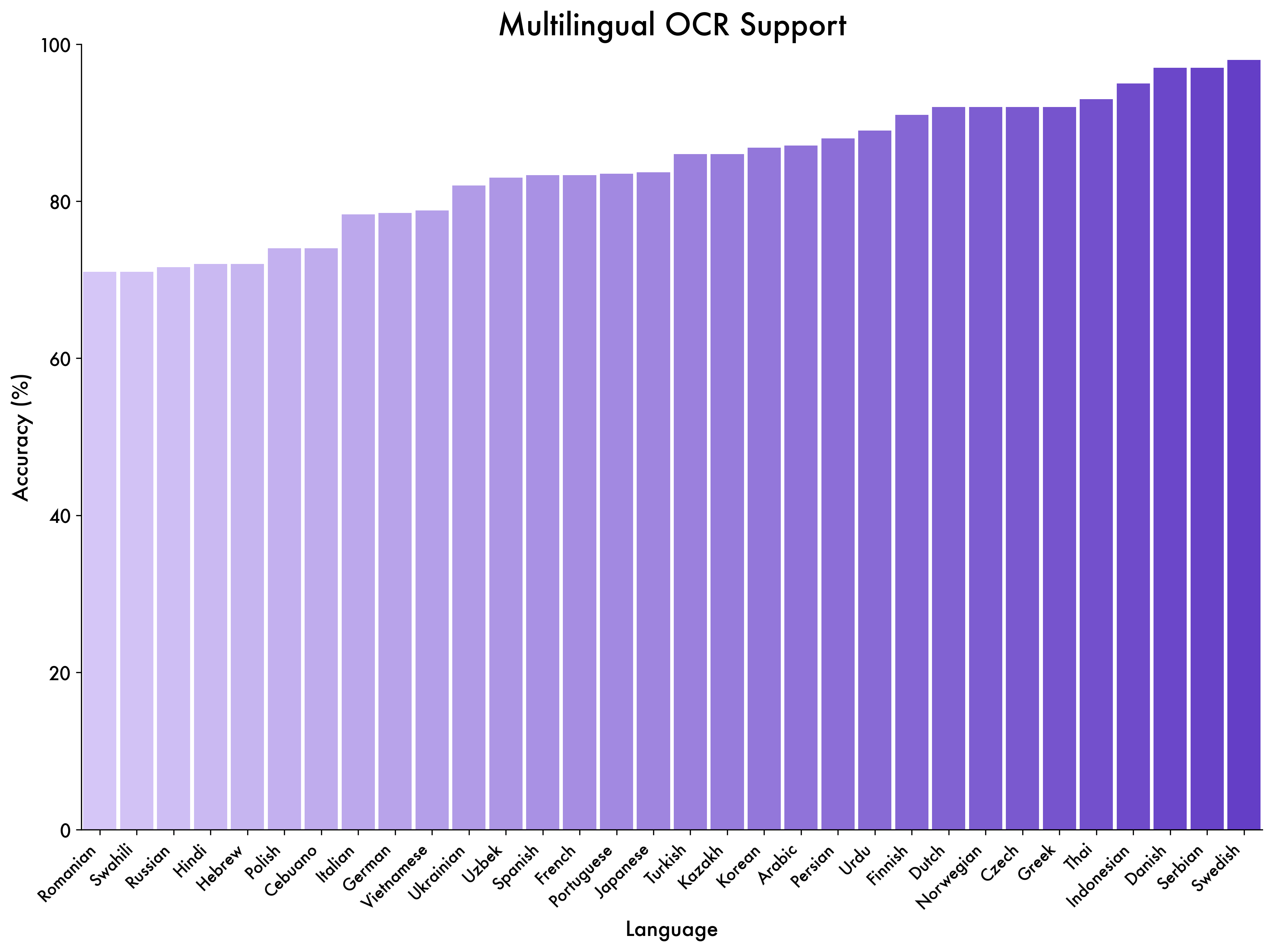
To test multilingual text recognition beyond Chinese and English, we built a test set with 39 languages. The model achieves over 70% accuracy in 32 of them — reaching practical usability and showing strong multilingual generalization.
In terms of architecture, we still adopt the native dynamic resolution design, but we have updated the structural design in three aspects:
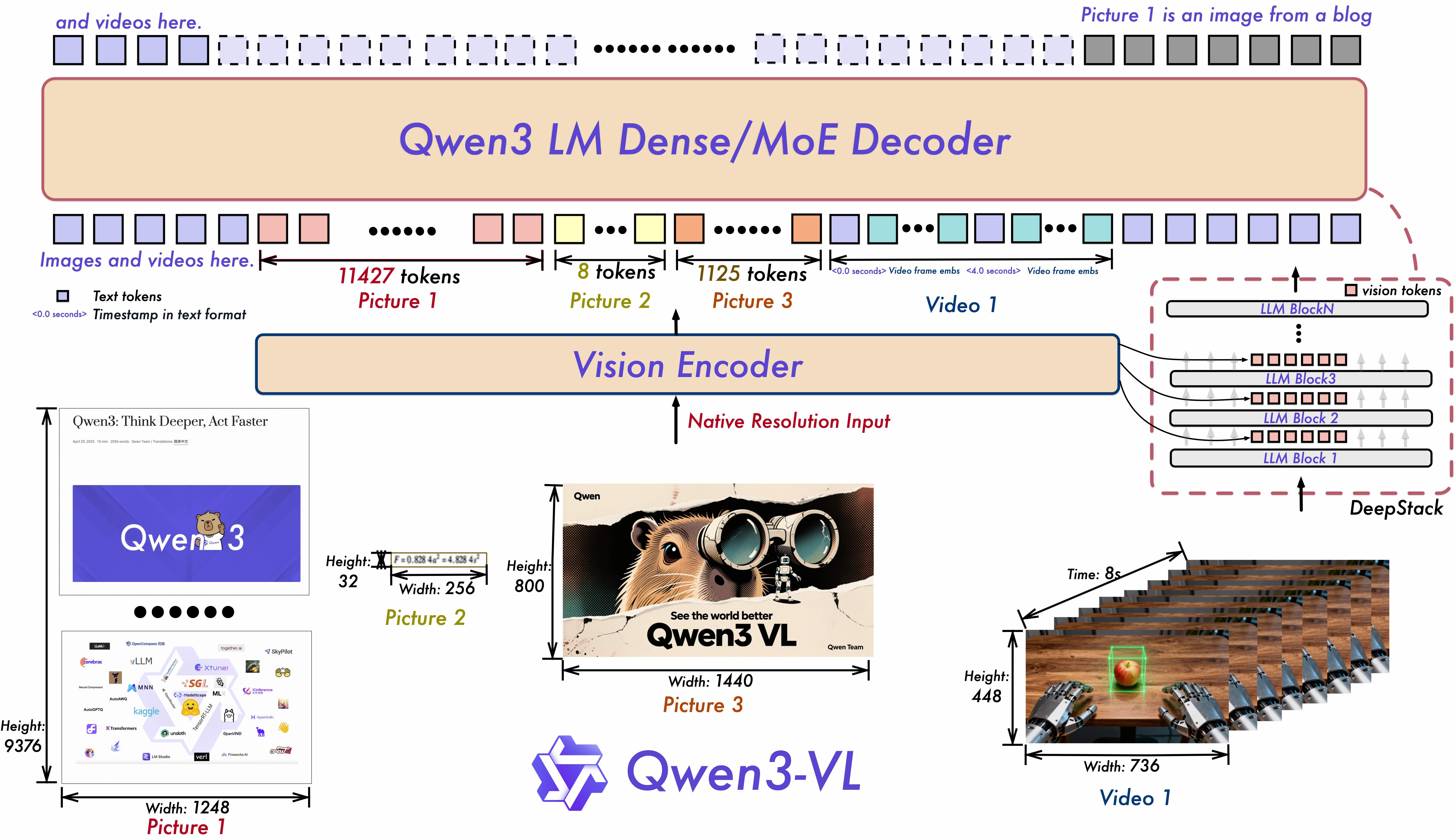
First, we employ Interleaved-MRoPE. The original MRoPE divides the feature dimensions into blocks along the order of time (t), height (h), and width (w), causing all temporal information to be concentrated in high-frequency dimensions. In Qwen3-VL, we instead distribute t, h, and w in an interleaved manner, achieving full-frequency coverage across time, height, and width. This more robust positional encoding ensures comparable image understanding capability while significantly improving long video comprehension.
Second, we introduce DeepStack technology to fuse multi-level features from ViT, enhancing visual detail capture and text-image alignment accuracy. Following the core idea of DeepStack, we shift from the conventional multimodal large model (LMM) practice of injecting visual tokens into only a single layer, to injecting them across multiple layers of the large language model (LLM). This multi-layer injection approach enables finer-grained visual understanding. Furthermore, we optimize the visual feature tokenization strategy: visual features extracted from different ViT layers are tokenized and used as visual inputs. This design effectively preserves rich visual information ranging from low-level to high-level features. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements across various visual understanding tasks.
Third, we upgrade the original video temporal modeling mechanism, T-RoPE, to a text-timestamp alignment mechanism. This mechanism adopts an interleaved input format of “timestamps-video frames”, enabling fine-grained alignment between frame-level temporal information and visual content. Additionally, the model natively supports two time output formats: “seconds” and “hours:minutes:seconds” (HMS). This improvement substantially enhances the model’s semantic perception and temporal localization accuracy for actions and events in videos, resulting in more robust performance and precise responses in complex temporal reasoning tasks—such as event localization, action boundary detection, and cross-modal temporal question answering.
Original source: https://qwen.ai/blog?id=99f0335c4ad9ff6153e517418d48535ab6d8afef&from=research.latest-advancements-list
Qwen3‑LiveTranslate: Real‑Time Multimodal Interpretation — See It, Hear It, Speak It!

1,333 posts | 466 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - January 14, 2026
Alibaba Cloud Community - September 27, 2025
Iain Ferguson - April 4, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - October 22, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - November 24, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 14, 2026

1,333 posts | 466 followers
Follow Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn More Alibaba Cloud for Generative AI
Alibaba Cloud for Generative AI
Accelerate innovation with generative AI to create new business success
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Platform For AI
Platform For AI
A platform that provides enterprise-level data modeling services based on machine learning algorithms to quickly meet your needs for data-driven operations.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community