By digoal
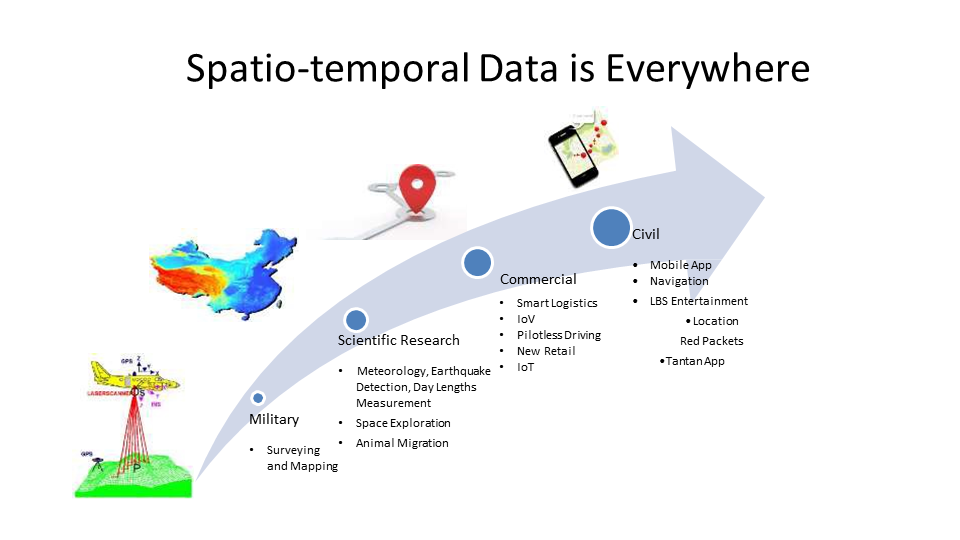
Spatiotemporal data is everywhere and will account for an increasing proportion in the future. The demand for spatiotemporal data in TP and AP scenarios will also increase.


PostgreSQL: ST_Value Function Usage Examples to Optimize Raster Data in a Database
digoal - July 24, 2019
Alibaba Cloud Community - January 5, 2026
digoal - September 20, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - July 29, 2019
digoal - July 25, 2019
digoal - May 16, 2019
 PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL
An online MPP warehousing service based on the Greenplum Database open source program
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL
An on-demand database hosting service for PostgreSQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More Database for FinTech Solution
Database for FinTech Solution
Leverage cloud-native database solutions dedicated for FinTech.
Learn MoreMore Posts by digoal