
With the growth of online collaboration office applications users in recent years, more and more developers and IT staffs build cloud services to process office documents. Many spreadsheets are used for enterprise informatization and digitalization progress reporting systems, data analytics, and processing in enterprise applications. The developers need to process office documents programmatically. Excelize was designed for these scenarios, it implements the complex spreadsheets format specifications protocol and provides easy to using and simple API for developers with high compatibility and performance.
Excelize is a library written in pure Go providing a set of functions that allow you to write to and read from XLAM / XLSM / XLSX / XLTM / XLTX files. Supports reading and writing spreadsheet documents generated by Microsoft Excel, Apache Office, Apple Numbers, KingSoft WPS, Google Sheets and other Office spreadsheets applications. Supports complex components by high compatibility, and provided streaming API for generating or reading data from a worksheet with huge amounts of data. This library needs Go version 1.16 or later.
GitHub: https://github.com/xuri/excelize
go get github.com/xuri/excelize/v2Here is a minimal example usage that will create spreadsheet file.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
// Create a new sheet.
index, err := f.NewSheet("Sheet2")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Set value of a cell.
f.SetCellValue("Sheet2", "A2", "Hello world.")
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2", 100)
// Set active sheet of the workbook.
f.SetActiveSheet(index)
// Save spreadsheet by the given path.
if err := f.SaveAs("Book1.xlsx"); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}The following constitutes the bare to read a spreadsheet document.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer func() {
// Close the spreadsheet.
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
// Get value from cell by given worksheet name and cell reference.
cell, err := f.GetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(cell)
// Get all the rows in the Sheet1.
rows, err := f.GetRows("Sheet1")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
for _, row := range rows {
for _, colCell := range row {
fmt.Print(colCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
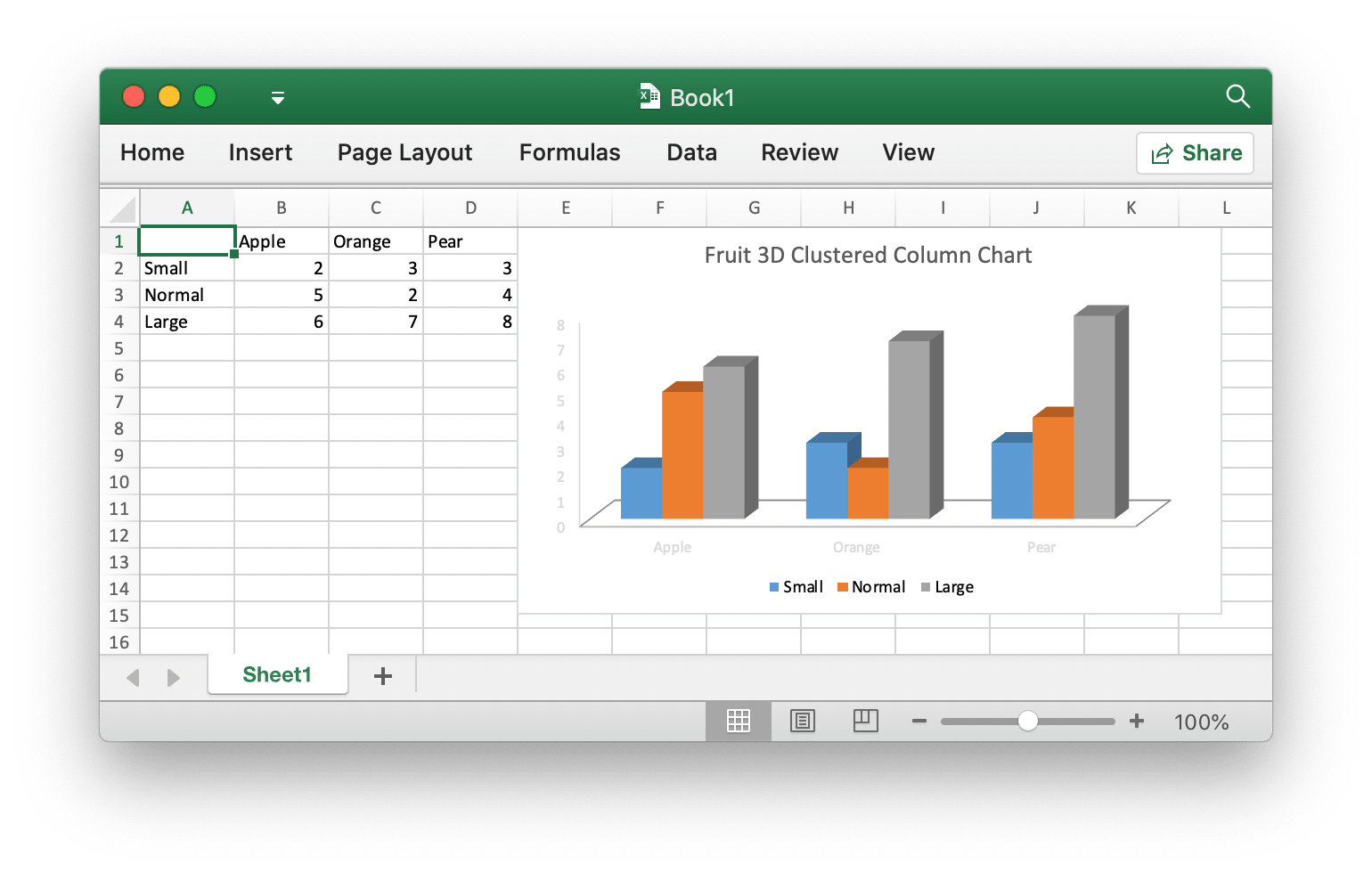
}With Excelize chart generation and management is as easy as a few lines of code. You can build charts based on data in your worksheet or generate charts without any data in your worksheet at all.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
for idx, row := range [][]interface{}{
{nil, "Apple", "Orange", "Pear"}, {"Small", 2, 3, 3},
{"Normal", 5, 2, 4}, {"Large", 6, 7, 8},
} {
cell, err := excelize.CoordinatesToCellName(1, idx+1)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
f.SetSheetRow("Sheet1", cell, &row)
}
if err := f.AddChart("Sheet1", "E1", &excelize.Chart{
Type: excelize.Col3DClustered,
Series: []excelize.ChartSeries{
{
Name: "Sheet1!$A$2",
Categories: "Sheet1!$B$1:$D$1",
Values: "Sheet1!$B$2:$D$2",
},
{
Name: "Sheet1!$A$3",
Categories: "Sheet1!$B$1:$D$1",
Values: "Sheet1!$B$3:$D$3",
},
{
Name: "Sheet1!$A$4",
Categories: "Sheet1!$B$1:$D$1",
Values: "Sheet1!$B$4:$D$4",
}},
Title: excelize.ChartTitle{
Name: "Fruit 3D Clustered Column Chart",
},
}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Save spreadsheet by the given path.
if err := f.SaveAs("Book1.xlsx"); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}package main
import (
"fmt"
_ "image/gif"
_ "image/jpeg"
_ "image/png"
"github.com/xuri/excelize/v2"
)
func main() {
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer func() {
// Close the spreadsheet.
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
// Insert a picture.
if err := f.AddPicture("Sheet1", "A2", "image.png", nil); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Insert a picture to worksheet with scaling.
if err := f.AddPicture("Sheet1", "D2", "image.jpg",
&excelize.GraphicOptions{ScaleX: 0.5, ScaleY: 0.5}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Insert a picture offset in the cell with printing support.
enable, disable := true, false
if err := f.AddPicture("Sheet1", "H2", "image.gif",
&excelize.GraphicOptions{
PrintObject: &enable,
LockAspectRatio: false,
OffsetX: 15,
OffsetY: 10,
Locked: &disable,
}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Save the spreadsheet with the origin path.
if err = f.Save(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}If you need to create programs to process spreadsheet docs, for example: open and read the content of existing Excel documents, create new Excel documents, generate new Excel documents based on existing documents (templates), insert pictures, charts, tables and other elements into Excel documents, and maybe need to implement these operations across platforms. Using Excelize can easily implements for it, and it can be used to business system, cloud computing, edge computing and other systems. We can get more details for this open-source library from the homepage of it.
Excelize 2.8.0 Released - Powerful open-source library for spreadsheet (Excel) document
Alibaba Cloud Community - April 21, 2023
ApsaraDB - March 26, 2024
xuri - February 26, 2024
Mehmad - May 13, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - March 4, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - March 7, 2022
 Quick BI
Quick BI
A new generation of business Intelligence services on the cloud
Learn More Realtime Compute for Apache Flink
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink offers a highly integrated platform for real-time data processing, which optimizes the computing of Apache Flink.
Learn More Hologres
Hologres
A real-time data warehouse for serving and analytics which is compatible with PostgreSQL.
Learn More Data Lake Analytics
Data Lake Analytics
A premium, serverless, and interactive analytics service
Learn MoreMore Posts by xuri