Power your innovations with Alibaba Cloud FinTech Support Plan and save up to $5,000 for your cloud adoption.
Liu Weiguang is a Vice President of the Alibaba Group and the General Manager of Intelligent New Finance at Alibaba Cloud. In this blog, we'll be sharing Liu Weiguang's insights into the future of, financial technology (Fintech), and discuss how it will be the most important driver of the development of our commercial society.
Fintech is an important tool that can help guide and achieve the high-level integration of business, business optimization, and new business creation. This presentation will explore the differences between Fintech, financial IT, and information-driven finance in the practices of Alibaba and Ant Financial. In addition, it introduces the five key Fintech technologies of today. Together, the five technologies will effectively realize the potential of the Internet and digital finance.
The following content is based on the video of his speech and the accompanying PowerPoint slides.
From the Internet to the mobile Internet to the Internet of Everything, Internet technology has gone through several different development phases. The first and second generations of technology emphasized connectivity, information acquisition, and social networking. Today, with the ongoing development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G, connectivity between things and people, things and information, and things and networks are becoming the new trend.
In the commercial society of the future, we expect the next generation of Internet technology to place greater emphasis on the "Internet of Value." The Internet of Value emphasizes the transmission and interaction of commercial value and valuable information over networks in the service of the online operations of our commercial society. In the era of intelligent business, technologies such as high-speed connection, security technology, and privacy protection as well as the development of digital assets, cross-institution trust-based collaboration, smart contracts, the Internet of Value, and the sharing economy, more digital economies will realize their potential through the Internet of Value.
A great deal of technology has been required to support each stage in the development of the Internet. Such technologies include big data, mobile application, biometric recognition, IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time data analysis. Today, the emergence and development of blockchain and secure multiparty computation (MPC) have opened up the possibility of the Internet of Value and intelligent commercial society operations.
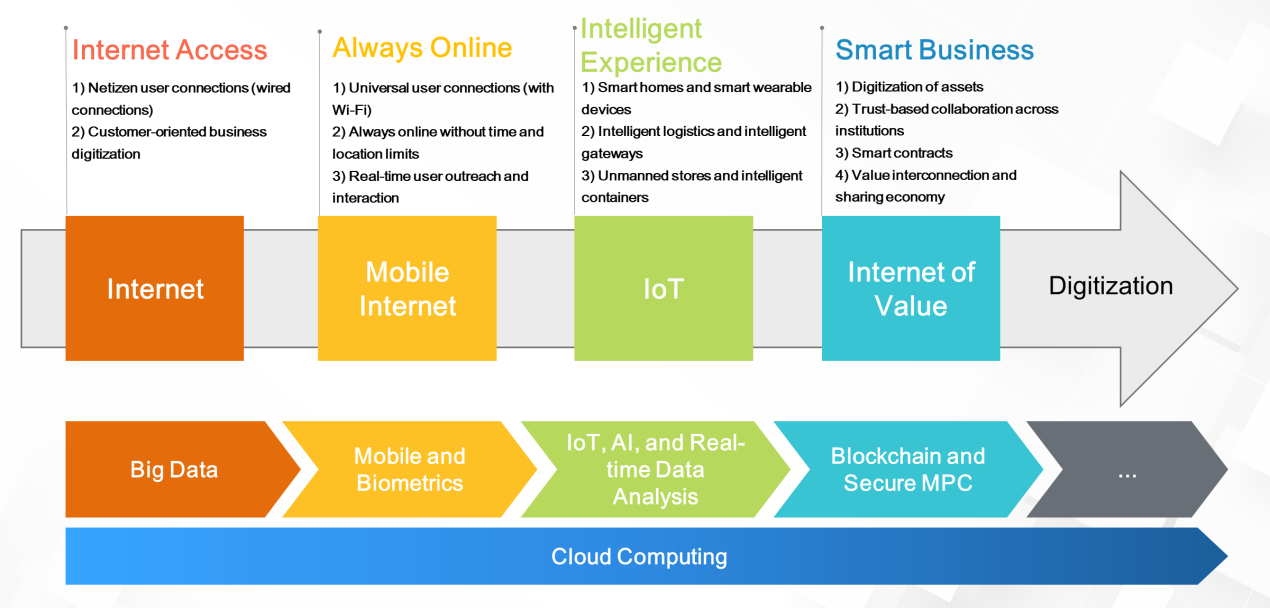
Based on the reports published in the MIT Technology Review, new technologies, such as biometrics in 2017, various combinations of AI with business and finance in 2019, and blockchain in 2020, have driven the development of digital currencies, achieved technological breakthroughs, and promoted the evolution of financial engineering. Therefore, the technologies of the future will not only support the financial and business fields but also drive new developments in the financial industry.

Fintech is the core competency required for high-quality development: Between 2019 and 2020, the People's Bank of China published several reports on the impact of Fintech on the development of the Chinese banking industry. Fan Yifei, the President of the People's Bank of China, pointed out that Fintech will be a strategic sector in the future global competition in the financial industry. Whoever masters this technology will be the strongest player in the financial industry. This opinion is widely held in the industry. Banks are increasingly aware of the role of technology in driving their current and future business development and are attentive to the ways technology can support their future digital upgrades and transformations.
Today, China is already the world leader in mobile payment technology. In 2018, over 530 billion mobile payments were processed in China, with a total value of more than RMB 440 trillion. This was 4.89 times China's GDP for that year.
Intelligent credit services, such as MYbank's 310, have made it easier and cheaper for small, micro, and private enterprises to raise funds. Small, micro, and private enterprises in China face common difficulties in data acquisition, security and privacy protection, syndicated loans, and fraud prevention. In the future, services that combine data and intelligence will lead to major breakthroughs in this field. Going forward, businesses will be able to access comprehensive, multi-level, and intelligent online financial services through apps and open APIs. This integration of online and offline business will usher in the era of inclusive banking and finance. We will see an increasing number of ecosystems that span and combine different industries, such as banking, securities, and insurance. The emergence of new needs will impose an impact on traditional technology architectures. As users increasingly demand more efficient, inclusive, and diversified financial services, financial transactions will come to be characterized by high concurrency, frequency, and traffic volumes. The rapid development of online businesses will have a major impact on existing business systems and the centralized architecture currently adopted in the financial industry. In this context, financial institutions must accelerate their transitions to distributed architectures, respond to market demands more efficiently, and embrace online-offline integration.
For commercial banks, they need to address the shortcomings in credit services for small, micro, and private enterprises, transition from the customer market to the business market, establish industrial partnerships throughout the enterprise lifecycle, and explore new growth opportunities. Human brains and experience alone are not enough to accomplish this task. It is also necessary to establish connections between groups by digital means to reasonably and legally obtain data to provide financial services with enhanced precision.
We can see that Fintech is the critical core competitiveness in agriculture, various key development areas, and digital transformation and for retail, small, micro, and private enterprises.

The financial industry is highly dependent on information technology (IT). The technological level and IT capabilities of China's banking and financial industry place them in a leading position in the country. General technologies, such as hosts, storage, computing, networks, databases, and data warehouses, can all be applied in the financial industry and other industries. These general technologies have supported the development of the financial industry. They are also facing challenges from new cloud computing and big data technologies along with technological innovations and upgrades.
Financial technologies are specific to the financial industry. They are highly integrated with specific businesses. Business and technology grow together and support each other. This means they are not general technologies. Fintech promotes and creates business developments and optimizes existing workflows.
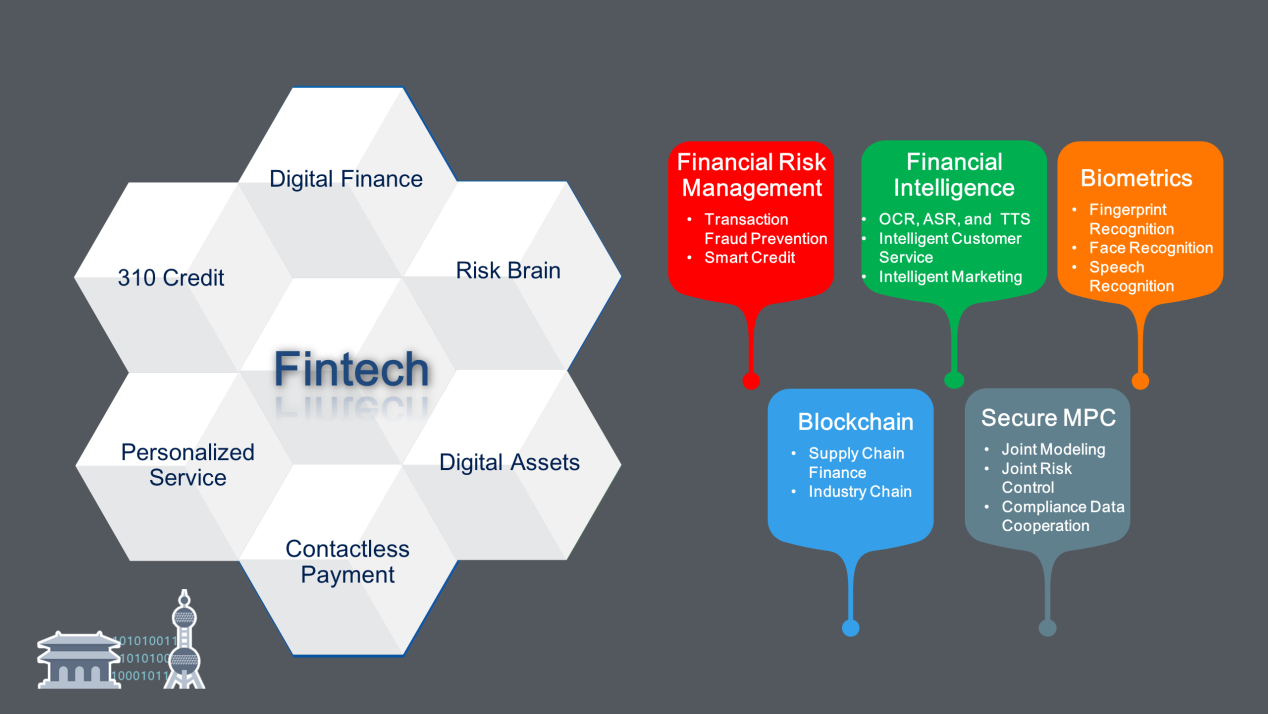
Biometric technologies include fingerprint, voiceprint, face, iris, and speech recognition. Financial-grade biometric technology will significantly change existing processes for remittances, transfers, operations involving large sums, withdrawals, and corporate banking.
AI needs to be deeply integrated with big data. By incorporating the transactional principles of finance and economics, AI can better adapt to the financial industry and penetrate every transaction process. The current COVID-19 pandemic has shown that insurance processes that require the signing of paper contracts are impractical during certain special events. AI technology is already becoming heavily involved in insurance approval, claims settlement, and underwriting. In addition to intelligent customer service and intelligent marketing, financial intelligence will increasingly penetrate transaction verification and query scenarios, greatly streamlining processes that must currently be performed manually.
First-generation risk control systems were based on rules, second-generation systems used big data, and third-generation systems emphasized intelligent risk control. Intelligent risk control requires the integration of AI and fraudulent transaction prevention technologies. In the future, intelligent risk control will become a new type of global risk control system that brings together online, offline, small, and micro businesses.
Secure MPC shows great promise in the financial industry. Its emergence is likely to play a major role in the improvement of joint modeling, joint risk control, and compliance data cooperation.
Later in my presentation, I will describe the use of blockchain in transaction scenarios in various industries, where it is used in applications such as value delivery, privacy and security, process optimization, digital connectivity, and the Internet of Value. Blockchain can make significant improvements to financial scenarios, such as industrial finance, IoT, logistics finance, bills, and industry chains.
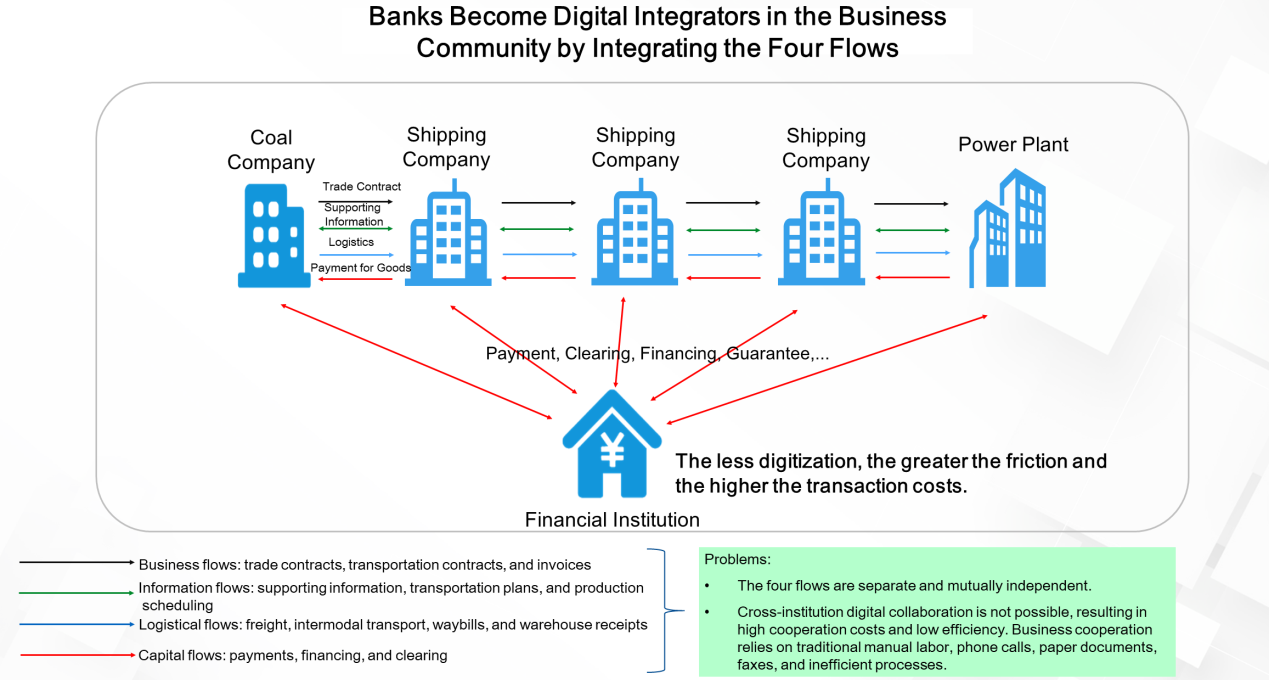
From physical assets to digital assets: The following figure shows an example from the transportation industry. In this example, coal is transported from a coal company to shipping company A, on to shipping company B, then to shipping company C, before finally arriving at the power plant. For financial institutions, each entity is a financial customer that needs services.
Business flows, information flows, logistical flows, capital flows, and other relationships exist between enterprises, connecting them closely together. In the past, banks needed to connect with each enterprise at a single point, so they could not understand the operational capabilities and efficiency of enterprises or the cooperation and capital flows among enterprises. The operational processes between enterprises were mutually separate and independent. If digital platforms can help to connect enterprises digitally, they can significantly reduce transaction friction and costs. In the future, financial institutions will need to integrate and optimize various business processes through digital means to provide precise financial services to customers.
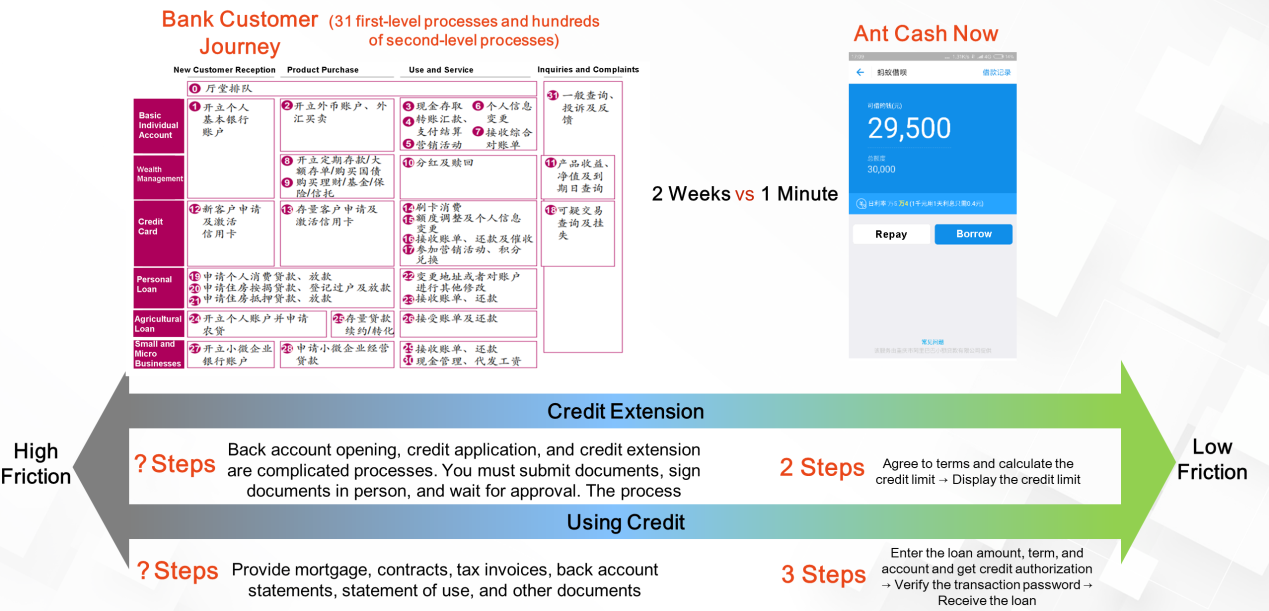
From digital connection to digital credit: The following figure shows a typical case of connecting digital data to digital credit through digital connectivity.
The journey of a bank customer includes 31 first-level processes. This involves many of the bank's internal management modules, human interactions, and a large number of approval processes. As a result, the process is not smooth and efficient. Instead, it can take two to four weeks to go through, and the result may be unsatisfactory. Ant Cash Now can do the same thing in one minute or less.
The biggest differences between the two processes lie in their information acquisition channels, information interaction methods, digital connection processes, and the use of AI technology to optimize each connection. To shorten the customer journey, we need to use a platform to manage, collect, and operate all the digital information, as well as digital and AI technologies to make decisions at each step. This greatly reduces friction and streamlines the process.
Intelligent voice service and robots: Financial intelligence must be highly integrated with financial scenarios to provide users with precise and efficient intelligent services. During the pandemic, many companies launched robots to serve customers. Based on the combination of information from various organizations and the Internet, China's health codes system can quickly determine an individual's interactions and health information. Health codes are a typical example of MPC technology. Such computation requires the association of large volumes of data and powerful computing capabilities. Through the combination of AI and cloud computing, we can quickly provide precise health services for each individual during the current pandemic.
AI is also used to provide intelligent customer service in many fields, but this is far from its expected coverage for full play. Instead, AI should also be introduced into speech technology, natural language understanding, computer vision, and decision-making intelligence. In the future, AI will be combined with finance and apply deep learning to the rules of financial transactions. This will allow AI to provide end-to-end judgment and verification capabilities, ultimately achieving decision-making intelligence.
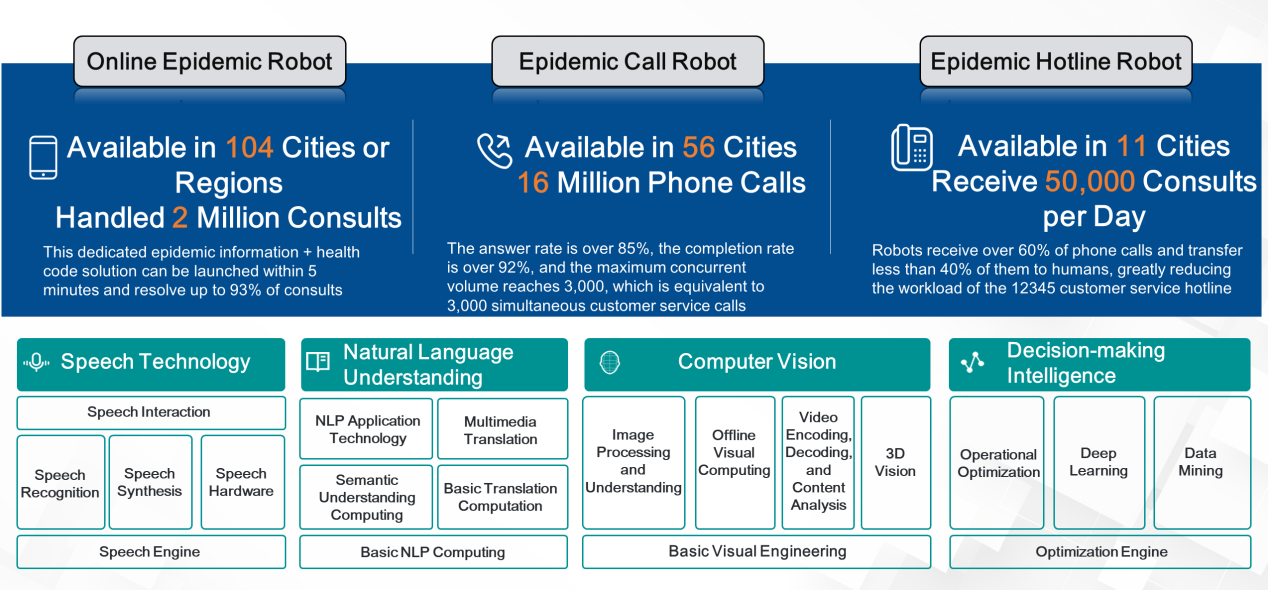
Financial services (smart speech + financial mini programs): If terminals can be globally distributed to banking, insurance, and securities customers, network connections, user profiling, and big data analysis can be used to provide customers with convenient financial management and financial assistant services through these devices. Then, financial intelligence would be everywhere.
Today, no technology can develop in complete isolation. The combination of Fintech and other technologies can improve capabilities in existing financial scenarios. For example, the combination of IoT devices, AI, and big data will allow us to provide precise financial services to every customer. This is also an important path in the future development of financial intelligence.

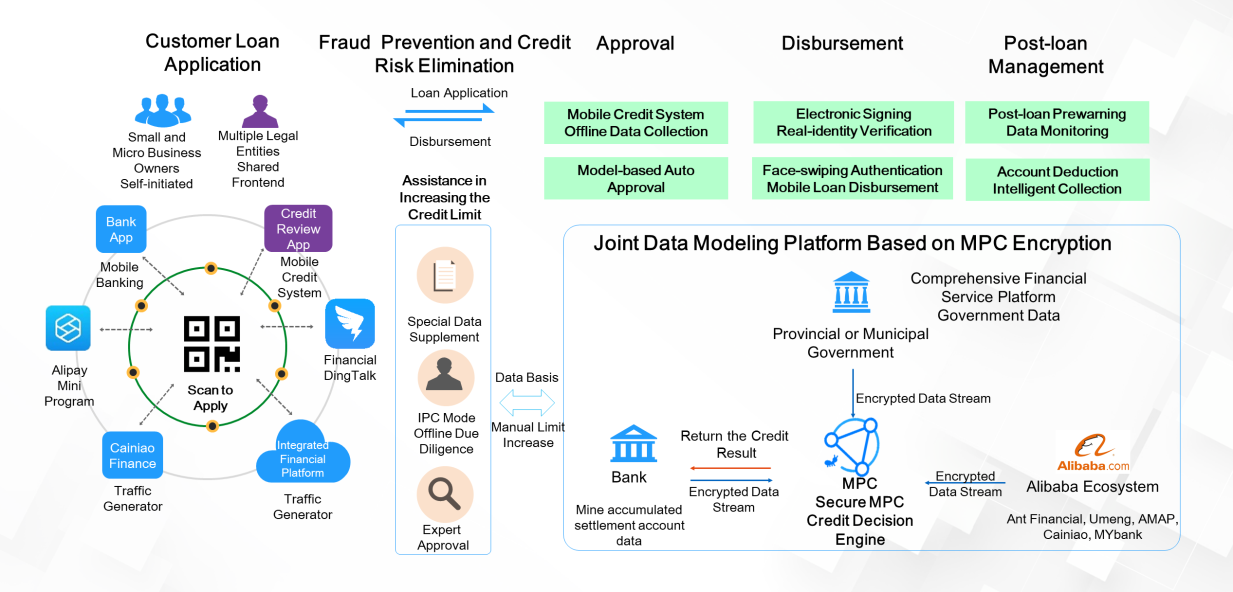
Joint risk control (compliance data cooperation): All financial institutions must ensure the privacy of data. Data is critical to financial institutions, due to the requirements of both regulatory supervision and their businesses. In the future, data cooperation will be essential in cross-industry operations, joint risk control, insurance, and other scenarios. Data cooperation not only refers to cooperation within the financial industry but also the combination of the financial industry and government data. This can provide high-quality business services for the development of digital government and finance.
Large data volumes are lacking in the small- and micro-business and agricultural financing fields. Data is definitely a resource that every financial institution needs. Therefore, joint operations are needed between banks and between banks and insurance companies. Joint computing is an important technological trend that will break down the boundaries between different data domains. It may lead to many new services. Through the combination of government data and the capabilities of the financial industry, precise services can be provided to customers and labor costs can be slashed.
As shown in the following figure, banks, the government, and Alibaba can jointly create a data modeling platform based on a secure MPC engine. This platform can provide customers with new types of precision microfinance services. However, secure MPC cannot fulfill this alone. Instead, it can only solve data problems, and the support of an underlying platform is required. With blockchain's consensus, privacy protection, and tamper-proof capabilities, it is possible to collect data reasonably, legally, and accurately and to perform computations across different data resources.
In short, many technologies must be used in combination to provide efficient business support. Let's consider a joint data modeling platform as an example. As the platform's key business technology, secure MPC relies on the underlying blockchain platform and AI modeling to implement the modeling platform and provide customers with precise financial services.
In the Internet of Value, blockchain can reduce collaborative friction among enterprises through the following mechanism. Blockchain exploits the combination of many traditional technologies and incorporates a great deal of research on security, privacy, and cryptography. By integrating a large number of algorithms, blockchain provides a basis for digital currencies. Beyond the field of digital currency, blockchain also plays a role in many other business processes.
As shown in the following figure, in traditional business processes, business flows, information flows, logistical flows, and capital flows across institutions are separated. As a result, cooperation suffers from various labor costs, high collaboration costs, and low efficiency. However, if each institution can put its information on the chain, all the institutions would be able to see the relevant information of the other entities involved in the transaction process. The information transparency, security, privacy, and resistance to tampering provided by blockchain ensure that the four flows can cooperate on the chain. This allows all the relevant information to be registered on a single public and trusted platform so that financial services can be provided more efficiently. Ultimately, this can minimize friction during collaboration in these four flows. This allows for shared accounting ledgers and instant transaction settlement across institutions while avoiding complex cross-institution reconciliation. A bank can be introduced into the overall platform as a supernode to approve loans and provide precise financial services for each enterprise by managing shared ledgers.
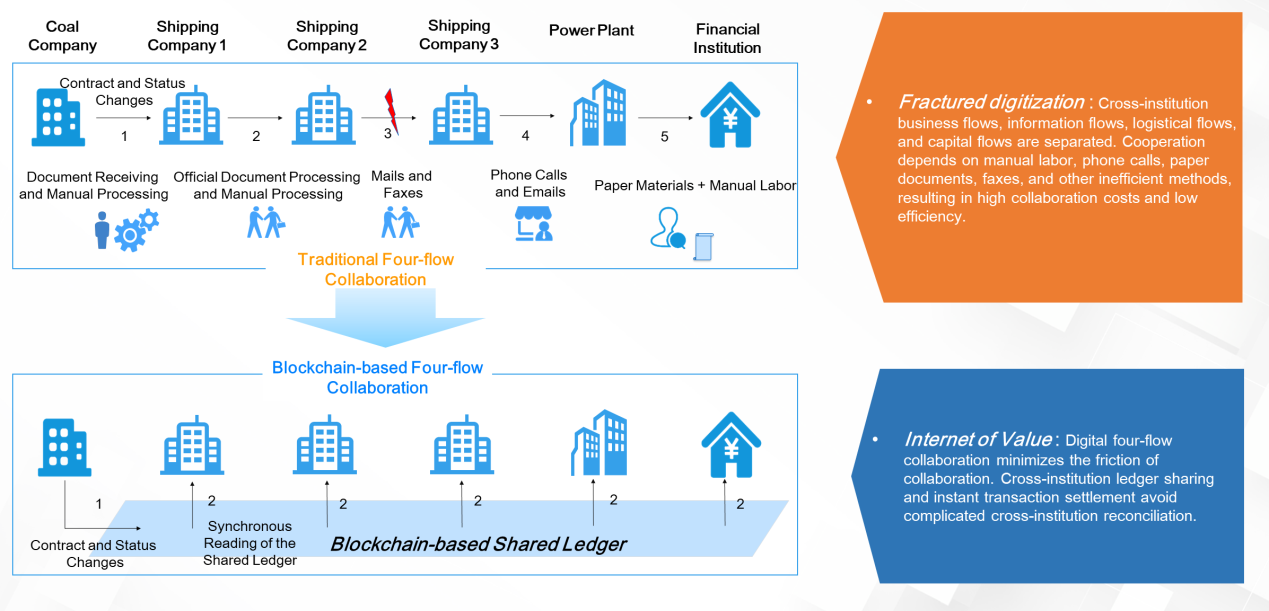
When blockchain is fully integrated into an industry, it also promotes the digitization of the industry's assets. Without digital assets, industry players cannot interact with other entities in the transaction process. Once similar enterprises digitize their assets through blockchain, other enterprises are prompted to quickly follow suit. Therefore, blockchain not only enables transparent interaction in information flows and simplifies the process, but it also accelerates the digitization of assets in all industries and sectors. Blockchain is not designed to solve the internal problems of an organization. Instead, it solves the problem of interactions with asymmetric information across institutions, organizations, industries, and countries. For financial information interactions between institutions, blockchain optimizes processes that require a high level of manual intervention or online-offline integration.
The emergence of local area networks (LANs) for industry collaboration: Through the collaboration of Alibaba and Ant Blockchain, we have implemented over 40 blockchain scenarios, including blockchain tracing, leasing, payments, invoices, contracts, on-chain logistics, blockchain for charitable donations, and financing. Ant Blockchain has filed the most blockchain-related patent applications in the world, placing it far ahead of the domestic competition. Alibaba is not just applying blockchain to its own businesses. It is also exploring the application of blockchain to more business scenarios to create a community based on the Internet of Value.
Although Alibaba and Ant Blockchain are still immature in many business scenarios, we are constantly working to accelerate the digitization of the business community. The following figure shows information about the use of blockchain for bills. Bill businesses can incorporate blockchain to increase efficiency while reducing information asymmetries. In addition, blockchain can be used to achieve multi-layer supply chain penetration, solve information asymmetries, and provide transparent, fast, and accurate financial services for each merchant in the supply chain. As more judicial proceedings move online, they need to use a judicial chain to ensure the credibility of the large amounts of evidence stored on the chain.

Blockchain for electronic invoices: After a business system submits invoicing information, invoicing logic verification is performed at the blockchain invoicing mid-end. Then, the system encapsulates an invoicing request and sends it to the blockchain invoice network for primary verification. The system interacts with the internal system of the State Administration of Taxation for tax management and also interacts with the risk control system.
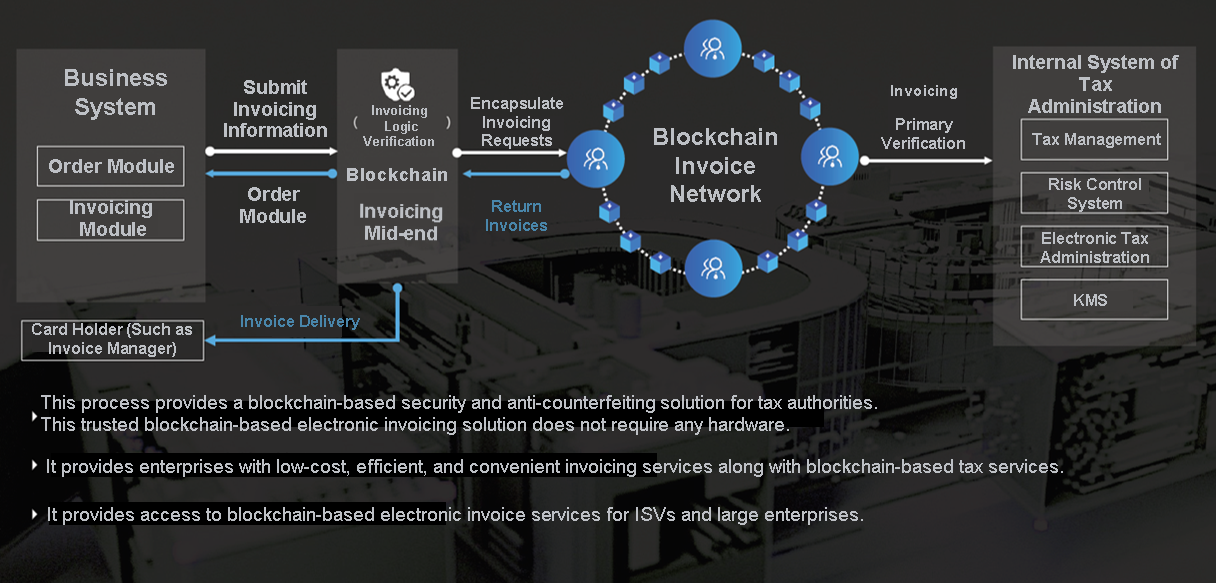
This process provides blockchain-based security and anti-counterfeiting solution for tax authorities. This trusted blockchain-based electronic invoicing solution does not require any hardware. This transparent and quick method provides access to blockchain-based electronic invoice services for independent software vendors (ISVs) and large enterprises. It provides enterprises with low-cost, efficient, and convenient invoicing services along with blockchain-based tax services.
Obviously, blockchain technology cannot provide a complete business information solution on its own. Blockchain is like a platform, which provides important technologies that cannot be implemented by traditional methods, such as security and privacy, cryptography, and secure MPC. It also requires the help of application systems, such as data and risk control systems. When a business moves from a traditional platform to blockchain, its workflow can be greatly accelerated.
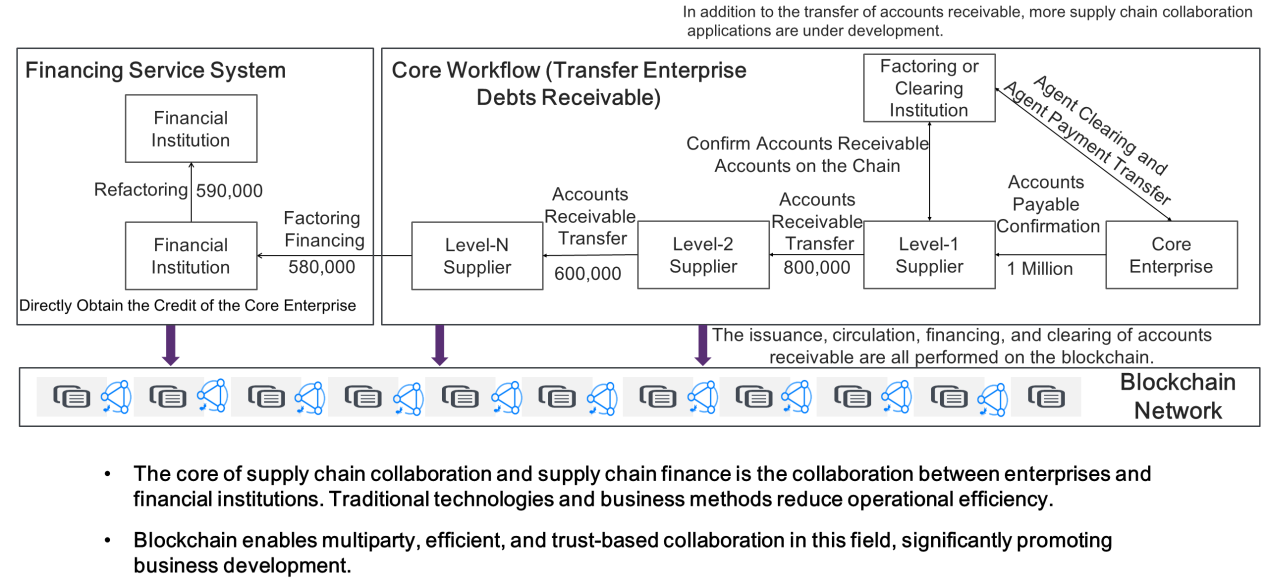
Blockchain for supply chain finance: In the past, supply chain collaboration and supply chain finance posed great difficulties. Traditional technologies and business methods could not penetrate the management of key enterprises and processes, and the risks of financial fraud, counterfeit bills, and contracts had to be addressed.
After a blockchain network platform is built, blockchain can provide security and privacy technologies. At the same time, the development modules for applications such as issuance, circulation, financing, and clearing are run on the blockchain. After data circulation, data routing and data verification are performed on the blockchain network. The financial institution, as a supernode on the blockchain network, can view the business information and provide the required services to each organization. Ultimately, this will solve the difficulty and high cost of financing.
The key to supply chain finance is that blockchain allows financial institutions and enterprises to cooperate in a multiparty manner, solving the inefficiencies arising from single points of connection between institutions. Blockchain enables multiparty, efficient, and trusted collaboration in this field. It also helps avoid fraud and promotes business growth.
Blockchain applications in the insurance industry: The Chinese insurance industry has been exploring blockchain applications since 2016. The following figure shows the applications and platforms that have been launched so far. As you can see, the insurance industry is currently looking into blockchain mainly in the areas of rights and points. The industry is working to achieve interchangeable rights and has explored some superficial innovations. Blockchain has not yet fully penetrated existing application scenarios.
More often than not, innovative businesses in the insurance industry are of minor importance compared to existing businesses. The true potential of blockchain depends not on how many innovative scenarios it can develop, but its replacement of the traditional architecture of existing businesses. By running existing businesses on a blockchain platform, we can tap into the real commercial value of blockchain. To achieve this, we cannot rely on blockchain technology alone. We must incorporate other technologies as well.

The following figure presents the categories of blockchain applications currently used in China's insurance industry. As you can see, blockchain technology is still in the exploratory stage and is being used in cutting-edge and innovative businesses in the insurance industry.

The value of blockchain is present at three levels: At the financial level, the consortium chain mechanism allows financial institutions to perform reviews so that financial-level businesses can support logistics finance, supply chain finance, asset-backed securities (ABS), trade finance, and thoroughgoing management. To truly implement financial-grade distributed blockchain technologies, we must also incorporate financial biometrics, credit, and risk control technologies. Alibaba and Ant Blockchain primarily focus on enterprise-level features. First, we adopt a large number of security and privacy protection technologies, which are suitable for financial transactions between enterprises. Second, we have designed many consortium chain and cross-chain technologies. In the future, all chains must be connected. Therefore, Alibaba and Ant Blockchain must fuse their chains with those of other financial institutions. Ant Financial is exploring the use of cross-chain technology in consortium chains to find ways to connect different systems through chains. Alibaba also hopes to use cross-chain technology to quickly integrate multiple chains to allow for data interaction with privacy protection.
Transactions are another area where we can see the value of blockchain. Today, no digital currency can compare with mobile payments or offline transactions. Currently, no technology can support the large-scale concurrency required to run just one-tenth of the data from transaction scenarios on a blockchain. Therefore, Alibaba and Ant Financial also need to explore how to combine blockchain with large-scale distributed computing capabilities. We hope that blockchain can enhance enterprise-level functions, implement advanced technologies, and provide high concurrency and availability to support the large-scale business operations of the future.
The third area of exploration is evidence preservation. Ant Financial has extensively explored evidence preservation technology. This technology is not limited to blockchain's tamper prevention technology, but also includes robust privacy protection for sensitive data. Additionally, by allowing access to large volumes of third-party data, blockchain facilitates joint and federated computing. Ultimately, this ensures financial-level data privacy.
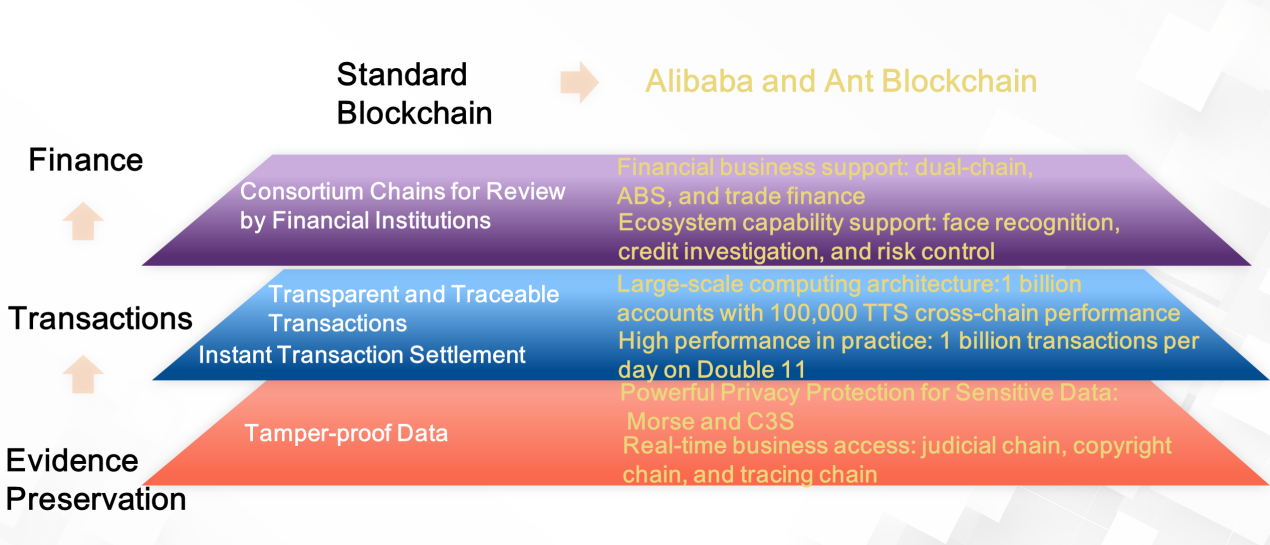
From evidence preservation to transactions to finance, Alibaba and Ant Blockchain help financial institutions transition from the tamper resistance, transparent transactions, and review through the consortium mechanism of traditional blockchain to financial-level business support, ecosystem support, large-scale computing support, and new privacy protection technologies. Once again, we must realize that blockchain technology alone is not enough to replace existing business scenarios. Instead, it must be combined with other technologies.
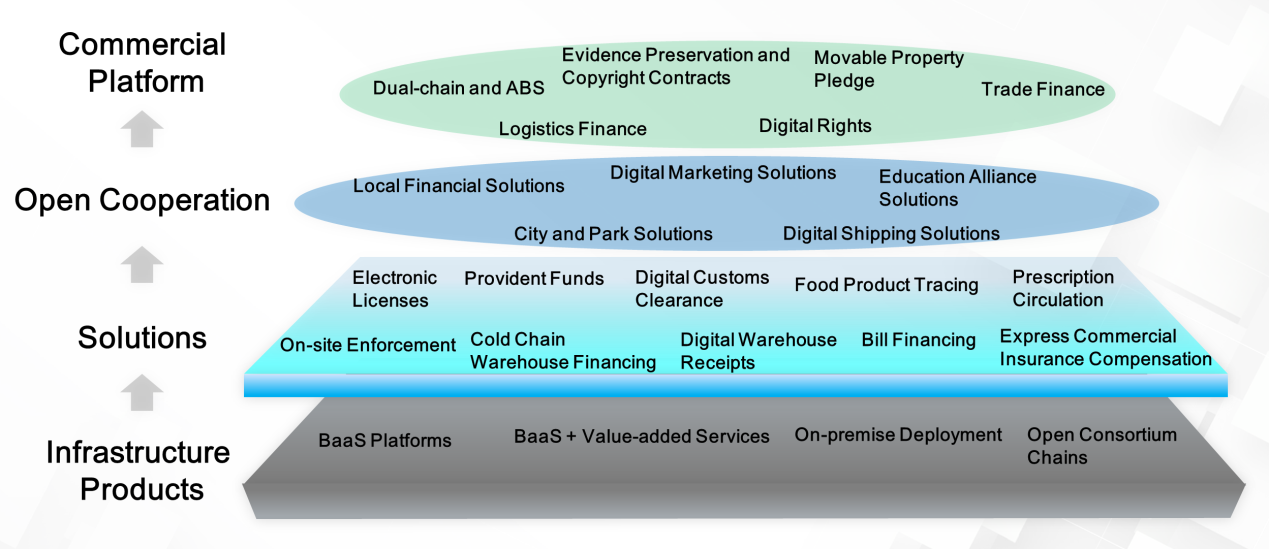
Chains and the Internet of Value: As shown in the following figure, the underlying infrastructure product layer of the Internet of Value built upon blockchain includes Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms, BaaS + value-added services, on-premise deployment, open consortium chains, large-scale computing, and high concurrency. In terms of industry applications, blockchain will play an important role in electronic licenses and housing provident fund operations. At the same time, blockchain will create more opportunities for marketing solution cooperation and exploration in more fields, such as cities and parks, digital shipping, and educational alliances. In the financial sector, blockchain can be applied in many commercial platforms, such as dual-chain and ABS platforms, logistics finance platforms, and digital rights platforms.
Each business scenario needs to be further integrated with IoT and risk control technologies to ensure the speedy circulation of key information, sensitive information, valuable information, and contract information through the blockchain. This will allow us to provide precise services for users in the business community.
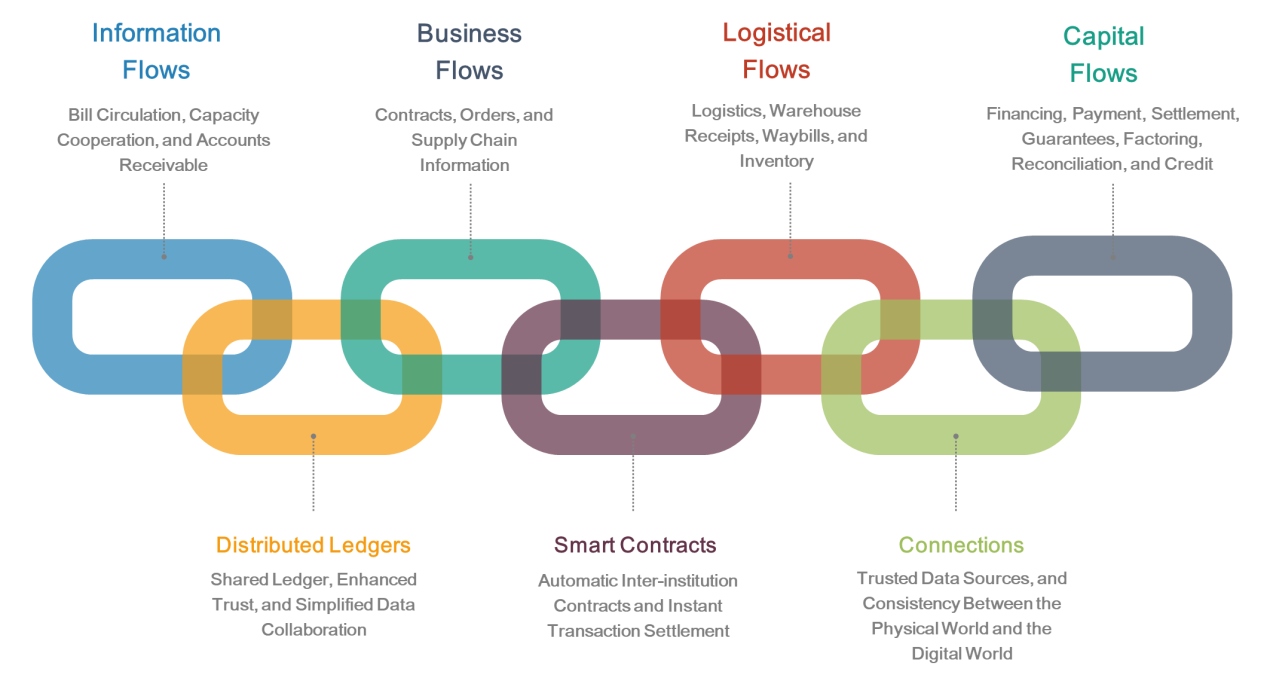
Trust in the Internet of Value: The combination of blockchain technology, distributed ledgers, smart contracts, and other IoT technologies can enable more connections in information flows, business flows, logistical flows, and capital flows through cross-chain and consortium chain technologies. This simplifies the Internet of Value and consolidates trust.
Ant Financial emerged when Alipay wanted to simplify its transactions and base them on mutual trust. Now, Zhima Credit and other companies have used big data, risk control, AI, and other technologies to further simplify mortgages and other transactions. Blockchain is the core technology that will be used to build the Internet of Value. Networks built on blockchain are enterprise-grade Internets. The blockchain community wants to incorporate many technologies to promote trust between enterprises.
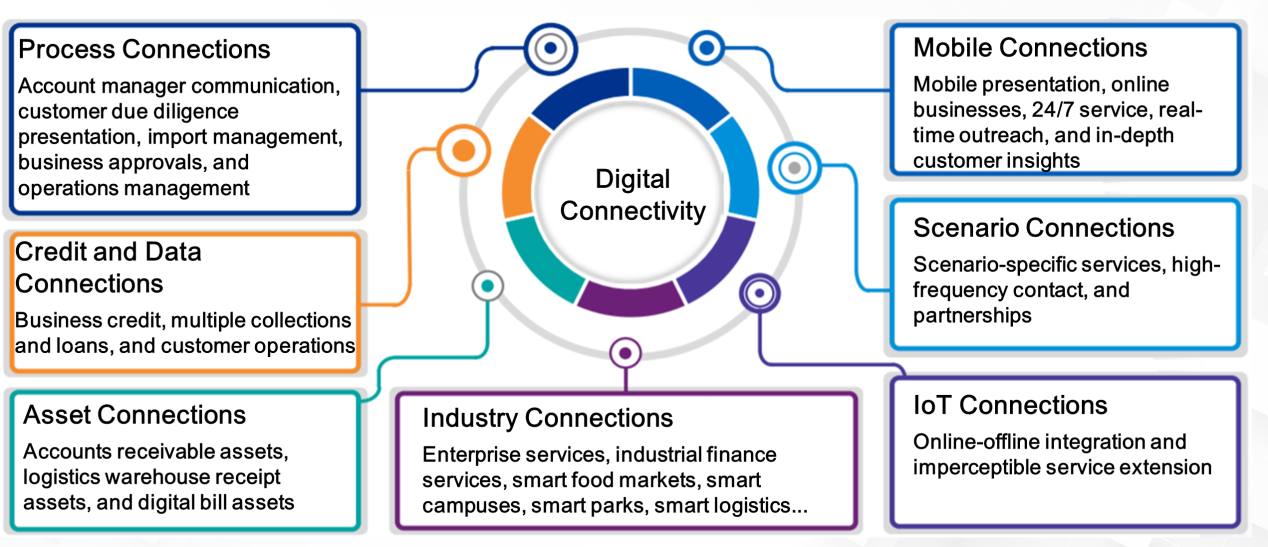
Comprehensive and multi-layered digital connectivity is the core of transformation: In the future, as blockchain is integrated into more transaction scenarios, this will encourage other industries to embrace the chain and digitize their assets. Future digital transformations will not only depend on traditional technologies but also mobile terminals, big data, and cloud computing platforms. Even more, enterprises will have to connect to blockchains to establish digital connections with external organizations and transaction scenarios. This way, they can make transactions more convenient and trust each other easier.
For enterprises, digital transformations go beyond improvements to their capabilities. They also involve comprehensive and multi-level connections, including process connections, credit and data connections, asset connections, connections between industries and the outside world, IoT connections, scenario connections, and mobile connections. The platform that can enable these connections will become the primary platform for the integration of blockchain and other technologies, making it the hub that interconnects commercial value.
Get to know our core technologies and latest product updates from Alibaba's top senior experts on our Tech Show series

2,593 posts | 792 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - September 28, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Community - July 6, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Blockchain Service Team - January 17, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Community - May 13, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Blockchain Service Team - January 17, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Experts Column - September 20, 2022

2,593 posts | 792 followers
Follow Cloud Migration Solution
Cloud Migration Solution
Secure and easy solutions for moving you workloads to the cloud
Learn More LedgerDB
LedgerDB
A ledger database that provides powerful data audit capabilities.
Learn More FinTech on Cloud Solution
FinTech on Cloud Solution
This solution enables FinTech companies to run workloads on the cloud, bringing greater customer satisfaction with lower latency and higher scalability.
Learn More Black Friday Cloud Services Sale
Black Friday Cloud Services Sale
Get started on cloud with $1. Start your cloud innovation journey here and now.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder